The COSO Framework, by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, is a key tool for enhancing governance and managing risks within organizations.
It includes components like Control Environment, Risk Assessment, and Control Activities to establish an effective system of internal controls. This framework helps align control activities with company objectives, monitor control effectiveness, and manage risks in line with tolerance levels thus effective internal controls.
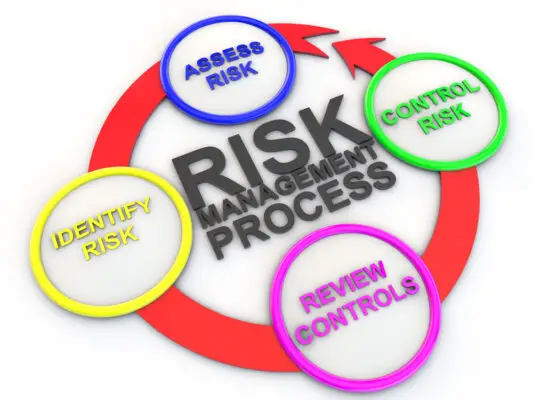
By implementing COSO, businesses and several private sector organizations can improve operational efficiency, strengthen risk mitigation, ensure legal compliance, and enhance overall performance. Understanding its components and practical application can greatly benefit organizations seeking to enhance their internal control systems and ensure the effectiveness of the organization’s internal control system in managing risks and achieving objectives.
Understanding the COSO Framework
The COSO Framework comprises five key components:
- Control Environment.
- Risk Assessment.
- Control Activities.
- Information and Communication.
- Monitoring.
Each plays an essential role in establishing robust internal controls. Understanding these components is important for organizations looking to have established controls and effectively implement the framework to achieve operational, reporting, and compliance objectives.
Framework Components Overview
Consisting of five integral components, the COSO Framework provides a structured approach to internal control that supports organizations in achieving their objectives. These components work together seamlessly to establish internal control objectives in operations, reporting, and compliance.
- Control Environment sets the tone for internal control
- Risk Assessment identifies and manages risks
- Control Activities are the policies and procedures in place to mitigate risks
Information and Communication ensure the effective flow of information, internal and external communications while Monitoring involves ongoing evaluations to guarantee the effectiveness of internal controls and prompt reporting of deficiencies.
This thorough framework plays a critical role in enhancing organizational performance and governance of public and publicly traded companies everywhere.
Importance of Implementation
Implementing the COSO Framework within organizations is crucial for establishing a robust culture of internal control and risk management. It guarantees that risks are identified, assessed, and managed in alignment with the organization’s risk tolerance.
Control activities defined by the framework help mitigate risks, support business performance, and prioritize risks that align with company objectives. Regular monitoring activities evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls and report deficiencies promptly.
Practical Application Tips
When utilizing the COSO Framework, organizations can benefit from involving various levels of management in evaluating and enhancing internal controls. Senior management plays an essential role in appraising and strengthening internal controls to guarantee effective operations, compliance, and reporting. Management accountants are professionals who play a crucial role in evaluating and enhancing internal controls within the COSO framework.
Lower-level managers and employees also contribute valuable insights to enhance the internal control system. Establishing a committee dedicated to brainstorming ideas for improved internal controls is recommended to leverage the diverse expertise within the organization.
By engaging individuals at different hierarchical levels, organizations can create a robust internal control environment that aligns with the principles of the COSO Framework.
Engage senior management in appraising internal auditor, and enhancing internal controls.
Encourage input from lower-level managers and employees to strengthen the internal control system.
Establish a dedicated committee to brainstorm ideas and implement controls for improved internal controls.
Components of the COSO Framework
The Components of the COSO Framework, including Control Environment, Risk Assessment, Control Activities, Information and Communication, and Monitoring Activities, play vital roles in ensuring effective internal control within organizations.
Each component addresses specific aspects such as establishing a culture of internal controls, identifying and managing risks, implementing control measures, facilitating information flow, and monitoring control effectiveness.
Understanding these components is essential for organizations to establish robust internal control systems that support their objectives and compliance efforts.
Control Environment Overview
Within the COSO Framework, the Control Environment stands as a pivotal component that sets the tone for internal controls within an organization. This critical aspect of the framework encompasses management integrity, ethical values, and a strong commitment to internal control.
The Board of Directors plays a significant role in overseeing the Control Environment, ensuring its effectiveness in promoting regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards. By emphasizing legal liability reduction, operational integrity, and alignment with industry risk standards, the Control Environment aims to establish a foundation for robust internal controls.
- Management integrity
- Ethical values
- Commitment to internal control
Risk Assessment Importance
Highlighting the foundational role of enterprise risk management and assessment within the COSO Framework, organizations are tasked with identifying and managing potential risks to support the effectiveness of their internal control systems. Effective enterprise risk management and assessment is vital for achieving operational, reporting, and compliance objectives.
Within the COSO Framework, risk assessment involves evaluating risks based on the organization’s risk tolerance to minimize potential harm. This process guarantees that identified risks are aligned with the organization’s internal control system, supporting the organization in meeting its goals.
Control Activities Examples
Control activities within the COSO Framework encompass a range of policies, procedures, and actions that play a pivotal role in mitigating risks and ensuring operational effectiveness.
Examples of these critical control activities include:
- Segregation of duties: Assigning different responsibilities to different individuals to reduce the risk of errors and fraud.
- Authorization procedures: Establishing protocols for approving transactions and activities to maintain control over organizational processes.
- Physical security measures: Implementing safeguards such as access controls and surveillance to protect assets and sensitive information.
These control activities are instrumental in aligning with operational objectives, enhancing the financial statements reporting accuracy, managing risks effectively, ensuring compliance with regulations, and ultimately supporting the organization’s goals through robust internal control systems external financial reporting.
Monitoring Activities Significance
The significance of monitoring activities within the COSO Framework lies in their essential role in ensuring the ongoing effectiveness of internal controls.
By conducting regular evaluations, organizations can identify any potential risks and maintain the integrity of their internal control systems. Monitoring activities not only help in detecting weaknesses but also play a crucial role in holding individuals and departments accountable for their responsibilities.

Reports generated from these activities provide valuable insights to the Board of Directors financial executives, and upper management, enabling informed decision-making regarding the organization’s internal control status. This proactive approach to monitoring ensures that any changes in the organization’s environment are promptly addressed to prevent exposure to new risks.
Implementing the COSO Framework
When implementing the COSO Framework, organizations should focus on key implementation steps to monitor adherence guarantee alignment with strategic goals
Integration with existing systems is essential to streamline internal control processes effectively.
Key Implementation Steps
To successfully implement the COSO Framework within an organization, the key steps involve aligning the internal control framework with the strategic roadmap, evaluating internal control maturity, addressing control gaps, utilizing Compliance management software, and planning remediation steps according to COSO guidelines.
Key Implementation Steps:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the internal controls program to identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Develop a detailed remediation plan outlining specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities for addressing control deficiencies.
- Utilize compliance management software to streamline control activities and guarantee adherence to COSO requirements.
Integration With Systems
Integration with systems plays a pivotal role in implementing the COSO Framework effectively within an organization, ensuring that internal controls are aligned with operational processes and technology infrastructure.
Strategic alignment of internal controls with the organization’s systems is essential for seamless integration. Compliance management software can aid in coordinating control activities in accordance with the COSO Framework, facilitating efficient monitoring and reporting.
Developing a detailed plan based on COSO principles is vital to establish robust internal controls that mitigate risks effectively. Evaluating the maturity of the internal controls program helps in identifying control gaps and prioritizing remediation actions.
Benefits of Using COSO
In addition, utilizing the COSO Framework offers organizations the opportunity to enhance their operational efficiency by standardizing processes and improving overall performance.
This framework also aids in strengthening risk mitigation fraud deterrence strategies, enabling businesses to detect and prevent fraudulent activities effectively.
Furthermore, organizations can benefit from COSO by ensuring compliance with laws and regulations, providing assurance and support in maintaining operational integrity.
Operational Efficiency Enhancement
Enhancing operational efficiency through the utilization of the COSO Framework results in standardized processes, improved risk management, and enhanced compliance measures within organizations.
The framework aids in:
- Standardizing business processes to streamline operations and reduce inefficiencies.
- Detecting fraudulent activities early on, safeguarding the organization’s assets and reputation.
- Facilitating compliance monitoring to guarantee adherence to legal requirements and industry standards.
Risk Mitigation Strategy
The implementation of the COSO Framework in organizational risk management fosters a thorough approach to identifying and addressing potential risks. By integrating the COSO Framework, businesses can develop a robust risk mitigation strategy aligned with their organizational objectives.
This approach enhances decision-making processes by systematically understanding and managing risks that could impact operations, reducing the likelihood of financial loss, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
Through the implementation of effective risk controls, organizations can proactively respond to emerging risks and uncertainties, safeguarding assets and ensuring the achievement of business objectives.
The COSO Framework provides a systematic and exhaustive methodology for managing risks, enabling organizations to navigate challenges and uncertainties effectively.

Compliance Assurance Support
By implementing the COSO Framework, organizations can greatly enhance their compliance assurance capabilities. This framework provides essential support in various aspects of reasonable assurance, such as standardizing internal control processes to guarantee consistency and reliability.
Detecting and preventing fraudulent activities is another key benefit of the COSO Framework, safeguarding the organization’s assets and reputation. Additionally, it helps in enhancing operational efficiency, which can lead to cost reductions and improved overall performance.
Through the adoption of COSO, organizations can effectively adhere to legal and ethical requirements, mitigate risks, and implement best practices that support sustainable profitability.
The framework not only aids in reducing costs but also ensures that ethical requirements are met, promoting a culture of integrity and accountability within the organization.
Challenges With the COSO Framework
Businesses may encounter hurdles when implementing the COSO Framework. Challenges include monitoring its effectiveness and adapting to evolving regulatory requirements.
The broad scope of the framework and the need for thoughtful decision-making can make its implementation complex.
Addressing these challenges is vital for private sector organizations seeking to derive maximum benefit from the COSO Framework.
Implementation Hurdles Faced
Implementing the COSO Framework often presents organizations with formidable obstacles in aligning their internal control objectives with its extensive scope. Organizations may struggle with the rigid structure of the framework and face challenges in categorizing processes into the framework’s defined components.
Some find the limited prescriptive guidance overwhelming, necessitating additional support to navigate the complexity of the framework. To overcome these hurdles, businesses must adapt their organizational structure to align with the COSO Framework’s requirements, making tough decisions along the way.
Implementing internal controls within the framework can be a challenging task, requiring thorough understanding and careful planning to guarantee effective integration into the organization’s operations.
Monitoring Effectiveness Challenges
Organizations implementing the COSO Framework encounter significant challenges in effectively monitoring the framework’s controls and processes to guarantee ongoing compliance and control effectiveness. Ensuring that changes in processes are promptly identified poses a key challenge, as does the complex task of monitoring for compliance deficiencies and control effectiveness.
“Internal auditors and external auditors play an important role in this process, yet coordination and communication challenges can impede their effectiveness. Timely and accurate reporting of deficiencies to the board of directors is essential for maintaining control effectiveness.
Additionally, as key business processes evolve, organizations may find it difficult to consistently monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls. These challenges highlight the importance of a robust monitoring system to adapt to the evolving landscape of business processes and regulatory requirements.
Addressing Evolving Regulatory Requirements
Managing the challenges posed by evolving regulatory requirements, the COSO Framework encounters the need for ongoing updates to maintain alignment with changing regulations and reporting standards. Changes in regulations and reporting standards necessitate continuous updates to uphold the framework’s relevance.
This demands flexibility and adaptability within the COSO Framework to stay responsive to regulatory demands.
Organizations utilizing the COSO Framework must actively monitor and adjust implement internal controls, to meet new regulatory requirements effectively. The evolving regulatory landscape underscores the importance of a dynamic and responsive internal control system under the COSO Framework.
- Flexibility and Adaptability
- Monitoring Controls for Compliance
- Responsive Internal Control System
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does a COSO Work?
A COSO framework operates by integrating five key components – control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring – to establish effective internal control systems and operating environments that align with organizational objectives and regulatory requirements.
What Is the COSO Internal Control Integrated Framework Used to Do?
The COSO Internal Control Integrated Framework is utilized to provide assurance in achieving organizational reporting objectives and, overseeing internal controls for operations, reporting, and compliance, with key components including control environment, risk assessment, control activities, communication, and monitoring.
What Are the Principles of COSO Framework?
The principles of the COSO Framework encompass Control Environment, Risk Assessment, Control Activities, Information and Communication, and Monitoring Activities. They guide organizations in establishing robust internal control systems, emphasizing leadership commitment, and risk assessments and management, operational controls, communication, and ongoing monitoring.
What Is COSO Known For?
COSO is known for its contribution to advancing internal control practices through a structured approach that emphasizes a strong control environment and effective risk management. It is recognized for its collaboration with major accounting and finance organizations.
Conclusion
To sum up, the COSO Framework is a structured approach to internal control practices that helps organizations manage risks, reduce costs, guarantee financial reporting integrity, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with regulations.
By leveraging its five components – control environment, control responsibilities, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring activities – organizations can establish a solid foundation for achieving their objectives and maintaining transparency and accountability in their operations.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

