ESG, an Environmental, Social, and Governance acronym, has emerged as a critical framework for evaluating businesses‘ sustainability and ethical practices. The concept of ESG goes beyond the traditional financial metrics to analyze a company’s impact on the environment, its employees and other stakeholders, and its governance practices.
As such, it has become an essential consideration for investors, regulators, and society in assessing a business’s long-term viability.
ESG is not just about compliance or reputation management but also about creating value for all stakeholders.
In this article, we explore what ESG means in business and why it is vital for companies to integrate these considerations into their strategies.
We also examine how businesses measure and report on ESG factors while highlighting some challenges when implementing a practical ESG framework.
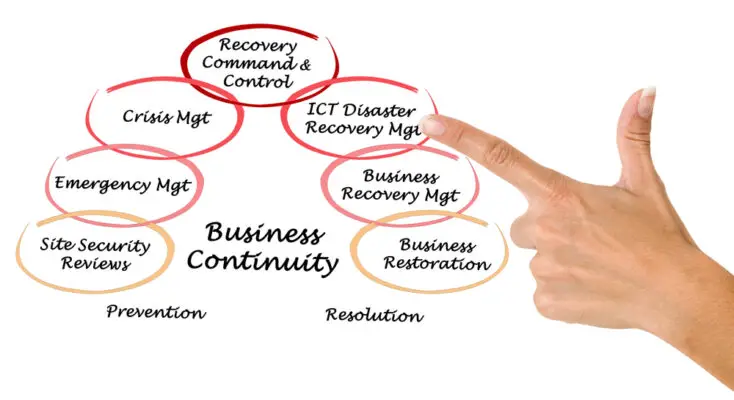
Definition and Overview of ESG
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It’s a set of criteria that socially conscious investors use to screen potential investments. Here’s a quick overview:
Environmental Criteria: These examine how a company performs as a steward of the natural environment. It includes waste and pollution, resource depletion, greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and climate change.
Companies with vital environmental considerations have policies and procedures to manage these issues and are less likely to encounter regulatory fines, litigation, and reputational damage.
Social Criteria: This looks at how a company manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates. Social criteria include labor standards, employee health and safety, human rights, diversity, customer satisfaction, and community development.
Companies that score well in social criteria are often seen as more sustainable, improving employee morale, customer loyalty, and public perception.
Governance Criteria: This deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, and internal controls, shareholder rights, and transparency.
Governance criteria ensure that companies make decisions in the best interest of their shareholders, employees, and customers. Good governance can result in better long-term performance and fewer corporate scandals.
Together, these criteria aim to measure a company’s sustainability and societal impact, factors that many investors believe are important in determining the future financial performance of a company.
Many fund managers now use ESG ratings to assess the sustainability and ethical impacts of an investment in a company. In contrast, some investors use them to screen potential investments for their social or ethical impact.
Investors are increasingly demanding ESG data from companies, which has led to a growth in ESG reporting standards and frameworks, such as those provided by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
ESG criteria are used by investors, analysts, and other stakeholders to assess the sustainability and ethical impact of a company’s operations.
ESG factors include environmental issues such as climate change, pollution prevention, and natural resource management; social concerns such as labor practices, human rights policies, and community relations; governance considerations such as board composition, executive compensation structure, and shareholder rights.
Companies prioritizing ESG criteria tend to operate ethically and sustainably while generating long-term value for shareholders.
ESG should not be confused with Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), an older concept focusing on how businesses can contribute to society beyond profits.
While CSR focuses more on philanthropic activities like charitable donations or employee volunteer programs aimed at giving back to society, ESG is a broader framework for evaluating corporate behavior based on its impact on key stakeholders like employees, customers, suppliers, communities & the environment.
Importance of ESG for Businesses
Incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors in business decision-making is becoming increasingly important as research shows that companies with strong ESG practices tend to outperform their peers financially.
For example, a study by MSCI found that companies with high gender diversity on their boards had a Return on Equity (ROE) of 10.1%, compared to 7.4% for those without diverse boards. This suggests that companies prioritizing ESG factors in their operations may have a competitive advantage over those not.
Implementing ESG practices can also lead to other benefits for businesses beyond financial performance. These include improved brand reputation and customer loyalty, increased employee satisfaction and retention rates, and reduced risk from potential legal or regulatory issues related to environmental or social concerns.
However, there are also drawbacks to implementing ESG practices, such as the potentially higher costs associated with sustainable initiatives and the need for additional resources dedicated to monitoring and reporting these efforts.
Overall, it is clear that incorporating ESG factors into business decision-making can significantly impact financial performance and overall company success.
While there may be challenges associated with implementation, the potential benefits make this an essential consideration for any organization looking towards long-term sustainability and success in today’s business landscape.
Measuring and Reporting ESG Factors
To measure these factors accurately, businesses must determine which data sources are most relevant to their industry and specific objectives. For example, a manufacturing company may focus on tracking emissions and waste reduction efforts, while a financial institution may prioritize diversity and inclusion metrics.
Once data sources have been identified, businesses must develop industry-specific metrics that can effectively capture the impact of their ESG initiatives.
These metrics should be based on rigorous quantitative and qualitative data analysis. Additionally, they should be designed with stakeholder expectations in mind to communicate the business’s progress toward its ESG goals effectively.
Reporting ESG factors is also critical for businesses seeking to build stakeholder trust. This requires regular communication about progress made towards achieving targets and any challenges faced along the way.
When done effectively, transparent reporting can help businesses foster positive relationships with customers, investors, employees, regulators, and other key stakeholders increasingly demanding accountability from companies across all industries.
Incorporating ESG Considerations into Business Practices
Incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into organizational practices has become increasingly crucial as stakeholders demand greater accountability and transparency from companies across various industries.
Sustainability initiatives and social responsibility programs are two ways businesses can incorporate ESG considerations into their practices.
Social responsibility programs, on the other hand, focus on contributing to the well-being of society by supporting local communities or promoting diversity and inclusion within the workplace.
One example of a company successfully incorporating ESG considerations into its business practices is Unilever. The multinational consumer goods company has made sustainability a core part of its business strategy through its Sustainable Living Plan.
This plan sets out specific targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving water efficiency, reducing waste, promoting sustainable agriculture, and increasing access to hygiene products in developing countries.
Additionally, Unilever’s social responsibility programs include initiatives to promote gender equality within the workplace and support smallholder farmers in developing countries.
Incorporating ESG considerations into business practices not only benefits society but also brings economic benefits to companies themselves.
Businesses can improve brand reputation and increase customer loyalty by minimizing environmental impact and enhancing stakeholder engagement through social responsibility programs.
Furthermore, integrating these considerations into decision-making processes can lead to more informed strategic decisions considering long-term impacts on financial performances and societal well-being.

Challenges and Future of ESG
Analyzing the challenges and prospects of integrating ESG considerations into organizational practices reveals the need for a comprehensive approach that addresses various issues.
One critical challenge is data quality, given that many existing ESG metrics fail to provide accurate and reliable information on companies’ environmental, social, and governance performance.
Furthermore, ESG reporting lacks standardization, which makes it difficult for stakeholders to compare different organizations’ ESG performance or track their progress over time.
To overcome these challenges, companies must invest in robust data collection processes and adopt standardized frameworks for reporting ESG performance.
Another significant challenge facing companies is regulatory compliance. As governments worldwide introduce new regulations promoting sustainable business practices, organizations face increased pressure to comply with these laws.
However, regulatory requirements often vary across jurisdictions and can be complex and costly.
Companies must develop a thorough understanding of relevant regulations in each market they operate in to ensure compliance while balancing their financial goals.
Despite these challenges, the prospects for integrating ESG considerations into business practices are promising.
As consumers become more socially conscious and investors increasingly prioritize sustainability factors when making investment decisions, companies demonstrating strong ESG performance will likely outperform their peers financially.
Additionally, by proactively addressing environmental and social risks through effective governance structures and stakeholder engagement strategies, companies can reduce reputational harm associated with negative impacts on communities or ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of ESG on a company’s stock performance?
Investors increasingly rely on ESG impact metrics to evaluate a company’s potential for long-term success.
According to a recent study by MSCI, companies with strong ESG performance have consistently outperformed their peers over the last five years.
This data point serves as a powerful metaphor for the impact of ESG on a company’s stock performance.
Investors’ perception of a company’s commitment to environmental, social, and governance issues can significantly affect its valuation in today’s market.
Companies prioritizing sustainability and ethical business practices are more likely to attract investment and achieve sustainable growth.
How do investors incorporate ESG factors into their investment decisions?
When making investment decisions, investors often consider ESG factors, which include environmental, social, and governance aspects of a company’s operations. Incorporating these factors into investment strategies can help investors identify companies prioritizing sustainability and ethical practices.
To do so, investors may rely on ESG reporting requirements set by regulatory bodies or corporate social responsibility initiatives undertaken by companies.
These initiatives can include reducing carbon emissions, promoting diversity and inclusion in the workplace, or implementing strong governance structures to prevent corruption.
Are there any industries that are exempt from ESG considerations?
Industries are not exempt from ESG considerations, as environmental regulations and ethical sourcing have become increasingly important factors in business decision-making.
Businesses across all sectors must consider the potential impact of their operations on the environment and society when making strategic decisions.
Firms that fail to do so face legal penalties, reputational damage, and economic losses.
As such, companies must incorporate ESG factors into their core business practices and engage with stakeholders to ensure they meet the evolving expectations of investors, customers, employees, and regulators alike.
How do small businesses incorporate ESG considerations into their operations?
Small businesses face significant challenges in incorporating ESG considerations into their operations. One of the biggest challenges is the lack of resources and expertise to develop an ESG strategy and implement it effectively.
Additionally, small businesses may struggle to navigate the complex reporting requirements associated with ESG, which can be time-consuming and costly.
To address these challenges, small businesses must first identify their key sustainability risks and opportunities and engage stakeholders to understand their expectations around ESG performance.
They can then develop a targeted approach that aligns with their business objectives while meeting reporting requirements.
What role do governments and regulatory bodies play in promoting ESG practices?
Government incentives and regulatory bodies are pivotal in promoting ESG practices among businesses. Corporate responsibility programs may not always be sufficient, given that companies may prioritize short-term profits over long-term sustainability goals.
Hence, governments can create financial incentives for companies to adopt ESG practices via tax breaks or subsidies. Regulatory agencies can also mandate reporting requirements for environmental, social, and governance factors as part of their compliance framework.
This approach will encourage business transparency and accountability while giving investors the information they need to make informed investment decisions.

Conclusion
ESG, or Environmental, Social, and Governance, is a term that has gained significant traction in the business world. It refers to the three critical areas businesses must consider when making decisions. ESG factors have become increasingly important due to a growing awareness of businesses‘ impact on society and the environment.
This article has provided an overview of ESG, discussed its importance for businesses, and explored some challenges associated with incorporating ESG considerations into business practices.
Measuring and reporting on ESG factors is essential for companies looking to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices. However, this process is not always straightforward.
The lack of standardized reporting frameworks makes it difficult for investors and stakeholders to compare different companies or assess their performance over time. Additionally, there may be concerns about data accuracy or reliability.
Despite these challenges, there are many compelling reasons why businesses should embrace ESG considerations as part of their decision-making processes. By taking a proactive approach towards environmental issues, social responsibility, and good governance practices, companies can improve their reputation among customers, employees, and investors alike.
Moreover, embedding sustainability into core business practices can drive positive change in society while improving long-term financial returns.
Economic growth must be balanced with environmental protection and social responsibility. Businesses must embrace ESG considerations as part of their decision-making processes.
Sustainable development is imperative for all organizations seeking long-term success. It’s no longer just about profit but also about what’s right for people, the planet, and our future generations.
Investors, society, and customers expect nothing less than transparency, responsibility, and accountability from organizations that want to survive today’s global market.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

