Risk is a fundamental concept that pervades various domains of human existence, ranging from finance to health and safety. It refers to the possibility of an undesirable event occurring and the potential consequences that may follow.
With its inherent uncertainty, risk assessment becomes crucial in identifying and evaluating potential hazards, allowing for informed decision-making and proactive management strategies for own risk.
This article aims to provide an objective understanding of what constitutes a risk by exploring its definition, key components, and the processes involved in managing risks effectively.
In order to comprehensively comprehend the concept of risk and defining risk, it is essential to delve into the field of risk assessment. Risk assessment involves systematically identifying potential hazards, analyzing their likelihood of occurrence, and assessing their potential impact on individuals or organizations.
Using employing scientific approaches such as data analysis and modeling techniques, this process enables quantification of risks for better understanding and subsequent prioritization. Moreover, effective risk assessment facilitates proactive measures to mitigate or eliminate identified risks altogether.
Consequently, it plays a pivotal role in safeguarding against undesirable events while aiding in resource allocation optimization for maximum benefit attainment.

Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a systematic process that evaluates the potential risks associated with a particular activity or decision, allowing individuals and organizations to make informed choices while minimizing potential harm.
It involves identifying and analyzing risk factors, safety risks, and health risks that may arise from a specific situation. The primary objective of risk assessment is to assess risks accurately and determine appropriate control measures to mitigate or eliminate them.
The first step in risk assessment is hazard identification. This involves identifying the potential hazards or sources of harm that could lead to adverse outcomes. These hazards can be physical, chemical, biological, or psychosocial in nature.
For example, in a workplace setting, hazards may include dangerous machinery or equipment, hazardous chemicals, infectious diseases, or stressful work conditions. By identifying these hazards, individuals and organizations can gain insight into the potential risks they pose.
After hazard identification comes risk evaluation. This step involves assessing the likelihood and severity of the identified hazards leading to unwanted consequences. By evaluating the potential impact of each hazard on safety and health, individuals and organizations can prioritize their efforts towards mitigating high-risk situations.
Risk evaluation also takes into account factors such as exposure duration and frequency when determining the level of risk associated with a particular hazard.
Once risks have been assessed, control measures are implemented to manage or eliminate them. Control measures can include engineering controls (modifying equipment or processes), administrative controls (changing work practices), or personal protective equipment (providing employees with safety gear). These measures aim to reduce exposure to hazards and prevent accidents or illnesses from occurring.
Risk assessment plays a crucial role in decision-making by providing an objective evaluation of potential risks associated with an activity or decision. It helps identify hazard sources and evaluate their likelihood and severity for better understanding their impact on safety and health.
Implementing appropriate control measures based on this evaluation, individuals and organizations can effectively minimize potential harm while making informed choices.

Managing Health and Safety Risks
Managing health and safety risks involves implementing proactive measures to ensure the well-being of individuals within an organization. This includes creating a safe working environment and providing adequate training on hazard identification and mitigation.
A potential danger occurs whenever a person is affected by a danger. Health safety hazards at work must be managed either by reducing risks or minimising risks. Risk management is a continuous process to improve workplace safety. Its primary purpose is to define and assess a problem (identifying hazards), gather the information on it, and solve it.
Risk analysis is an essential component of managing health and safety risks, as it helps in identifying hazards and evaluating their potential consequences.
A systematic approach is crucial when managing health and safety risks. Organizations need to have a structured process in place to identify, assess, and control occupational health hazards effectively. This involves conducting regular risk assessments to identify potential sources of harm in the workplace.
Systematically analyzing these risks, organizations can prioritize their efforts towards implementing appropriate controls to mitigate or eliminate them.
Furthermore, managing health and safety risks requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation. It is not enough to implement measures once; they need to be reviewed regularly to ensure their effectiveness. Regular inspections, audits, and feedback from employees can help identify any gaps or areas for improvement in the existing risk management system.
Continuously monitoring the effectiveness of these measures, organizations can adapt their strategies accordingly and provide a safer working environment for their employees.
Managing health and safety risks involves taking a proactive approach towards ensuring the well-being of individuals within an organization. This requires conducting risk analysis, identifying hazards, assessing potential consequences, and implementing a systematic approach for controlling these risks.
Ongoing monitoring and evaluation are essential to maintain an effective risk management system that adapts to changing circumstances while prioritizing employee safety at all times.
Health, safety, and environment risks
Safety and environment (HSE) is a separate discipline but is often linked. This relates typically in part to organizational governance structures, although there exist strong links between those disciplines. Generally speaking, an event with one or more risks can impact both of these areas, although at varying time scales.
Uncontrolled releases of a radiation-related substance or chemical can lead to immediate and prolonged health impacts, environmental effects or even longer.
Safety risk
Safety involves various risks that may have a negative impact on people, property, and the environment. Risk is commonly defined as the probability and severity of dangerous situations. Risks can be mitigated using a risk management approach.
High reliability organizations (HROs) require complex operations in environments requiring catastrophic accidents. Some examples are airplane carriers, airport control, aerospace, and nuclear facilities. A HRO manages risks by measuring them quantitatively.
What is a Hazard?
A hazard is a potential source of harm or danger within an organization, like a smoldering fire that could engulf the entire building if left unattended.
A danger is anything that has a risk that could harm someone. Some hazards for your company include: loud machinery, forklifts moving chemicals or electricity.
In the context of risk management, hazards are identified as potential events or conditions that have the capacity to cause negative consequences or harmful effects.
Hazards can arise in various forms, such as physical, chemical, biological, ergonomic, and psychosocial. They can exist in any workplace setting and pose risks to the health and safety of employees.
Identifying hazards is a crucial step in managing health and safety risks within an organization. It involves recognizing and assessing potential sources of harm that could lead to accidents, injuries, illnesses, or property damage.
Systematically identifying hazards through risk assessments and inspections, organizations can take appropriate preventive measures to eliminate or minimize the associated risks.
This may involve implementing control measures such as engineering controls (e.g., installing safety guards on machinery), administrative controls (e.g., developing safe work procedures), or personal protective equipment (e.g., providing workers with gloves or goggles).
The presence of hazards necessitates effective risk management strategies to mitigate their potential negative impacts on individuals and organizations. While hazards represent potential sources of harm or danger, it is important to note that not all hazards result in actual harm if appropriate precautions are taken.
Therefore, understanding the nature of hazards and their associated risks allows organizations to prioritize their efforts towards implementing suitable control measures that reduce the likelihood and severity of adverse events.
Proactively addressing hazards in the workplace through proper risk management practices, organizations can create safer environments for employees while also minimizing credit risk by avoiding costly incidents that could impact their reputation and financial stability.
Examples of what are a hazard and risk
Workplace danger can arise in several ways. General examples include all substances, materials or processes that may cause injury or damage to people. Workplace Hazard includes practices that release energy without control measures.
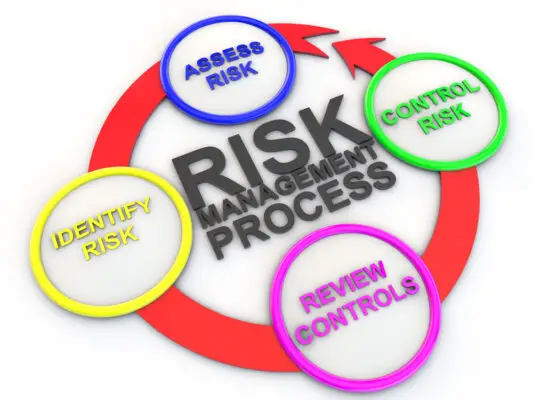
Risk Management Process
The risk management process involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards within an organization. It is essential for organizations to proactively manage risks in order to minimize negative outcomes and maximize success.
Risk is widespread throughout life and it is important to manage risk consciously as well as intuitively. Intelligent risk management will also be covered below. Psychology. Risks. Risk management describes the methodical management of risks and is often the profession that does that.
Risk management is generally defined as “the coordination of actions to manage risk within the organisation”. ISO 3 1000, the global standard for the risk management [6] defines an integrated risk management process involving:
The first step in the risk management process is hazard identification, where potential hazards are identified through various methods such as inspections, audits, and historical data analysis. Once hazards are identified, they are assessed to determine the likelihood and severity of their impact on the organization. This assessment helps prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively.
In order to control risks, organizations implement strategies and measures to reduce or eliminate the likelihood of occurrence and mitigate the impact of hazards.
These strategies can include implementing safety protocols, providing training and awareness programs for employees, conducting regular inspections, and improving infrastructure or equipment.
Actively managing risks through these control measures, organizations can minimize their exposure to uncertain events that may lead to negative outcomes.
Furthermore, risk management plays a crucial role in project management by ensuring that potential risks are identified early on in the planning phase. Through effective risk management practices, project managers can develop contingency plans and allocate resources accordingly to mitigate potential risks throughout the project lifecycle.
Additionally, insurance contracts can be utilized as a form of risk transfer mechanism where organizations transfer some of their financial burden associated with potential losses due to hazards onto insurance providers.
Overall, the risk management process is a vital aspect of organizational functioning as it enables businesses to proactively identify potential hazards and take necessary steps to mitigate them.
Systematically addressing risks through hazard identification, assessment, and control measures; organizations increase their chances of achieving successful outcomes while minimizing negative impacts associated with uncertain events or exposures.
Identify hazards
Identifying hazards involves finding anything which might cause people injury. Generally, these aspects of work can cause dangers, examples being dangerous hands-on activities, unsafe chemicals, and electricity use in wet areas. How are workplace hazards detected and identified?
Workplace hazards can be detected and identified through a systematic approach known as a hazard assessment or risk assessment. This involves conducting a thorough examination of the workplace and its processes to identify potential hazards and assess the level of risk they pose to employees.
The process typically includes reviewing incident reports, conducting inspections, consulting with employees, and analyzing data on workplace injuries and illnesses. Additionally, hazard identification can be facilitated through the use of checklists, safety audits, and job hazard analyses.
Regular communication and collaboration between management, supervisors, and employees are essential to ensure that hazards are effectively detected and identified. Once hazards are identified, appropriate control measures can be implemented to mitigate the risks and ensure a safe working environment.
Assess risks
The risk assessment will identify the order in which you should prioritize your risk management objectives. Under the Work Health and Safety Regulation 2012 and Regulations (the WSH Regulations), risk assessments must be carried out when performing dangerous activities. In analyzing risks, we have to consider the risk of injury increases with increased risks for humans.
In order to assess risks effectively, it is essential to consider various factors that can contribute to the likelihood and severity of potential injuries. These factors may include the nature of the activity or task being performed, the environment in which it takes place, the competency and experience of individuals involved, and any relevant legal or regulatory requirements.
A comprehensive risk assessment should involve the identification and evaluation of hazards, as well as the determination of appropriate control measures to mitigate or eliminate those hazards. This process may involve gathering information from various sources such as incident reports, historical data, industry standards, and expert opinions.
Additionally, it is important to consider the potential consequences of risks, such as the impact on individuals’ health and well-being, financial implications, and potential damage to property or equipment. Prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and severity, organizations can allocate resources and implement control measures more effectively to minimize the overall level of risk.
Regular review and updating of risk assessments are also crucial, as new hazards may emerge or existing ones may change over time.
Maintaining an ongoing risk management approach, organizations can ensure that they are continually identifying and addressing potential risks to safeguard the health and safety of their workers and stakeholders.
Control risks
Managing risks involves using the most effective protection strategies that offer the highest level of dependability. This approach is referred to as ‘hierarchical risk control.’ Strive to implement robust risk management practices whenever feasible.
Hierarchical risk control involves implementing a series of control measures in a prioritized manner to effectively manage risks. The first step is to eliminate the risk altogether, if possible. This could involve redesigning a process or removing a hazardous substance from the workplace.
If elimination is not feasible, the next step is to substitute the risk with a less hazardous alternative. For example, replacing a toxic chemical with a less harmful one. If substitution is not an option, engineering controls can be implemented to minimize the risk, such as installing safety guards or ventilation systems.
Administrative controls, such as implementing procedures and training, can also be introduced to further reduce risks. Lastly, personal protective equipment (PPE) can be used as a last line of defense to protect workers from potential hazards. Following this hierarchical approach, organizations can effectively reduce risks and create a safer work environment.
Risk Factors
One important aspect to consider when evaluating potential hazards within an organization is the identification and understanding of risk factors.
Risk factors are elements or variables that contribute to the likelihood and severity of different hazards. These factors can vary across industries and organizations, but their understanding is crucial in order to effectively manage risks.
High-risk factors are those that have a higher probability of causing negative effects or harm. These can include external factors like economic conditions, political stability, or technological advancements, as well as internal factors such as organizational culture, employee competence, or financial resources. Identifying these high-risk factors allows organizations to prioritize their efforts in managing the most critical risks and allocating resources accordingly.
Another important consideration when analyzing risk factors is understanding the general definition of risk itself. Risk refers to the possibility of loss or harm resulting from exposure to a hazard. This includes both the likelihood and severity of an adverse event occurring.
Identifying risk factors, organizations gain insights into which hazards are more likely to occur and have a greater impact on their operations. This knowledge enables them to implement appropriate measures for prevention, mitigation, or response.
Evaluating risk factors plays a significant role in effective risk management within organizations. By recognizing high-risk elements and comprehending the general definition of risk, companies can better assess potential hazards they face.
This allows for targeted strategies that minimize negative effects by reducing both the likelihood and severity of adverse events. Understanding risk factors empowers organizations with valuable insights necessary for informed decision-making aimed at protecting their interests and ensuring continuity in operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common methods used for risk assessment?
Common methods for risk assessment include quantitative and qualitative techniques. Quantitative methods involve numerical calculations to assess the probability and impact of a risk, while qualitative approaches rely on expert judgment and subjective criteria to evaluate risks.
How can an organization effectively manage health and safety risks?
To effectively manage health and safety risks, an organization should implement a systematic approach that includes identifying hazards, assessing their potential impact, implementing controls to mitigate risks, monitoring effectiveness, and continuously improving the risk management process.
What is the difference between a hazard and a risk?
A hazard refers to a potential source of harm, while a risk is the likelihood and severity of that harm occurring. In other words, a hazard is an inherent danger, whereas a risk involves the assessment of the probability and impact of that danger.
Can you provide an overview of the risk management process?
The risk management process involves identifying potential hazards, assessing their likelihood and impact, implementing measures to mitigate or control the risks, and continuously monitoring and reviewing these measures to ensure effectiveness in minimizing negative consequences.
What are some common risk factors that organizations should consider?
Common risk factors that organizations should consider include financial risks, operational risks, strategic risks, compliance risks, and reputational risks. These factors can pose threats to the achievement of organizational objectives and must be carefully managed through effective risk management processes.

Conclusion
Risk assessment is a crucial process in various industries and organizations, as it helps identify potential hazards and evaluate the associated risks.
Identifying hazards, such as chemical exposure or workplace accidents, risk assessments enable companies to implement effective control measures to mitigate these risks.
The risk management process involves five key steps: hazard identification, risk evaluation, risk control implementation, monitoring and review of control measures, and communication of findings.
Through this systematic approach, organizations can ensure the safety and well-being of their employees while also complying with legal requirements.
Managing health and safety risks requires a comprehensive understanding of potential hazards within a specific environment.
Hazards can be categorized into different types such as physical (e.g., noise or machinery), chemical (e.g., toxic substances), biological (e.g., infectious diseases), ergonomic (e.g., poor workstation design), or psychosocial (e.g., work-related stress).
Effective risk management involves assessing each hazard’s likelihood and severity to prioritize resources for control measures.
This proactive approach enables organizations to create safer working conditions by implementing appropriate controls based on the level of identified risks.
In conclusion, risk assessment plays a vital role in managing health and safety risks within organizations.
Systematically identifying hazards and evaluating associated risks, companies can implement targeted control measures to protect their employees from harm.
The risk management process ensures that hazards are effectively controlled through continual monitoring and review.
It is essential for organizations to understand the different types of hazards they may encounter in order to prioritize resources efficiently.
Overall, prioritizing employee safety through comprehensive risk assessment is not only ethically necessary but also legally required in many jurisdictions.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

