A contingency plan is a course of action designed to help an organization respond effectively to a significant future event or situation that may or may not happen. It’s essentially a backup plan that outlines procedures that should be followed to minimize the negative effects of certain risks or disruptions.
A contingency plan usually includes the following:
Identification of risks: It begins with a risk assessment process where potential threats or disruptions are identified.
Plan Development: Once risks are identified, a detailed plan is created for each one. This involves defining the specific steps to be taken, the personnel involved, the resources required, and communication strategies.
Responsibility assignment: Each action step in the plan is assigned to a person or team responsible for implementing it in the event of a contingency.
Backup plans for resources: If the event might cause a shortage of necessary resources (like equipment, supplies, or personnel), the plan will detail alternative ways to obtain those resources.
Recovery strategies: These detail how the organization plans to return to normal operations after the event.
Training and rehearsal: After the plan is developed, everyone involved must be trained to carry out their roles effectively. The plan may also be tested or rehearsed to ensure it works as expected.
Review and update: The plan should be regularly reviewed to accommodate organizational or environmental changes.
Contingency plans are a key part of risk management and are especially important for dealing with risks that have a potentially high impact, even if they are unlikely to occur. They help ensure that organizations are prepared to respond quickly and effectively to disruptions, minimizing damage and downtime.
A contingency plan is a critical component of risk management for any organization. It is a proactive approach to dealing with unexpected events or emergencies that can disrupt normal operations and cause financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal liabilities.
A well-designed contingency plan outlines an organization’s procedures and protocols if something goes wrong, ensuring it can respond quickly and effectively to minimize the event’s impact.
The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of what a contingency plan is, how it works, and why it is essential for businesses.
We will explore the key elements of developing a contingency plan, including identifying potential risks, creating response strategies, testing the plan’s effectiveness through simulations or drills, and updating and maintaining the plan over time.
Definition of a Contingency Plan
Contingency plans are critical in any industry as they help organizations prepare for potential disruptions that could affect their operations. They are developed to ensure businesses can continue functioning despite unexpected situations such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, supply chain disruptions, and pandemics.
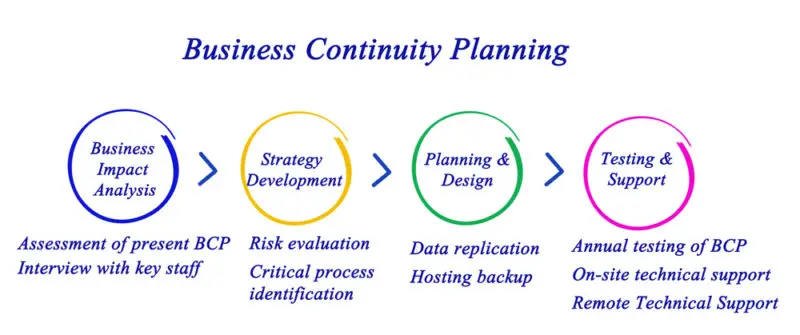
Contingency plans typically include several elements and components, including risk assessment, business impact analysis, communication strategies, and emergency response procedures.
The first step in creating a contingency plan involves assessing all potential risks that could negatively impact business operations. This includes identifying internal and external threats from various sources, such as equipment failures, legal disputes, financial loss, or data breaches.
Once these risks have been identified, the next step is to analyze how they affect business operations and determine which ones require immediate attention. Examples and importance are two key aspects when discussing contingency planning.
A well-designed contingency plan can make the difference between an organization quickly recovering from an unexpected event versus suffering significant losses or even going bankrupt due to prolonged disruption of operations.
Identifying Potential Risks
Risk mitigation involves assessing and prioritizing potential hazards impacting an organization’s operations, reputation, or financial stability. Hazard assessment can be conducted through various methods, such as brainstorming sessions, surveys, and data analysis.
Organizations must consider internal and external factors affecting their operations to identify potential risks effectively. Internal factors include organizational structure, employee behavior, and technology infrastructure.
External factors may include economic conditions, regulatory changes, and natural disasters. Organizations can develop a more robust risk management plan.
Once potential risks have been identified and assessed, organizations can prioritize them based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. This allows for the development of targeted strategies to mitigate each risk effectively.
Organizations can minimize negative outcomes and maintain business continuity by taking proactive measures to manage risks before they occur rather than reacting after the fact.
- Conduct hazard assessments through various methods such as brainstorming sessions or data analysis.
- Consider both internal and external factors when identifying potential risks.
- Prioritize identified risks based on the likelihood of occurrence and potential impact.
- Develop targeted strategies to mitigate each risk effectively.
Incorporating a comprehensive risk management plan into an organization’s overall strategy is essential for long-term success. Identifying potential risks through hazard assessments allows for proactive measures to be taken to mitigate negative outcomes before they occur.
Ultimately this approach leads to better financial performance compared to those who do not take adequate steps towards managing their organizational risk profile, according to Deloitte study findings.
Developing the Contingency Plan
The goal of developing such a plan is to minimize the impact of these disruptions on the organization’s ability to function.
Developing a contingency plan involves several steps. Here’s a general overview of the process:
Risk Assessment: Identify the potential risks or threats that your organization may face. This could include anything from natural disasters and cyber attacks to financial instability or loss of key personnel.
Prioritize Risks: After identifying potential risks, prioritize them based on the likelihood of occurrence and the potential impact on your organization. This will help you focus your planning efforts on the most critical risks.
Identify Preventive Measures: For each identified risk, determine if measures can be taken to prevent or reduce the likelihood of the risk occurring. For example, installing fire suppression systems can reduce the risk of fire damage, while regular data backups can mitigate the risk of data loss.
Develop Response Plans: For each risk, develop a specific action plan that outlines what needs to be done if the risk event occurs. This should include the following:
Assign Responsibilities: Assign responsibilities for each action in the plan. Everyone should know their roles and responsibilities in the event of a contingency.
Develop a Recovery Strategy: Outline how your organization will recover from the event and return to normal operations. This might include strategies for managing business interruptions, restoring data or systems, repairing physical damage, and communicating with customers and stakeholders.
Test the Plan: Conduct drills or exercises to test your contingency plan and ensure everyone knows what to do. This will help identify any gaps or areas of confusion in the plan.
Review and Update the Plan Regularly: Regularly review and update your contingency plan to ensure it remains relevant and effective. This should be done annually or when significant changes to your organization or its environment occur.
Remember, a good contingency plan should be comprehensive, clear, and well-communicated to all relevant parties. It should aim to minimize the impact of risk events and enable your organization to recover as quickly and efficiently as possible.
There are many benefits associated with having a well-developed contingency plan. Chief among them is the peace of mind that your organization has a clear roadmap for responding to unexpected events.
Additionally, by anticipating potential risks and planning for them in advance, organizations can significantly reduce their downtime if they experience an interruption in service.
Finally, having a contingency plan can help maintain stakeholder confidence during times of crisis by demonstrating your organization’s preparedness and commitment to continued operations.
Despite all these advantages, organizations also make common mistakes when developing their contingency plans. One common error is failing to involve key stakeholders in the planning process.
Without input from those who an event may directly impact, it can be difficult to create an action plan that adequately addresses all possible contingencies. Another mistake is creating a static document that doesn’t allow for flexibility or modification as circumstances change over time.
To avoid these pitfalls, it’s crucial for organizations to carefully consider both the content and execution of their contingency plans on an ongoing basis.
Prioritizing stakeholder involvement and ongoing assessment will help ensure this vital document remains relevant and effective over time – providing much-needed peace of mind during periods of uncertainty or disruption.
Implementing and Testing the Plan
One such aspect is the training of employees to ensure they are aware of their roles and responsibilities during a crisis.
Regular testing and evaluations are also necessary to identify potential weaknesses in the plan and rectify them promptly.
It is imperative to conduct these exercises occasionally to maintain an effective plan that can mitigate risks effectively.
Training Employees
Effectively preparing staff members through comprehensive education and development programs can be crucial in ensuring the successful implementation of a backup strategy in case of unexpected events.
This training should include role-playing exercises and simulation software replicating potential emergency scenarios. Immersing employees in simulated situations, they can learn how to respond appropriately under pressure and become more confident in executing their roles during a crisis.
Training sessions should also cover the various aspects of the contingency plan, including communication protocols, evacuation procedures, resource allocation, and documentation requirements.
Employees must understand their individual responsibilities within the plan and how their actions contribute to the overall success of the strategy.
Additionally, regular refresher courses should be provided to ensure that personnel are up-to-date with any modifications or updates made to the plan over time.
Through proper employee training, organizations can increase their preparedness for unexpected events and minimize any potential negative impacts on operations.
- Simulation software allows for realistic emergency scenario testing.
- Role-playing exercises help employees respond confidently under pressure.
- Communication protocols are vital components of a contingency plan.
- Regular refresher courses ensure staff members remain up-to-date with changes to the plan.
Conducting Regular Testing and Evaluations
It is important to provide adequate training to ensure that employees are fully prepared for any potential crisis. However, simply providing training is not enough. Regular testing and evaluations must also be conducted to assess the effectiveness of the contingency plan and identify areas where improvements can be made.
One key aspect of conducting regular testing and evaluations is the importance of feedback. Employees must receive feedback on their performance during simulations or drills to understand what they did well and what areas need improvement.
Feedback can also help management identify strengths and weaknesses in the current contingency plan and make necessary adjustments.
Another important aspect is analyzing failures. When a simulation or drill does not go according to plan, it provides an opportunity to analyze why things went wrong and develop strategies for preventing similar failures in the future.
Updating and Maintaining the Plan
Regularly revising and enhancing the contingency strategy is crucial in ensuring a business remains prepared for unforeseen circumstances, mitigating potential risks, and safeguarding its operations.
Updating and maintaining the plan involves thoroughly evaluating previous testing results, identifying areas requiring improvements, and implementing appropriate changes. The importance of communication cannot be overstated during this process as it ensures all relevant stakeholders are aware of any changes made to the plan.
Continual improvement is a critical aspect of updating and maintaining a contingency plan. It involves regularly assessing the effectiveness of existing strategies and making adjustments where necessary. This allows businesses to adapt to changing circumstances, such as new threats or evolving technological advancements.
Contingency plans must also consider potential future scenarios that could impact business operations, which require frequent updates based on new information or insights gained from ongoing risk assessments.
Updating and maintaining a contingency plan is an ongoing process that requires dedication, resources, and expertise. It requires businesses to remain vigilant about emerging threats while proactively mitigating risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common mistakes to avoid when developing a contingency plan?
Two of the most prevalent errors in developing a contingency plan are a lack of testing and insufficient resources.
Firstly, failing to test a contingency plan can lead to significant issues in an emergency. Without proper testing, it is difficult to determine if the plan will work as intended or identify any potential flaws that need addressing.
Secondly, developing a contingency plan without sufficient resources allocated can result in the inability to execute critical functions during an emergency. Adequate funding and personnel must be assigned to ensure that all aspects of the contingency plan can be implemented effectively.
How often should a contingency plan be reviewed and updated?
It is important to recognize that a contingency plan should not be a static document but a living one that adapts to changing circumstances.
The frequency with which it needs to be reviewed and updated will depend on the nature of the organization and its operations. For instance, an organization operating in a stable environment may only need to review and update its contingency plan annually, while an organization operating in a dynamic environment may need to do so more frequently.
Regardless of the frequency, reviewing and updating the plan cannot be overstated. It ensures that it remains relevant and effective in mitigating risks when they arise.
What are some best practices for communicating the contingency plan to stakeholders?
To effectively communicate a contingency plan to stakeholders, it is important to prioritize the clarity of the message and engage with key individuals throughout the process.
Clarity cannot be overstated when communicating a contingency plan, as stakeholders must understand their roles and responsibilities in an emergency or unforeseen circumstance.
Additionally, stakeholder engagement should be an ongoing effort involving regular updates and opportunities for feedback.
How can a company ensure employees are trained and prepared to execute the contingency plan?
Companies can implement various training methods such as simulations, online courses, and in-person training sessions to ensure that employees are trained and prepared to execute the contingency plan.
These training can help employees understand their roles and responsibilities during an emergency and how to communicate with other team members effectively.
In addition to formal training methods, employee engagement is crucial for the successful execution of the contingency plan.
Companies can encourage employee participation in drills or exercises, provide regular updates on the plan, and create a culture of preparedness.
What are some legal and regulatory considerations that should be taken into account when developing a contingency plan?
Legal compliance and risk assessment are crucial considerations that should be considered when developing a contingency plan.
To ensure the plan is legally compliant, it is important to identify and adhere to all relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This includes understanding any legal obligations or requirements related to data privacy, confidentiality, or intellectual property rights.
Additionally, conducting a thorough risk assessment can help identify potential sources of disruption or failure, allowing for proactive measures to be put in place. This may include implementing regulatory controls or seeking out insurance coverage for potential losses.
Conclusion
A contingency plan is essential in mitigating potential risks and ensuring business continuity. It involves identifying possible threats and developing a strategic plan to address them. The implementation and testing of the plan should be done regularly to ensure its efficacy during times of crisis.
Ironically, some organizations may underestimate the importance of a contingency plan until a disaster strikes. However, it may be too late to salvage the situation or minimize any damages incurred by then.
In short, investing time and resources into developing a comprehensive contingency plan can save businesses from significant losses or even closure in the future.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.



