Governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) is a framework that helps organizations effectively manage their operations and mitigate risks. It involves the integration of different business functions such as legal, finance, IT, and operations to ensure that an organization meets its regulatory obligations while maintaining ethical standards.
In today’s dynamic business environment where regulations are constantly evolving, GRC has become an essential component of organizational strategy.
It enables organizations to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in their processes and systems, assess the impact of these risks on their operations, and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.

Understanding the Basics of GRC
GRC is an approach that integrates governance, risk management, and compliance management activities to enhance organizational performance. The framework adopts a holistic approach to managing risks by aligning business objectives with practices that ensure regulatory compliance.
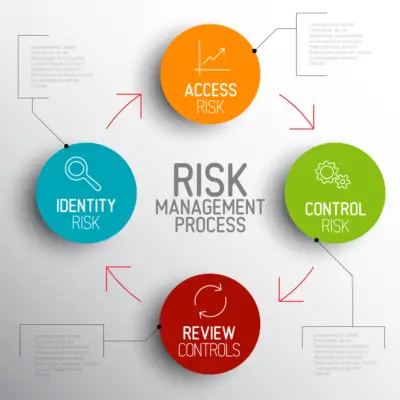
The GRC framework comprises three primary components: governance, risk management, and compliance. Governance refers to the overall decision-making processes that guide the organization towards achieving its objectives. It involves establishing policies, procedures, and guidelines for employees to adhere to while executing their duties.
Risk management is concerned with identifying potential risks that could prevent the organization from achieving its objectives and developing strategies for mitigating these risks.
Compliance management involves ensuring adherence to relevant laws, regulations, standards, policies, and procedures.
Incorporating GRC frameworks into organizational operations can lead to numerous benefits such as improved operational efficiency and effectiveness across all departments. With an effective integrated GRC system in place, organizations can reduce duplication of efforts associated with separate risk management or compliance systems while improving communication among different departments within the organization.
As such, integrating GRC has become an essential component of modern business operations as it promotes better decision-making by aligning internal processes with external requirements while enhancing transparency around organizational goals.
The Benefits of GRC Implementation
The implementation of a comprehensive governance, risk management, and compliance framework has been found to offer numerous advantages in terms of mitigating potential risks and ensuring regulatory compliance across various industries.
One of the benefits of GRC implementation is increased compliance. Through the integration of GRC into an organization’s operations, it becomes easier to maintain compliance with laws and regulations that govern the industry. This helps to avoid costly penalties, legal disputes, and reputational damage that can arise from noncompliance.
Another benefit of GRC implementation is improved risk management. In identifying potential risks and implementing effective controls to mitigate them, organizations can reduce their exposure to unexpected losses or disruptions in their operations.
The use of analytics tools within a GRC framework can also help organizations identify emerging risks quickly so that they can take action before they become major issues.
Overall, the adoption of a comprehensive GRC framework offers organizations the opportunity to improve their ability to identify and manage risks while ensuring regulatory compliance.
As such, it is becoming increasingly important for companies across all sectors to incorporate GRC into their operations as a means of achieving long-term success in today’s highly regulated business environment.

Best Practices for GRC Implementation
To optimize the implementation of a comprehensive governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) framework, organizations need to follow certain best practices.
First and foremost, it is essential to set clear objectives for the GRC program that align with organizational goals. This requires identifying relevant risks and regulatory requirements that impact the organization’s operations.
Additionally, organizations should establish policies and procedures that provide guidance on how to manage risks effectively.
Another best practice for GRC implementation is to ensure effective communication among stakeholders across various departments within the organization. All employees should be aware of their roles and responsibilities in managing risks and complying with regulations.
Regular training sessions can help improve awareness levels, ensuring everyone understands the importance of proper GRC practices.
Measuring GRC effectiveness is also critical in determining whether an organization’s efforts have been successful or not. Organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure the effectiveness of their GRC program against established objectives.
These KPIs must be reviewed periodically to ensure they remain relevant to the organization’s evolving needs. In monitoring these KPIs regularly, organizations can identify gaps in their GRC program and take corrective action as needed to address them.
Implementing a robust GRC framework requires careful planning and execution by following best practices such as setting clear objectives aligned with organizational goals, establishing effective communication channels across different departments within the organization, and measuring effectiveness through KPIs periodically.
GRC in Various Sectors
An examination of the application of governance, risk management, and compliance frameworks in different sectors provides insight into the challenges and opportunities associated with implementing such programs.
In healthcare, GRC aims to ensure that patient safety is maintained by adhering to regulatory requirements while minimizing risks associated with medical procedures.
The complexity of healthcare systems, involving multiple stakeholders including patients, hospitals, insurance companies, and government agencies makes GRC implementation a daunting task. However, effective execution of GRC can improve the quality of care provided to patients through the reduction in errors and better management of risks.
GRC implementation in finance aims to mitigate financial risks while ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. The financial sector is highly regulated due to its impact on national economies and the potential for systemic failures. Financial institutions are required to have adequate systems and controls in place to monitor their activities effectively.
These include risk assessment processes aimed at identifying potential threats, monitoring tools for continuous evaluation of performance against targets or benchmarks, and robust internal controls for detecting fraud or other abuses that could cause significant damage if left unchecked.
Successful implementation of GRC requires an understanding of unique challenges faced by different sectors such as healthcare and finance. Organizations must identify areas where they need improvement in governance structures, risk management practices or compliance requirements before initiating any program.
Furthermore, collaboration between stakeholders is critical for shared ownership and buy-in from all parties involved in implementing these initiatives effectively.
GRC Tools and Technologies
The use of GRC software options has become increasingly popular as organizations seek to streamline their processes, reduce costs, and improve their overall performance.
These software solutions are designed to automate a range of tasks associated with GRC activities, including risk assessments, policy management, compliance monitoring, and reporting. One of the key benefits of using GRC software is that it enables organizations to achieve greater efficiency by automating many manual processes.
This automation allows for faster decision-making based on real-time data insights while also reducing the risk of human error.
In addition to this increased efficiency, GRC automation advancements have also led to better scalability and flexibility in managing complex regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions. Overall, the adoption of GRC tools and technologies has become increasingly important for organizations looking to remain competitive in today’s business landscape.
Through leveraging these solutions to optimize their governance practices while minimizing risks associated with non-compliance or operational inefficiencies, businesses can position themselves for long-term success.
It is essential for companies across all sectors to explore the full range of available GRC software options in order to identify which solutions best align with their specific needs and goals.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the legal consequences of non-compliance with GRC regulations?
Non-compliance with GRC regulations can have severe legal implications, resulting in hefty financial penalties. Companies that fail to comply with these regulations risk damaging their reputation, facing lawsuits and regulatory fines, and even being shut down entirely.
The consequences of non-compliance are akin to a ticking time bomb – the longer it goes unaddressed, the greater the likelihood of an explosion. The metaphor highlights how ignoring GRC regulations can lead to disastrous outcomes for organizations.
Thus, it is imperative for businesses to prioritize compliance with GRC regulations to avoid costly legal implications and ensure long-term success.
How does GRC implementation affect employee productivity and job satisfaction?
The implementation of GRC practices has been found to have a significant impact on employee engagement and job satisfaction, ultimately affecting performance measurement. Engaged employees are more likely to be productive and committed to their work, leading to better organizational outcomes.
Moreover, the proper use of GRC can positively impact the perception of fairness among employees, fostering a sense of trust in management and promoting job satisfaction. In contrast, non-compliance with GRC regulations can result in negative consequences such as legal issues or reputational damage.
Therefore, organizations that prioritize GRC implementation for ethical reasons and not just compliance purposes can reap the benefits of increased employee productivity and satisfaction while also mitigating potential risks.
Can GRC software be customized to fit the specific needs of my organization?
Customization options for GRC software vary depending on the technical requirements of each organization. Some GRC solutions offer more flexibility than others, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs through various customization options.
These options can include configuring workflows, creating custom reports and dashboards, and modifying security settings. However, it is important to note that certain technical requirements may limit the extent of customization available.
Therefore, organizations should carefully evaluate their needs and select a GRC solution that offers adequate customization capabilities while also meeting their technical specifications. By doing so, organizations can ensure that their GRC software fits seamlessly into their operations and supports effective risk management practices.
What are the common challenges faced during GRC implementation and how can they be overcome?
GRC implementation challenges are common across organizations, and overcoming these obstacles requires a strategic approach. Some of the most significant challenges include resistance to change, lack of stakeholder buy-in, inadequate resources, and poor communication.
To address these issues, it is essential to involve all stakeholders in the process from the outset and communicate clearly the objectives and benefits of GRC implementation. Investing in training and education for employees can also help mitigate resistance to change and increase adoption rates.
Additionally, dedicating adequate resources to the project and developing a comprehensive plan with measurable goals can ensure the successful integration of GRC into an organization’s operations.
How does GRC address ethical considerations in addition to regulatory compliance?
In today’s business environment, companies are expected to adhere to ethical principles and regulatory compliance standards. GRC (governance, risk management, and compliance) is a framework that helps organizations manage their policies and procedures to ensure they comply with legal regulations while mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
The implementation of GRC has a significant impact on corporate culture by promoting transparency, accountability, and responsibility among employees. Ethical considerations play a crucial role in the successful implementation of GRC as it ensures that the company operates in an ethical manner.
Conclusion
GRC, or Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance is a framework that helps organizations manage their operations in a more efficient and effective manner.
This article has provided an overview of the basics of GRC, its benefits, best practices for implementation, and its application in various sectors. The benefits of GRC implementation are numerous.
It helps organizations to identify potential risks before they become major issues and provides a structured approach to managing those risks. Additionally, it ensures compliance with regulatory requirements which reduces the risk of legal penalties or reputational damage.
Best practices for GRC implementation include establishing clear policies and procedures for governance, risk management, and compliance; training employees on these policies; regularly monitoring performance; and continuously improving processes.
GRC is an essential framework for any organization looking to improve its operations by managing risks effectively while ensuring compliance with regulations. Implementing best practices for GRC can help businesses achieve better outcomes by reducing costs associated with non-compliance or risk management failures.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.