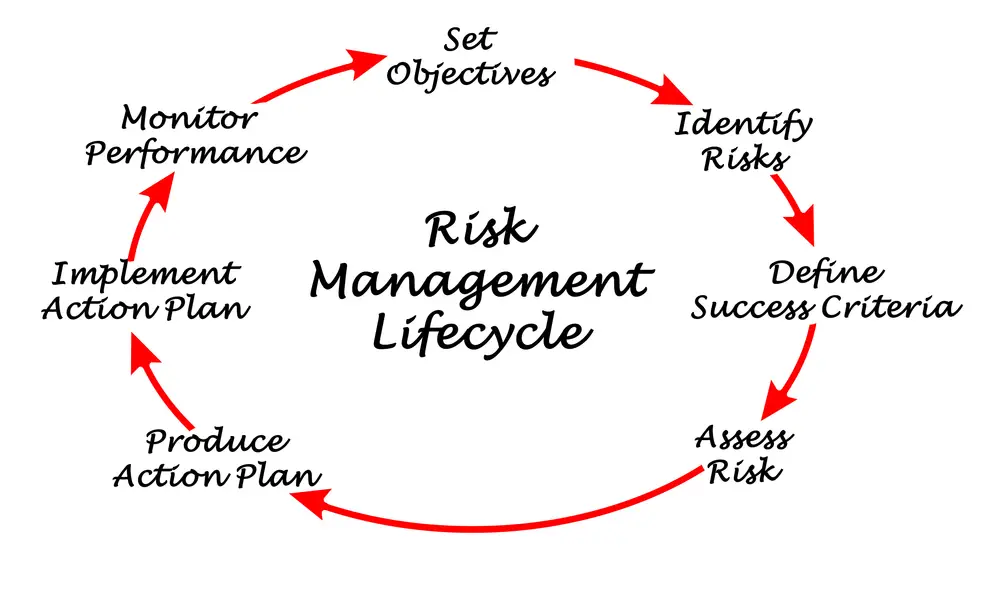
Project and risk management life cycles and cycles often comprise five key stages: introduction, preparation, execution, control, monitoring, executing, and closure/handover. Project risk management occurs over the course of lifecycles, the processes differing by phase.
Effective risk management is crucial for the successful execution of any project. understanding and addressing risks throughout the project lifecycle, organizations, risk owners, and risk managers can minimize potential negative impacts confirmed risks and improve project outcomes.
Risk management is a vital aspect of project management, ensuring that organizations can identify, assess, and mitigate risks throughout the project lifecycle.
On following these best practices, organizations can minimize potential negative impacts to risk management, improve project outcomes, and foster a risk-aware culture.

Project risk management is a critical aspect of successful project execution, ensuring that organizations can proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks throughout the project lifecycle.
In this blog post, we will explore the different stages of the risk management lifecycle, define the core steps of the enterprise risk management process, and provide valuable insights into effective risk management techniques that can help organizations identify new threats and learn from existing risk scenarios.
The Five Key Stages of the Risk Management Lifecycle
risk management lifecycle typically aligns with the project lifecycle and consists of five key stages:
a. Initiation:
During this stage, organizations establish project objectives, scope, and stakeholders, laying the groundwork for effective risk management
The first stage in the risk management lifecycle aligns risk ownership with the project initiation phase. At this critical juncture, organizations set the foundation for effective risk management by establishing project objectives, scope, and stakeholders.
Define Project Objectives:
Clearly outlining the project’s objectives is the first step in initiating the risk management process. By setting measurable, achievable, and time-bound goals, organizations can better understand the potential risks associated with their project and develop strategies to address them.
Determine Project Scope:
Establishing the project scope is essential for identifying risks that may impact the project’s success. By defining the project’s boundaries, deliverables, and constraints, organizations can effectively focus their risk management efforts on areas of greatest concern.
Identify Stakeholders:
Stakeholders play a crucial role in the risk management process, as their input and feedback can help the risk management process identify all potential risks and inform risk response strategies. During project initiation, organizations should identify all relevant stakeholders, including project managers, sponsors, team members, clients, and suppliers, and involve them in the risk management process.
Develop a Risk Management Plan:
A well-structured risk management plan is essential for guiding and managing risk through identification, assessment, and risk mitigation and efforts throughout the project. At the project initiation stage, organizations should develop a comprehensive risk management plan that outlines risk governance structures, policies, procedures, and tools that will be used to manage risks.
Establish a Risk Management Team: A dedicated risk management team is crucial for effectively managing risks during the project lifecycle. Organizations should assemble a team of risk management professionals with diverse skills and expertise who can collaboratively identify, assess, and mitigate risks. Establishing enterprise risk management team and breakdown structure with clear roles and responsibilities for each team member promotes accountability and ensures that risk management activities are executed efficiently and effectively.
Conduct a Preliminary Risk Assessment: During project initiation, organizations should conduct a preliminary risk assessment to identify and prioritize potential risks. This initial assessment should consider factors such as project complexity, resource availability, and stakeholder expectations, as well as historical data, industry trends, and lessons learned from previous projects. By proactively identifying and assessing risks at the outset, organizations can develop risk response strategies and allocate resources appropriately to mitigate potential impacts.
Communicate and Engage: Effective communication is essential for fostering a risk-aware culture and ensuring that risk management activities are integrated throughout the full project life cycle. Organizations should establish communication channels and mechanisms to keep stakeholders informed of risk management progress, as well as to solicit feedback and input. This engagement encourages stakeholder buy-in and ensures that risk management remains a priority throughout the project lifecycle
the project initiation financial planning stage sets the foundation for effective risk management throughout the project lifecycle. By defining project objectives, scope, and stakeholders, developing a risk management plan, assembling a dedicated risk management team,
conducting a preliminary risk assessment, and fostering open communication, organizations can establish a strong risk management framework that will guide them through each stage of the project, ultimately improving project outcomes and reducing potential negative impacts.
b. Planning:
In the planning stage, organizations devise a comprehensive risk management plan that includes risk governance structures, policies, procedures, and tools to guide risk identification, assessment, and mitigation efforts throughout the project.
During this phase of risk center, organizations devise a comprehensive risk management strategy that encompasses risk governance, policies, procedures, and tools to guide risk identification, assessment, and risk mitigation plans and efforts.
Develop a Risk register: A risk register is a centralized repository for capturing and tracking identified risks, their likelihood, potential impact, and mitigation strategies.
Creating a risk register during the project planning phase enables organizations to systematically manage risks and ensure that all relevant information is readily accessible for decision-making.
Establish Risk Criteria: To objectively assess and prioritize risks, organizations should establish risk criteria that reflect the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance levels. These criteria will guide the risk assessment process, helping the team to identify high-priority risks that require immediate attention and resources.
Implement Risk Identification Techniques: Effective risk management relies on the ability to proactively identify potential risks. Organizations should employ various quantitative risk assessments and identification techniques
During the project planning phase, such as brainstorming sessions, expert interviews, historical data, risk analysis,, and scenario planning, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of potential risks and their implications.
Develop Risk Response Strategies: Based on the risk assessment, organizations should devise appropriate risk response strategies to address identified critical risks above. These critical risk response strategies may involve risk avoidance, transfer, reduction, or acceptance, depending on the nature of the risk and its potential impact on project objectives.
Developing these strategies during project planning ensures that the team is well-prepared to respond to risks as they arise.
Allocate Resources: Effective risk management requires the allocation of sufficient resources, such as personnel, time, and budget, to address identified risks.
During project planning, organizations should consider the priority and potential impact of risks when allocating resources, ensuring that high-priority risks receive the necessary attention and support.
Integrate Risk Management into Project Schedule and Budget: To ensure that risk management activities are effectively integrated throughout the project, organizations should incorporate risk management milestones and tasks into the project schedule and budget during the planning phase and project budget.
This integration ensures that risk management remains a priority and that resources are allocated appropriately to support risk management efforts.
Develop a Risk Monitoring and Reporting Framework: Continuous risk monitoring and reporting are vital for maintaining an up-to-date understanding of risks and their potential impacts on project objectives.
Organizations should develop a risk monitoring and reporting framework during the project planning phase, outlining the frequency and format of risk updates, as well as the channels and stakeholders to whom updates will be communicated.
Conduct Risk Management Training and Awareness: Ensuring that project team members and key stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities in the risk management process is essential for fostering a risk-aware culture.
During project planning, organizations should provide risk management training and awareness programs to equip team members with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively manage risks throughout the project lifecycle.

c. Execution:
As the project advances, organizations actively monitor and manage risks, implementing risk response strategies and taking corrective actions as needed to the risk treatment ensure project success.
The third stage in the risk management lifecycle is project execution, where the planned risk management strategies are put into action.
During this phase, organizations must proactively manage risks to ensure that project objectives are met and potential negative impacts are minimized. Let’s examine the key aspects of risk management during project execution, maintaining an engaging and formal tone.
Implement Risk Response Strategies: As the project progresses, risks that were identified during the planning phase may materialize. Organizations should execute the risk response strategies devised earlier, adjusting them as necessary based on the evolving project landscape.
Monitor and Control Risks: Continuous risk monitoring and control are essential during project execution to before project failure, track the effectiveness of risk response strategies and identify any emerging risks.
Organizations should use the risk monitoring and reporting framework established during project planning to regularly review risk assessments, update risk registers, and communicate risk-related information to both internal and external stakeholders.
Escalate Risks When Necessary: Some risks may exceed the risk tolerance levels defined during project planning or may require executive-level intervention.
Organizations should have a clear escalation process in place to ensure that such significant risks, are promptly communicated to the appropriate stakeholders for timely decision-making and resource allocation.
Regularly reviewing and updating risk assessments enables organizations to proactively manage risks and adjust risk response strategies as necessary.
Foster a Risk-Aware Culture: During project execution, organizations should continue to promote a risk-aware culture by encouraging open communication and collaboration among project team members and stakeholders.
Regular risk management training and awareness sessions can help reinforce the importance of risk management and empower team members to effectively manage risks throughout the project lifecycle.
Document Lessons Learned: As risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated during project execution, valuable lessons can be learned about the organization’s risk management process and capabilities.
Review Risk Management Performance: Periodic reviews of the risk management process during project execution can help organizations assess the effectiveness of their risk management strategies and identify opportunities for improvement.
d. Monitoring and Control:
Organizations continuously track and evaluate the effectiveness of risk management efforts throughout the project, making adjustments to risk management plans and strategies as necessary to address changing conditions or emerging threats.
e. Closure:
At the end of the project, organizations conduct a thorough review of the risk management process, capturing lessons learned and updating risk management practices for future projects.
The final stage in the risk management lifecycle is project closure, where organizations wrap up the risk occurring project and evaluate its overall performance, including the effectiveness of risk management efforts.
Conduct a Post-Project Risk Review: As part of project closure, organizations should conduct a comprehensive review of the risk management process, assessing the effectiveness of the risk identification process, assessment, response strategies, monitoring, and control.
This review can help with project costs, identify areas for improvement and highlight best practices that can be carried forward into future projects.
Document Lessons Learned: Throughout the project lifecycle, organizations will have encountered various risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Project closure provides an opportunity to document these lessons learned, capturing valuable insights that can inform and enhance risk management practices in future projects.
Evaluate Risk Response Strategies: During project closure, organizations should evaluate the risk response strategies implemented throughout the project, assessing their effectiveness in mitigating risks and minimizing potential impacts.
This evaluation can provide valuable insights into the appropriateness of different risk response strategies and help organizations refine their risk management evaluation approach for future projects.
Review Risk Governance and Policies:The project closure stage is an ideal time to review the risk governance framework and policies that guided the risk manager or former project manager’s risk management efforts.
Organizations should assess whether these frameworks and policies were effective in supporting risk management and make any necessary adjustments to better align with organizational objectives and industry best practices.
Communicate Risk Management Outcomes: As part of project closure, it’s essential to communicate the outcomes of risk management efforts to project stakeholders, including senior risk management experts, project directors, sponsors, and team members.
This communication should highlight successes, challenges, and lessons learned, demonstrating the value of risk management in achieving project objectives and fostering a risk-aware culture.
Update Risk Management Processes: Based on the lessons learned and insights gained during project closure, organizations should update their risk management processes, tools, and templates to better support future projects.
This continuous improvement ensures that organizations remain agile and responsive to changing risk landscapes and are better equipped to manage new risks, in future projects.
Celebrate Successes: Finally, project closure provides an opportunity for project management office to recognize and celebrate the successes of the project manager and team in managing risks and achieving project objectives.
Acknowledging these achievements can help build a risk-aware culture, motivate team members, show risk management excellence and reinforce the importance of risk management in delivering successful projects.

Defining the Core Risk Management Process Steps
Risk management varies between different phases; organizations sometimes include additional measures to keep specific demands from falling through the nose of the snout. Action may involve assignments to roles and duties or measures to gauge risk tolerance at a company level.
Many business units use an integrated business process, that describes the steps required for identifying, monitoring risks evaluating and implementing risk management. An organization can identify new threats by using risk management techniques while evaluating the lessons learned from existing risk scenarios.
While risk management processes may vary between organizations and project phases, there are several core steps that are essential for effective risk management:
a. Risk Identification:
Organizations should proactively identify risks and document potential risks that could impact project objectives, drawing on input from various sources, such as historical data, stakeholder feedback, and industry trends.
b. Risk Assessment:
Once risks have been identified, organizations should assess the likelihood, risk probability and potential impact of each identified risk, assigning a risk rating based on factors such as probability, severity, and velocity.
c. Risk Response Planning:
Based qualitative risk assessments and on the risk assessment, organizations should develop risk response strategies to address identified risks, selecting appropriate risk mitigation measures, such as avoidance, transfer, reduction, or acceptance.
d. Risk Monitoring and Control:
Throughout the life cycle of project, organizations should continuously monitor and control risks, ensuring that risk response strategies are effectively implemented and taking corrective actions as needed to address emerging threats or changing conditions.
e. Risk Review and Learning:
At the end of the project, organizations should review the risk management process, capturing lessons learned and updating risk management practices to improve future project outcomes.
Integrating Risk Management Techniques and Lessons Learned
Organizations can enhance their risk management capabilities by integrating proven risk management techniques and lessons learned from existing enterprise risk management scenarios:
a. Assigning roles and responsibilities:
Clearly defining risk management roles and responsibilities at all levels identify the role players who contributed to the initiation of a risk lifecycle within the organization ensures accountability and promotes a risk-aware culture.
b. Establishing risk tolerance:
Organizations should establish risk tolerance levels at the company level, guiding decision-making and resource allocation throughout the project lifecycle.
c. Adopting an integrated risk management approach:
Many organizations benefit from an integrated risk management approach or risk manager that encompasses all aspects of the project, from strategic planning to operations and performance measurement.
d. Leveraging technology and data analytics:
Advanced data analytics tools and technology solutions can provide valuable insights into risk exposure, helping organizations identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern.
e. Continuous improvement and learning:
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning, organizations can refine their risk management processes, adapt to changing conditions, and proactively address emerging threats.
Conclusion
Understanding and navigating the risk management lifecycle stages effectively is crucial for organizations to ensure the successful execution of their projects. By implementing the core risk lifecycle management process steps and integrating proven risk management techniques, organizations can proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could impact their project objectives.
Additionally, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning allows organizations to adapt to changing conditions and address emerging threats, ultimately improving project outcomes and achieving long-term success.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.