Operational risks refer to the potential for loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events. These risks can arise from various sources, such as fraud, errors, system failures, legal compliance issues, and cyber-attacks.
Operational risks are omnipresent in all business operations and can pose a significant threat to a company’s financial stability and reputation.
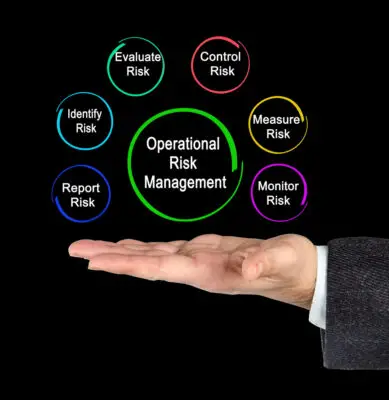
Organizations must understand operational risk management and its impact on their business to effectively mitigate the associated negative consequences.
This article delves into the definition of operational risks, including their causes and impacts on businesses. Additionally, it provides strategies for managing operational risks effectively and best practices for businesses’ effective implementation of these strategies.
Understanding these concepts can help organizations prevent significant losses resulting from operational risk events while ensuring long-term success.

Definition of Operational Risks
Organizations may face potential adverse outcomes due to internal processes, human errors, inadequate systems, or external events beyond their control. Operational risks are those risks that arise from day-to-day business activities and processes. Such risks can lead to financial loss and reputational damage for organizations.
Operational risk examples include system failures, frauds, cyber-attacks, and natural calamities such as earthquakes or floods disrupting operations. They can also include legal and regulatory compliance failures leading to fines and lawsuits against an organization. In short, any event that disrupts an organization’s daily operations can potentially cause operational risk.
Types of operational risks can be categorized into four broad categories: people risk, process risk, system risk, and external events risk. People-related risks include employee misconduct or negligence resulting in errors or fraud.
Process-related risks result from flaws in business processes, such as inadequate controls leading to errors. System-related risks stem from technology failures, such as computer crashes leading to data losses or breaches of sensitive information.
In contrast, External events-related risks result from unforeseen incidents like natural disasters impacting supply chains.
Given their diverse nature across industries worldwide today – it is essential for firms not only to identify but also take measures aimed at mitigating these types of threats regularly so they don’t become catastrophic ones over time!
Causes of Operational Risks
The multifarious and often unpredictable factors underlying malfunctions or disruptions in an organization’s processes are a pervasive concern for stakeholders seeking to mitigate the potential consequences of such events.
Operational risks can arise from internal or external sources, including human error, technology failures, natural disasters, cyber-attacks, and fraud.
Factors contributing to operational risks include inadequate risk management approach and insufficient risk assessment techniques. An effective management approach is essential for identifying and mitigating potential operational risks.
This includes implementing robust controls across the organization’s processes, monitoring performance metrics closely, and conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with regulations.
An effective management approach should also involve creating a culture of risk awareness where all employees understand their role in managing operational risks.
Risk assessment techniques are crucial in identifying potential sources of operational risks. Organizations must conduct comprehensive assessments that consider internal and external factors affecting their business operations.
This involves analyzing historical data on incidents within the organization and those experienced by similar organizations in the industry.
Using advanced analytical tools, organizations can identify emerging trends that may pose future operational risks and take proactive measures to prevent them.
Ultimately, having a sound management approach coupled with robust risk assessment techniques can help organizations manage operational risks effectively while minimizing negative impacts on their business operations.
Impact of Operational Risks
The consequences of malfunctions or disruptions in an organization’s processes can have far-reaching effects on stakeholders, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal implications.
For example, if a bank experiences a failure in its payment processing system, it may result in delayed payments to customers and merchants. This delay could lead to customer dissatisfaction and tarnish the bank’s reputation as a reliable service provider. The costs of compensating affected parties could also significantly impact the bank’s bottom line.
To mitigate operational risks, organizations can adopt various techniques such as contingency planning, redundancy measures, and regular testing of systems.
Contingency planning involves developing strategies for handling unexpected events that disrupt normal business operations. Redundancy measures involve having backup systems or resources that can be used in case of failures or disruptions. Regular system testing ensures that potential issues are identified early enough before they escalate into full-blown problems.
However, mitigating operational risks comes with cost implications for organizations. Such costs may include investing in new technologies or equipment to improve efficiency or hiring additional staff to handle unforeseen events adequately.
Nevertheless, these costs are usually outweighed by the benefits of avoiding significant financial losses or reputational damage resulting from operational failures. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to invest appropriately in mitigation strategies while taking into account their budgetary constraints and priorities.
Strategies for Managing Operational Risks
What are the effective strategies for managing potential disruptions and failures in an organization’s processes to ensure business continuity?
One of the most important steps is conducting a thorough risk assessment. This involves identifying all possible risks that could impact the organization’s operations, evaluating their likelihood and potential impact, and prioritizing them based on severity.
Another key strategy for managing operational risks is contingency planning. This involves developing plans and procedures to respond to disruptions or failures in critical processes. Contingency plans should include clear roles and responsibilities for employees and detailed instructions on how to respond to different types of disruptions.
Organizations should also regularly test their contingency plans through simulations or drills to ensure they are effective in practice.
Overall, effective management of operational risks requires a proactive approach that emphasizes prevention, preparedness, and continuous improvement. Through conducting regular risk assessments, developing robust contingency plans, and continuously monitoring and improving processes, organizations can minimize the likelihood of disruptions or failures occurring while ensuring they are well-equipped to respond if they do occur.
Best Practices for Effective Operational Risk Management
The first step is conducting a thorough risk assessment. This involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks that could impact the organization’s operations.
Risk mitigation is critical in operational risk management. Organizations should prioritize measures aimed at reducing their exposure to identified risks.
These measures may include implementing internal controls, improving employee communication channels, establishing backup plans for critical processes, and investing in technology solutions that automate key tasks while minimizing manual interventions prone to errors or fraud.
Another best practice is establishing a culture of risk awareness within the organization. All employees should be trained to identify potential operational risks and report them promptly using established reporting procedures.
In addition, performance metrics should be developed to track progress towards mitigating identified risks over time continually.
Adopting these best practices will help organizations manage operational risks effectively while ensuring business continuity even when unexpected disruptions occur.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common misconceptions about operational risks?
Contrary to popular belief, these risks are not limited to technical failures or external threats; they encompass a wide range of factors such as human error, inadequate processes and procedures, regulatory non-compliance, and even natural disasters.
For instance, the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill was caused by a combination of flawed equipment design, insufficient safety protocols, and poor decision-making by personnel.
How do different industries and sectors experience operational risks differently?
Industry-specific challenges are crucial in shaping how different sectors experience operational risks. As each industry has its unique characteristics, the potential sources of risk also differ significantly.
For instance, financial services firms are prone to cyber-attacks and fraud, while manufacturing companies face supply chain disruptions and equipment breakdowns. Risk management practices vary across industries as well. Some companies prefer a more centralized approach to risk management, while others rely on decentralized systems for better control over their operations.
Furthermore, regulatory requirements pertaining to risk management also vary between sectors, further complicating the process of managing operational risks effectively. Ultimately, it is essential for organizations to identify industry-specific challenges and tailor their risk management practices accordingly to minimize exposure to operational risks.
What role do employees play in identifying and managing operational risks?
Employee involvement is crucial in the identification and management of operational risks. According to a study conducted by Deloitte, organizations with effective risk management cultures are 15 times more likely to report employee involvement in managing risks.
This highlights the importance of creating a culture where employees understand their role in identifying and reporting potential risks. When actively involved in risk management, employees are better equipped to identify potential issues before they become major problems, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs for the organization.
Therefore, it is essential that companies prioritize establishing a risk management culture that encourages employee participation at all levels of the organization.
What are some emerging trends or technologies that can help mitigate operational risks?
The emergence of risk mitigation technologies has been a game changer in the field of industry-specific risk management. These technologies have enabled businesses to identify and manage operational risks more effectively than before.
One such technology is Artificial Intelligence (AI), which can analyze large amounts of data and identify potential risks before they become problematic.
Another technology that has gained popularity is Blockchain, which provides enhanced security and transparency in financial transactions, reducing the chances of fraud or errors.
These technologies have significantly improved risk management practices across various industries, leading to better decision-making and, ultimately, better outcomes for businesses.
How can organizations measure the effectiveness of their operational risk management strategies?
Effective measurement of operational risk management strategies is essential for organizations to ensure the adequacy and efficiency of their risk mitigation efforts.
Risk assessment is a crucial element in measuring the effectiveness of these strategies, as it helps organizations identify potential risks, evaluate their impact, and develop appropriate control measures.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) also play a vital role by providing metrics that enable organizations to monitor and assess the performance of their risk management strategies over time.
Through tracking KPIs such as incident frequency rates, loss severity levels, and compliance adherence statistics, organizations can adjust their risk management approach accordingly to manage emerging risks better and sustainably mitigate operational risks.

Conclusion
Operational risks are the threats that arise from internal processes, people, systems, or external events. These types of risks can significantly impact an organization’s financial stability, reputation, and operations.
Causes of operational risks include human errors, system failures, fraud, regulatory compliance issues, and natural disasters. The impact of these risks can range from financial loss to reputational damage.
Effective strategies for managing operational risks involve identifying potential threats and implementing controls to mitigate them. Best practices for effective operational risk management include conducting regular risk assessments, establishing clear policies and procedures, training staff members on risk management protocols, and maintaining open communication channels with stakeholders.
In conclusion, successful organizations must be aware of their potential operational risks and take proactive measures to manage them effectively. As the saying goes, ‘prevention is better than cure,’ so it is essential for businesses to prepare themselves adequately before any disaster strikes.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

