Creating a Risk Intelligent Organisation is a crucial aspect of modern business management. A risk-intelligent organization understands the importance of balancing risk and reward.
The company has implemented processes, tools, and governance to manage risk effectively.
To become a risk-intelligent enterprise, companies must align their people, processes, tools, technologies, and governance into an integrated risk management system tied to corporate strategy.
This requires a comprehensive approach that involves the entire organization, from the board of directors to front-line employees.
By doing so, companies can deliver actionable risk intelligence to the leaders who need it when they need it, enabling them to make informed decisions that drive growth and profitability.

Understanding Risk Intelligence
Risk intelligence is the ability to identify, assess, and prioritize risks across an organization. It involves analyzing data, monitoring trends, and making informed decisions to mitigate risks.
A risk-intelligent organization has integrated risk management into its culture, strategy, and operations.
To create a risk-intelligent organization, it is important to understand the key elements of risk intelligence. These include:
Risk Awareness
The first step in becoming a risk-intelligent organization is to develop a culture of risk awareness. This involves educating employees at all levels about the importance of risk management and how it impacts the organization.
Promoting risk awareness, employees are better equipped to identify potential risks and take appropriate action to mitigate them.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks to determine their potential impact on the organization. This involves collecting data, analyzing trends, and prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and potential impact.
Conducting regular risk assessments, organizations can identify emerging risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation involves taking action to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks. This can include implementing controls, developing contingency plans, or transferring risk through insurance.
Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring involves tracking and analyzing risks to ensure risk management strategies are effective. This involves collecting and analyzing data, monitoring trends, and adjusting risk management strategies as needed.
In summary, risk intelligence is identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks across an organization.
Developing a culture of risk awareness, conducting regular risk assessments, proactively mitigating risks, and monitoring risks over time, organizations can become more risk intelligent and better equipped to manage potential threats.
Establishing a Risk Intelligence Framework
Defining the Framework
Establishing a risk intelligence framework is crucial for any organization that wants to become risk intelligent.
The framework defines the organization’s approach to risk management and guides the development of risk management processes, tools, and technologies.
It also ensures that risk management is integrated with the organization’s overall strategy and objectives.
The risk intelligence framework should be based on the organization’s risk appetite, tolerance, and culture.
It should also take into account the organization’s stakeholders, including customers, employees, shareholders, regulators, and other external parties.
The framework should address all types of risks the organization may face, including strategic, operational, financial, legal, regulatory, and reputational risks.
It should also be flexible enough to adapt to changing risk environments and emerging risks.
Implementing the Framework
Implementing the risk intelligence framework requires a systematic approach that involves several steps.
The first step is to assess the organization’s current risk management capabilities and identify gaps and areas for improvement. This can be done through a risk assessment or a gap analysis.
The next step is developing and documenting risk management policies, procedures, and guidelines aligning with the risk intelligence framework.
These should cover all aspects of risk management, including risk identification, assessment, mitigation, monitoring, and reporting.
The organization should also establish a risk management governance structure that defines roles, responsibilities, and accountabilities for risk management.
This includes appointing a Chief Risk Officer or a similar position to oversee the risk management function.
Implementing the risk intelligence framework should also involve developing and deploying risk management tools and technologies. This includes risk management software, data analytics tools, and reporting tools.
Finally, the organization should establish a risk management culture that promotes risk awareness, transparency, and accountability.
This includes training and awareness programs for employees and stakeholders and regular communication and reporting on risk management activities and outcomes.
In conclusion, establishing a risk intelligence framework is essential for any organization that wants to become risk intelligent.
The framework should be based on the organization’s risk appetite, tolerance, and culture and should be designed to address all types of risks the organization may face.
Implementing the framework requires a systematic approach that involves several steps, including assessing current risk management capabilities, developing risk management policies and procedures, establishing a risk management governance structure, deploying risk management tools and technologies, and promoting a risk management culture.

Cultivating a Risk Intelligent Culture
To create a Risk Intelligent Organisation, it is essential to cultivate a Risk Intelligent Culture.
A Risk Intelligent Culture is an environment where every employee understands the organization’s approach to risk management, takes personal responsibility to manage risk in everything they do, and encourages others to follow their example.
This section will explore how to promote awareness and provide training and development opportunities to create a Risk Intelligent Culture.
Promoting Awareness
Promoting awareness is the first step in cultivating a Risk Intelligent Culture. Employees must understand the importance of managing risks and how their actions impact the organization’s risk profile.
Leaders can promote awareness through communication, training, and leading by example.
Communication is critical in promoting awareness. Leaders should communicate the organization’s risk management approach, policies, and procedures to all employees.
They should also communicate the importance of managing risks and how it aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Communication should be continuous and ongoing to ensure that employees understand the message.
Training is another effective way to promote awareness. Employees must understand how to identify and manage risks in their daily work. Leaders should provide training on risk management frameworks, policies, and procedures.
They should also provide training on assessing risks, prioritizing them, and developing risk mitigation plans.
Leading by example is also essential in promoting awareness. Leaders should demonstrate their commitment to risk management by following policies and procedures, assessing risks, and managing them appropriately.
When employees see leaders taking risk management seriously, they are likelier to do the same.
Training and Development
Training and development are critical components of creating a Risk Intelligent Culture. Employees need to have the knowledge and skills to manage risks effectively. Leaders should provide training and development opportunities to employees at all levels of the organization.
Training should be tailored to the employee’s role and responsibilities. Employees who work in risk management functions should receive more in-depth training on risk management frameworks, policies, and procedures.
Employees not working in risk management functions should receive training on identifying and managing risks in their daily work.
Leaders should also provide development opportunities to employees. Development opportunities can include job rotations, cross-functional projects, and leadership development programs.
These opportunities can help employees better understand the organization’s risks and how to manage them effectively.
In conclusion, creating a Risk Intelligent Culture is essential to creating a Risk Intelligent Organisation. Leaders must promote awareness and provide training and development opportunities to cultivate a Risk Intelligent Culture.
Leveraging Technology in Risk Intelligence
Risk intelligence is essential for organizations to make informed decisions and mitigate potential risks.
Leveraging technology can help organizations to create a risk-intelligent environment and improve their risk management practices.
This section will explore two key technologies that can be used to improve risk intelligence: risk management software and data analytics.
Risk Management Software
Risk management software can help organizations to automate their risk management processes and provide real-time risk information.
This software can help organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks more efficiently and effectively. Some of the key features of risk management software include:
- Risk identification and assessment: Risk management software can help organizations to identify and assess risks by providing a centralized platform for capturing risks and organizing data elements. This can help organizations to create a common language for risk management that is well-understood throughout the organization.
- Risk monitoring and reporting: Risk management software can provide real-time risk information and enable organizations to monitor risks continuously. This can help organizations to make informed decisions and take corrective action when necessary.
- Risk mitigation and control: Risk management software can help organizations to implement controls and mitigation strategies to reduce the likelihood and impact of risks.
Data Analytics
Data analytics can help organizations analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns and trends indicating potential risks.
This can help organizations proactively identify and mitigate risks before they become major issues. Some of the key benefits of data analytics in risk intelligence include:
- Predictive analytics: Data analytics can help organizations predict potential risks and identify trends indicating future risks. This can help organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate risks before they occur.
- Real-time monitoring: Data analytics can provide real-time risk information and enable organizations to monitor risks continuously. This can help organizations to make informed decisions and take corrective action when necessary.
- Improved decision-making: Data analytics can help organizations to make more informed decisions by providing actionable insights into potential risks and their impact on the organization.
In conclusion, leveraging technology can help organizations to create a risk-intelligent environment and improve their risk management practices.
Risk management software and data analytics are two key technologies that can be used to improve risk intelligence. By using these technologies, organizations can identify, assess, and mitigate risks more efficiently and effectively.
Monitoring and Reviewing Risk Intelligence
Monitoring and reviewing its risk intelligence regularly is important to ensure that a Risk Intelligent Organisation is running effectively.
This section will cover two sub-sections for monitoring and reviewing risk intelligence: Regular Audits and Continuous Improvement.
Regular Audits
Regular audits are an essential part of monitoring risk intelligence. These audits should be conducted by an independent party to ensure objectivity.
The audit should assess the effectiveness of the organization’s risk management program, including its policies, procedures, and controls.
The audit should also evaluate the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance levels to ensure they align with its strategic objectives.
The audit should provide recommendations for improvement, which can be used to refine the organization’s risk management program.
It is important to ensure that the recommendations are implemented in a timely manner to ensure that the organization is continuously improving its risk intelligence.
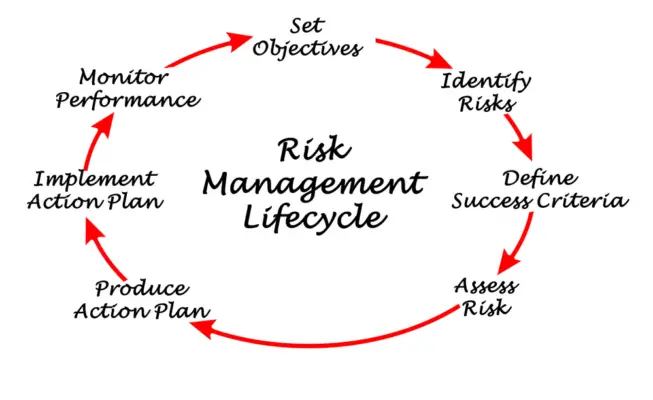
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is an ongoing process that involves refining the organization’s risk management program to remain effective.
This process should be driven by data and stakeholder feedback, including employees, customers, and suppliers.
One way to continuously improve risk intelligence is by using data analytics to identify risks and trends. This can help the organization manage risks and identify opportunities for improvement proactively.
The organization should also regularly review its risk appetite and risk tolerance levels to ensure they remain aligned with its strategic objectives.
Another way to continuously improve risk intelligence is by providing employee training and development opportunities.
This can help build a culture of risk awareness and ensure that employees have the knowledge and skills to manage risks effectively.
In summary, monitoring and reviewing risk intelligence is essential to building a Risk Intelligent Organisation.
Regular audits and continuous improvement are two key sub-sections that can help to ensure that the organization’s risk management program remains effective and aligned with its strategic objectives.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

