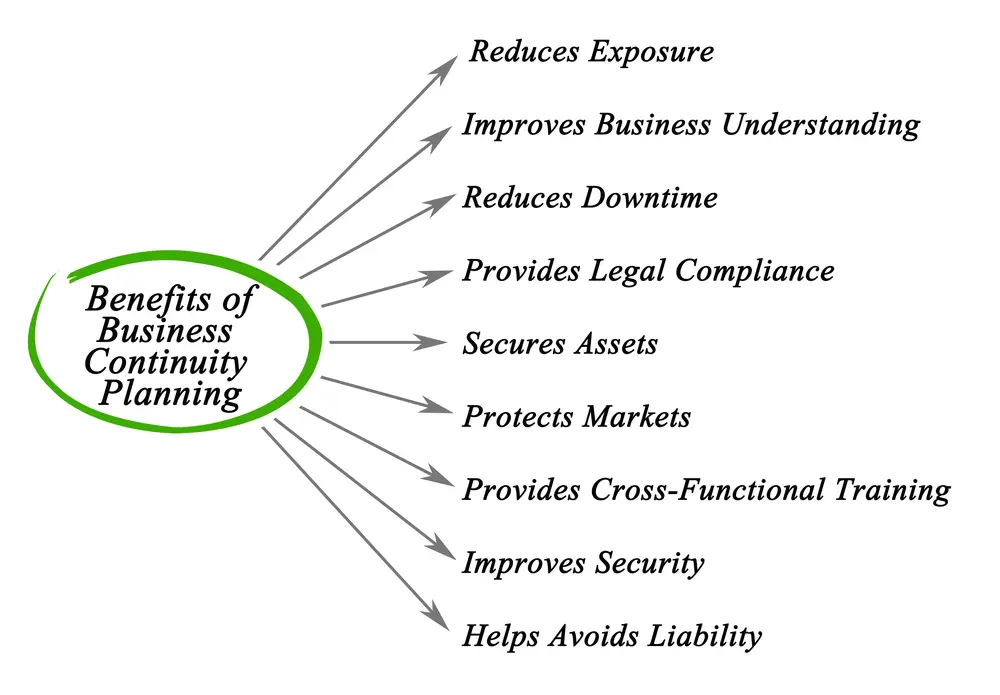
In today’s interconnected digital world, IT professionals and companies are in the unenviable position of managing an ever-evolving infrastructure to ensure business continuity. Potential disruptions are increasing – from cyberattacks and system failures to natural disasters for recovery procedures.
It’s essential to have a flexible and resilient business continuity plan (BCP) in place that guarantees the security of your organization’s data, applications, and IT systems in unprecedented situations. A study by Mercer found that 51% of companies worldwide did not have a business continuity plan in place before the COVID-19 pandemic, emphasizing the need for comprehensive risk management and planning.
Increased reliance on cloud-based services and a business continuity plan are more important than ever. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers an array of free tools and services that can be used for disaster recovery, but it’s up to you to create a comprehensive plan that meets your specific needs.
In this blog post, we’ll go over the basic steps for creating an AWS business continuity plan.
Step 1: Identify Your Critical Assets and System Requirements
The first step in creating an effective business continuity plan is identifying your critical assets and system requirements. This includes any data or systems that are essential for day-to-day operations—such as customer databases and financial records.
It also includes customer information and any systems that need to be backed up or recovered quickly in the event of a disaster. Once you’ve identified these assets, you can create a list of key contacts responsible for responding in the event of a disaster.
Step 2: Develop Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Once you’ve identified your assets and contact list, it’s time to develop your disaster recovery plan with AWS. This includes setting up backup schedules and procedures, establishing failover processes, setting up automated alerting systems, and testing your system regularly.
You should also make sure that all of your data is stored securely on the cloud using encryption technology so that even if it falls into the wrong hands, it remains secure.
Step 3: Test Your System Regularly
Testing is one of the most important steps in developing an effective business continuity plan with AWS. It’s crucial to test your system regularly so that you know exactly how it will respond in different scenarios or conditions.
You also want to ensure that backups are working correctly so that if there is ever a failure or outage, you can access recent versions of your data and recover it immediately. Additionally, consider doing stress tests on a regular basis to ensure that everything works as expected when under heavy load or stress.
Benefits of Aws business continuity plans
1. Embrace the Cloud With AWS business continuity plans
One of the key benefits of using AWS for business continuity planning is the ability to leverage the cloud’s inherent resilience and scalability. With 25 geographic regions and 81 Availability Zones worldwide, AWS delivers a highly available and fault-tolerant.
An infrastructure capable of withstanding multiple disruptions without compromising your data or applications’ integrity. This distributed approach ensures your organization can continue its operations even in the most challenging circumstances.
2. Harness the Power of AWS Storage Services
Data protection is a crucial aspect of any business continuity plan, and AWS offers a variety of storage options tailored to different use cases. These storage services are also designed with data durability in mind, ensuring your organization’s data is safeguarded from corruption or loss.
3. Recovery Strategies With AWS
A comprehensive BCP should incorporate a clear recovery strategy that outlines the steps to be taken in different disaster scenarios. AWS provides a multitude of tools to help IT professionals design and implement efficient recovery plans.
Services like Amazon RDS and AWS Backup automate data backups and enable point-in-time recovery, while AWS CloudFormation streamlines the rebuilding of infrastructures in alternate regions or accounts.
4. Leverage AWS’s Advanced Monitoring and Alerting Capabilities
An essential aspect of any BCP and recovery strategy is proactively identifying and addressing potential risks before they have a chance to escalate into catastrophic failures. With AWS’s extensive suite of monitoring and alerting tools like Amazon CloudWatch, IT professionals can establish and maintain critical visibility into their infrastructure.
This facilitates early detection of anomalies and enables quick response to potential disruptions, limiting the impact on the organization’s operations.
5. AWS’s Collaborative Approach to Business Continuity
AWS is committed to supporting IT professionals with their business continuity initiatives by continually improving its services, sharing lessons learned from real-world disasters and recovery efforts, and working collaboratively to ensure success.
Using WS can offer almost unlimited ways of avoiding recurring service interruptions and downtimes. It is important that load-balanced devices are able always to avoid downtime and lapses in the service using configuration drift.
AWS provides the ability to set up redundancy and availability during a crisis. Spin up the resources within one data center or in an available zone. This will reduce the cost at the expense.
During the last few years, we experienced an incredible change from what was previously considered unusual, anticipated, or unanticipated events into a new normal. The COVID-19 Pandemic has caused a growing number of businesses to create, prepare, and upgrade business continuity plans in a rapidly turbulent landscape.
Essential Components of AWS Business Continuity Plan
1. Risk Assessment: The first step in developing an AWS BCP is to identify potential risks that could impact your organization’s IT infrastructure.
This involves assessing external factors such as natural disasters, cybersecurity threats, and infrastructure failures, and internal factors like hardware or software failures, human errors, and more.
2. Disaster Recovery Strategies: Based on the identified risks, your BCP should incorporate disaster recovery (DR) strategies tailored for AWS. Depending on your organization’s specific needs, these strategies could involve Failover, Pilot Light, Warm Standby, or Multi-Site implementation.
3. Georedundancy and Backup Solutions: Proper data backup and geo-redundancy of your IT resources are crucial to ensure business continuity. AWS cloud solutions, like Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, and AWS Backup, provide the tools for efficient data backups, replication, and recovery across multiple Regions and Availability Zones.
4. Recovery Time and Point Objectives: Define Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) based on the organization’s mission-critical applications and tolerance levels. Once established, AWS services like AWS CloudFormation, AWS Config, and Amazon CloudWatch can help automate tasks and monitor the process of meeting your RTO and RPO targets.
5. Incident Response and Communication: Establish clear roles, responsibilities, and communication processes within your team during an incident. Tools such as AWS Health, AWS Personal Health Dashboard, and Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) can assist in monitoring, reporting, and alerting stakeholders during a disruption.
6. Testing and Maintenance: Regularly test and update your AWS BCP to ensure its effectiveness during an actual disaster. Incorporate various scenarios and technological advancements into your testing plans and document the results to make improvements.
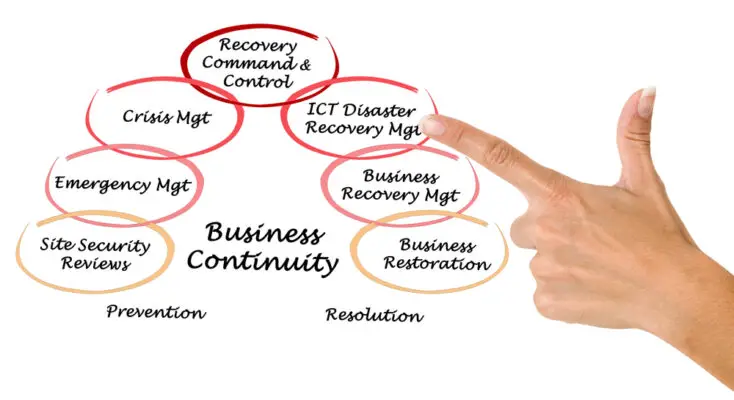
Conducting a business impact analysis for your SMB
BCP determines how your person or organization impacts other aspects and activities of your business outside the scope of your job. Business analysis is used to determine if there is a disruption in workload for internal and external customers
A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a crucial step in assessing the potential effects of a disruption to your small to medium-sized business (SMB) and identifying the most important aspects to prioritize during recovery. Conducting a BIA involves the following steps:
Define the scope: Determine the scope of your analysis by identifying the key departments, processes, and functions that are essential to your business operations. The defined scope will help you decide where to allocate resources during recovery.
Gather information: Collect information on the business functions, systems, and processes identified in the scope. This includes data on employees, suppliers, IT systems, equipment, and other resources supporting these functions.
Identify critical functions: Determine which business functions are the most critical to your SMB’s operations. These are the functions that, if disrupted, would have the most significant negative impact on your business.
Assess dependencies: Analyze the relationships between the critical functions and their dependencies on other functions, systems, or resources. This will help you understand the potential cascading effects of disruption and identify areas that need to be prioritized for recovery.
Determine the Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO): For each critical function, estimate the maximum amount of time that it can be disrupted before causing significant harm to your business. This Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO) will help you prioritize recovery efforts.
Estimate potential financial and operational impacts: Assess the potential financial and operational consequences of a disruption to your critical functions. Consider both direct costs (e.g., lost revenue, fines, or penalties) and indirect costs (e.g., damaged reputation, loss of customers, or long-term recovery expenses).
Identify recovery strategies and resources: Based on your assessment of the impacts, develop recovery strategies for each critical function. Identify the necessary resources (e.g., personnel, equipment, and facilities) to implement these strategies and ensure timely recovery.
Document the BIA findings: Compile the information collected during the BIA process into a comprehensive report. This document should outline the critical functions, their dependencies, MAOs, potential impacts, and recovery strategies.
Communicate the results: Share the BIA findings with key stakeholders, including employees, management, and any other parties responsible for business continuity planning. This will help ensure that everyone is aware of the potential risks and the steps that must be taken to mitigate them.
Update and review regularly: Business conditions, processes, and technologies change over time. Review and update your BIA regularly (at least annually) or whenever there are significant changes in your organization’s environment to ensure that it remains accurate and relevant.
Implementing a BCP
AWS has many options that can help you implement a business continuity strategy. Based on this Business Impact Assessment, you will be able to select AWS services for your BCP goal. One way of adding components from a BCP into a current BCP architecture in a new architecture is by using AWS management services.
AWS manages all operations in data centers while avoiding operational responsibilities in managing the operating system and application operations. Additionally, most Amazon Web Services offer consumption models whereby a client pays only for the available resources, reducing the cost of disaster recovery.
Here are some steps to consider when implementing a BCP using AWS:
Understand your organization’s requirements:
Begin by conducting a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) to identify your organization’s critical functions, dependencies, Maximum Acceptable Outages (MAOs), and potential impacts. This information will guide your BCP implementation.
Design for redundancy and high availability:
Leverage AWS’s global infrastructure to distribute your applications and data across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) within a region or even across multiple regions. This will minimize the risk of service disruptions due to infrastructure failures, natural disasters, or other incidents.
Utilize AWS services for backup and recovery:
Amazon S3: Use Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) for cost-effective storage and retrieval of your data. Enable versioning to maintain multiple versions of an object and use cross-region replication to copy data across regions for added redundancy.
AWS Backup: Automate and centrally manage backups across AWS services, including Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon EFS, Amazon EC2, and AWS Storage Gateway.
Implement data replication and failover mechanisms:
- Amazon RDS: Use Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) to set up a Multi-AZ deployment for automatic failover to a standby replica in another AZ within the same region.
- Amazon DynamoDB: Enable global tables for DynamoDB to replicate your data across multiple AWS regions, providing low-latency access and quick recovery in case of regional outages.
Establish an incident response plan:
Develop a plan for detecting, responding to, and recovering from incidents that affect your AWS infrastructure. Utilize AWS services such as Amazon CloudWatch, AWS Trusted Advisor, and AWS Personal Health Dashboard to monitor your resources and receive alerts for potential issues.
Test your BCP:
Regularly test your BCP to ensure it’s effective and up to date. Use AWS services like AWS CloudFormation to create isolated environments for testing and AWS CodePipeline for automated deployment of your applications.
Implement security best practices:
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): Utilize IAM to manage access to your AWS resources, applying the principle of least privilege and regularly reviewing user permissions.
Amazon VPC: Isolate your resources within a virtual private cloud (VPC) and implement security group rules to control inbound and outbound traffic.
AWS Shield and AWS WAF: Protect your infrastructure from DDoS attacks and application layer attacks with AWS Shield and the Web Application Firewall (WAF).
Train employees and stakeholders:
Ensure that all employees and stakeholders are familiar with the BCP and their roles in case of a downtime or an incident. Provide training and awareness programs to help them understand the importance of business continuity and their responsibilities.
Review and update your BCP:
Regularly review and update your BCP to account for changes in your organization, technology, and regulatory requirements. Monitor AWS announcements for new services or features that can enhance your business continuity strategy.

Conclusion
Creating an effective business continuity plan with AWS can seem daunting at first glance; however, taking the time to assess your company and system requirements and develop a comprehensive plan thoughtfully will ensure that your business has the best possible chance at weathering any disaster.
Amazon Web Services provides a robust foundation for your organization’s business continuity plan, equipping IT professionals with reliable and scalable infrastructure, advanced data storage options, effective recovery strategies, and powerful monitoring capabilities.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.