Risk Control Self-Assessment (RCSA) is a strategic, proactive process companies implement to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks. In our rapidly evolving and increasingly complex business environment, the significance of RCSA has never been more pronounced.
It helps companies navigate the labyrinth of potential hazards, turning unforeseen pitfalls into opportunities for growth and prosperity.
The Risk Control Self Assessment program (RCSA) is an important tool bank, financial institutions, and companies use to identify and manage operational risks. RCSA is a process that allows organizations to assess the effectiveness of their controls and identify potential areas of risk.
In today’s business world, it has become increasingly important for companies to understand how to utilize this process to properly ensure smooth and efficient operations.
This blog post will provide readers with an in-depth look at what RCSA is and how it can be used to manage risk. We’ll explore the methodology behind RCSA, discuss its benefits, and explain how organizations can use it to improve their operations.

Definition of RCSA
RCSA is formally defined as a methodology businesses use to evaluate and manage the risks and controls within their organization. Its roots can be traced back to late 2008 when corporate scandals and financial crises led to a greater emphasis on risk management practices.
Unlike traditional risk assessments that are typically reactive and focus on known risks, RCSA is proactive and seeks to identify potential unknown risks. It offers a holistic view of the organization’s risk landscape, making it a more comprehensive tool for risk management.
Purpose of RCSA
The primary purpose of RCSA is to fortify the company’s defences against potential threats that could hamper its operations, reputation, or bottom line. It serves as a protective shield, safeguarding companies from the turbulent winds of risk that could potentially disrupt their journey toward their objectives.
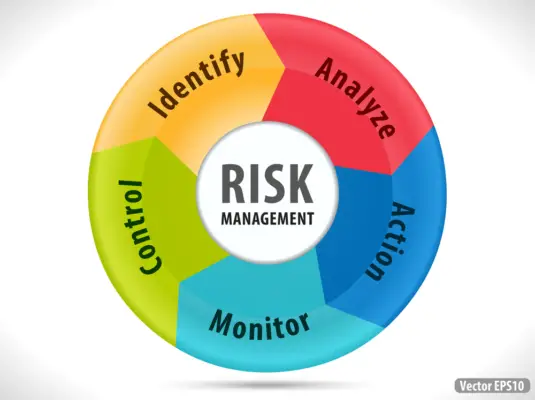
The Steps of RCSA
The RCSA process unfolds in several well-defined stages. First, it involves gathering data on potential risks from various internal and external sources. Once the data is collected, the next step in trend analysis is to assess the likelihood of each risk materializing and evaluate its potential impact on the organization.
This assessment forms the basis for prioritizing risks, with high-impact and high-probability risks receiving the most attention.
After ranking the risks, the next stage is to devise effective risk mitigation strategies. These strategies could involve taking preventive measures to minimize the likelihood of the risk and implementing controls to reduce the risk managers‘ impact on the risk control self-assessments.
Regularly monitoring and reviewing the risks and the controls’ effectiveness form the RCSA process’s final stage.
Risk and Control Self Assessment (RCSA) is a process organisations use to identify and name key risk indicators to assess the key operational risks they face. It involves six steps:
Document Control Environment – This step involves creating a document that outlines the internal control environment, such as policies and procedures, that will be used to manage risk.
Identification of Risks – Potential risks are identified and documented during this step.
Risk Evaluation – This step involves evaluating the potential risks to determine their impact on the organization.
Control Identification – Once risks have been evaluated, controls are identified to control weaknesses and mitigate them.
Risk Analysis – This step residual risk and involves analyzing the effectiveness of the controls in place to reduce risk exposure.
Risk Evaluation – Finally, the risk evaluation step determines if additional controls need to be implemented or if existing ones need to be modified or removed altogether.
Advantages of RCSA
RCSA offers a multitude of benefits to businesses. One of the key advantages is its ability to proactively identify risks, giving companies the upper hand in dealing with potential threats. Instead of being caught off guard, businesses can plan and prepare for risks, thus minimizing their potential impact.
Moreover, RCSA promotes a risk-aware culture within the organization. It encourages all employees to be vigilant about risks, enhancing the organization’s collective ability to identify and manage potential threats.
It also improves communication and collaboration across departments, leading to a more coordinated and effective approach to risk management.
Finally, RCSA can enhance a company’s reputation with key stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulators. Demonstrating a commitment to proactive risk management, businesses can increase trust and confidence among their stakeholders, leading to improved relationships and better business outcomes.
Proactive Risk Identification: RCSA aids in the proactive identification of risks, allowing organizations to anticipate potential threats and act in advance. This results in better preparedness and minimizes the impact of the risk, should it materialize.
Improved Decision-Making: RCSA empowers organizations with the insight needed for informed decision-making by thoroughly understanding the risk landscape. It allows companies to balance risk and return, leading to more strategic and effective business choices.
Operational Efficiency: With a clearer view of potential risks, organizations can streamline their business processes to mitigate these threats. This leads to improved operational efficiency and a better bottom line.
Risk Culture Enhancement: RCSA fosters a risk-aware culture within the organization. It encourages all employees, not just the management, to be vigilant about risks, strengthening the organization’s ability to identify and manage potential threats.
Regulatory Compliance: In many industries, regulatory bodies require companies to have robust risk management practices. RCSA helps organizations to stay compliant and avoid potential fines or penalties.
Stakeholder Confidence: An organization that proactively manages its risks will likely instil greater confidence in its stakeholders, including investors, customers, and suppliers. RCSA sends a strong signal about organizational risk appetite and its commitment to safeguarding its operations and reputation, which can enhance stakeholder trust and loyalty.
Resource Optimization: RCSA allows organizations to prioritize risks based on their potential impact, ensuring that resources are allocated where they are most needed. This results in optimal use of resources and cost-efficient risk management.
Business Resilience: By identifying potential threats and implementing appropriate controls adequately address risks, RCSA enhances the organization’s resilience. It enables businesses to bounce back from disruptions quickly, ensuring business continuity and long-term success.

What is Risk Control Self Assessment? And what are the benefits?
The RCSA operational risk assessment process is a process that identifies and assesses operational risks and assesses the effective control over such risks. It has many advantages for organizations, from quarterly operational risk reports enhancing effective control to increasing business performance.
The RCSA isn’t a standalone business unit but must be integrated within the organization’s operational risks management framework. RCSA can help assess operations risks and identify weaknesses in control measures, which helps raise awareness about operational risks within the company.
Understanding the RCSA process
Risk assessment involves several actions – this is explained below. The initial assessment of operational risks for the RCRA involves identifying potential risks and aggregating them within manageable categories.
This can usually happen by arranging a workshop with key parties that an expert can support. In other situations, companies may take surveys and questionnaires to collect the necessary data through workshops or alongside them. Several outside audits have a role.
Identify risk and assess risks identified against key business objectives
All business lines should determine the operating risk of their products. Identify risk through diverse sources like audits, real loss experience or regulatory reports. Upon identification of potential hazards, evaluate them by their degree: medium, moderate or poor.
Assess controls
Assess whether controls work as intended. The purpose of the self-rated process was to summarize the results of a comprehensive review of control processes and offer senior management a clear overview of the quality and status of the controls.
In terms of quality, the management environment is satisfactory or requires improvement if it is unsatisfactory. Once you have a control system, you should examine the risks remaining. The process should also include identifying appropriate risk owners responsible for managing particular risks.
What is operational risk?
Operational risks mean the risk a company may suffer if it has poor policies, practices or external events. This sense of operational risk management includes events that include human errors and fraud, pandemic events, natural disasters and terrorist attacks.
The impact of a hazard event on the operations could be huge. Business units should have an integrated management system for protecting the company against operational risks in different situations.
Operational risk is an important part of running a business. It is the risk of loss resulting from many normal aspects of business, such as failed processes, inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems, or external events that can disrupt operations. To effectively manage operational risk, several steps need to be taken.
The first step is to identify potential risks. This involves looking at all aspects of the business and assessing what could go wrong in each area. Once potential risks have been identified, they should be assessed to determine their likelihood and impact on the business.
The next step is to develop strategies for mitigating these risks. This may include implementing policies and procedures to reduce the chances of a risk occurring or taking steps to minimize the damage if it does occur. Additionally, businesses should consider investing in insurance coverage for any potential losses due to operational risk.
Finally, businesses should regularly monitor their operational risk management process and adjust as needed. This includes keeping up with technological changes, regulations, and other factors affecting the business’s ability to manage its risks effectively.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

