Disaster recovery (DR) refers to the set of policies, tools, and procedures to enable the recovery or continuation of vital technology infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster.
It is a subset of business continuity planning focused on the IT or technology systems that support business functions.
Disaster recovery is all about being prepared for and recovering from events that significantly negatively impact the IT systems of an organization. These events can include natural disasters like floods, fires, or earthquakes, as well as human-induced disasters such as cyberattacks, sabotage, or even accidental data deletion.
A disaster recovery plan (DRP) often includes the following elements:
Preventive measures: These aim to prevent a disaster from occurring. These measures could include using a surge protector, keeping equipment safe from water sources, or maintaining reliable backup power sources.
Detective measures: These aim to discover or detect undesirable events. Examples might include installing a fire alarm or intrusion detection system.
Corrective measures: These aim to restore systems after a disaster. Corrective measures could include maintaining off-site backup copies of data or using redundant systems that can be brought online to replace failed systems.
Disaster recovery is a critical component of any business operation, as it ensures the continuity of essential services in the face of disruptive events.
These disruptions can range from minor incidents such as power outages or server crashes to major catastrophes like cyber-attacks, hurricanes, earthquakes, and pandemics.
The goal of disaster recovery is to minimize downtime and data loss while maximizing the organization’s ability to continue operating during an interruption.
Organizations that invest in disaster recovery planning can reduce the risk of financial losses, reputation damage, and legal liabilities resulting from extended service outages.
This article will explore the basics of disaster recovery planning and how businesses can safeguard themselves against potential threats through effective preparation measures.

Understanding the Basics of Disaster Recovery
The fundamental principles and concepts underlying the implementation of disaster recovery strategies are essential for organizations to mitigate the impact of unexpected disruptions in their operations. The goal is to minimize downtime, data loss, and other negative consequences from such events.
Disaster recovery models provide organizations with a framework for developing effective disaster recovery plans. These models typically involve identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities and assessing the criticality of different systems and applications.
Developing backup and recovery procedures, testing those procedures regularly, and continuously monitoring the environment for new threats or changes that could affect the plan’s effectiveness. Disaster recovery software is crucial in implementing these models by automating many processes and providing real-time monitoring capabilities.
Effective disaster recovery planning requires careful consideration of various factors such as budget constraints, resource availability, regulatory compliance requirements, and organizational culture.
Organizations must also ensure that their disaster recovery plans are aligned with their overall business objectives and risk management strategies.
Identifying Potential Disruptive Events
Natural disasters include floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, tornadoes, and wildfires. Such disasters often cause physical damage to buildings and infrastructure, causing disruptions in normal business operations.
Man-made disasters refer to those caused by human error or malicious intent. One prominent example is cyber attacks, which can affect an organization’s data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
Cybercriminals may exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and networks to steal sensitive information, disrupt critical services, or launch attacks such as ransomware.
Identifying potential disruptive events is crucial for effective disaster recovery planning. Organizations must evaluate their risks based on their location (e.g., proximity to flood-prone areas), industry (e.g., financial institutions are more vulnerable to cyber attacks), assets (e.g., critical IT systems), and dependencies (e.g., suppliers).
They can develop contingency plans that address how they will respond in a disaster. This includes having backup systems, training employees on emergency procedures, and communicating protocols with customers, vendors, and regulators.
Developing a Disaster Recovery Plan
Crafting a well-thought-out plan to alleviate the impact of potentially disruptive events is crucial in ensuring organizational continuity and resilience. This plan is called the disaster recovery plan (DRP), which provides a comprehensive guide on how an organization should respond in a crisis or emergency situation.
The DRP should be developed based on an extensive risk assessment, which involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities that could cause significant disruptions to operations.
One of the primary components of a DRP is communication strategies. Establishing effective communication channels internally and externally during a crisis is essential.
An effective communication strategy can help prevent confusion, misinformation, and panic among employees, customers, suppliers, stakeholders, and the community.
The DRP should outline clear communication protocols, such as who will communicate with various stakeholders, what information needs to be shared, when it should be communicated, and through which channels.
A solid disaster recovery plan must consider all possible scenarios that could disrupt organizational operations and outline specific procedures for each scenario.
Furthermore, the plan must include well-defined communication strategies that enable timely information sharing among all stakeholders involved in disaster response efforts.
A comprehensive DRP can help organizations protect reputations while minimizing downtime from unexpected incidents or crises.
Implementing and Testing Your Plan
A well-designed plan is only as good as its execution, which requires thorough testing to identify any potential gaps or weaknesses that could compromise the plan’s effectiveness.
Testing procedures should be designed to simulate various disaster scenarios, such as power outages, data breaches, natural disasters, and cyber-attacks. This will help ensure that all aspects of the plan are functioning correctly and can be executed quickly when needed.
Communication protocols are a vital component of any disaster recovery plan. Communicating effectively during an emergency is critical for minimizing damage and preventing further harm.
It’s essential to establish clear communication channels internally and externally to ensure that everyone involved in responding to the situation can access accurate information at all times.
Communication protocols should also include instructions on how to notify stakeholders about the status of operations and what actions they need to take.
Once a disaster recovery plan has been implemented and tested, it’s important to conduct regular reviews and updates on an ongoing basis. Technology changes rapidly, so the plan must reflect these changes by incorporating new technologies or updating existing ones regularly.
Regular reviews will also help identify any new risks or threats that may have emerged since the last review was conducted, allowing organizations to adjust their plans accordingly before facing another crisis.
Ensuring Business Continuity with Disaster Recovery
Maintaining uninterrupted business operations during times of crisis is crucial, and a well-designed disaster recovery plan can act as a safety net to ensure that the show goes on, come what may.
However, a plan is insufficient since it requires effective stakeholder communication. Communication is essential in ensuring business continuity with disaster recovery by informing everyone about the situation.
The importance of communication cannot be overstated when it comes to disaster recovery planning. The lack of clear communication channels can lead to confusion and misinformation, which can ultimately result in further damage to your organization.
Effective communication ensures that everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities, preventing any disruption in the flow of information or processes.
Leadership also plays an integral role in ensuring business continuity planning since they are responsible for overseeing the implementation of the disaster recovery plan.
Leaders must create a culture where employees understand the importance of business continuity and take ownership of their roles in executing it.
They should also proactively identify potential risks and continuously refine the disaster recovery plan based on new developments or changes within their organization or industry.
A well-designed plan alone is insufficient if there are no proper channels for communicating information or leaders who take responsibility for its execution. By prioritizing these two elements, organizations can minimize disruption during times of crisis and continue providing reliable services to customers while maintaining their reputation within their industry.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between disaster recovery and business continuity?
The key differences between disaster recovery and business continuity lie in their scope and objectives. Disaster recovery focuses on restoring IT infrastructure, data, and applications after a disruptive event has occurred. In contrast, business continuity aims to maintain critical business functions during and after such an event.
Both are essential components of risk management as they help organizations minimize the impact of disruptions and ensure resilience.
When choosing disaster recovery solutions for your business, several factors must be considered, including the type and severity of potential threats, recovery time objectives (RTOs), recovery point objectives (RPOs), budget constraints, compliance requirements, and scalability.
It is crucial to have a well-defined disaster recovery plan that addresses these factors to mitigate risks effectively.
How can a company ensure its disaster recovery plan is up-to-date and effective?
To ensure that a company’s disaster recovery plan is up-to-date and effective, several measures must be taken:
-Regular testing and documentation updates allow for identifying potential gaps in the plan.
-Employee training ensures that everyone understands their roles during an emergency.
-Risk assessments help identify potential threats and vulnerabilities.
-Communication protocols ensure that all stakeholders are informed during an emergency.
-Technology updates should also be made to keep up with the latest trends in disaster recovery planning.
-Budget allocation must be sufficient to support all aspects of the disaster recovery plan, including necessary resources such as backup equipment and software.
-Emergency response drills enable employees to practice their roles in a simulated environment.
-Third-party vendor evaluations assess whether vendors can provide services needed during an emergency.
-Cloud-based solutions can offer increased flexibility and scalability for data storage and access during disasters.
What common mistakes do companies make when developing a disaster recovery plan?
One common mistake is failing to assess potential risks and vulnerabilities thoroughly, leading to inadequate planning and insufficient protection measures.
Another mistake is neglecting regular testing and updating of the disaster recovery plan, resulting in outdated strategies that are no longer effective.
It is essential for companies to follow best practices such as conducting regular risk assessments, involving all stakeholders in the planning process, maintaining offsite backups, and regularly testing and updating their plans.
How can a company prioritize which systems and data to recover in a disaster scenario?
Recovery prioritization involves identifying critical data that must be restored immediately to ensure business continuity.
This process requires careful consideration of the impact of data loss on various operational functions, including financial reporting, customer service, and regulatory compliance.
Critical data identification involves determining which systems contain essential information needed to maintain operations during recovery.
This is achieved by assessing all organizational functions and identifying the most critical processes that require immediate restoration in case of a disaster.
Once these priorities have been established, companies can develop an effective disaster recovery plan that ensures the timely restoration of critical business functions and mitigates potential losses caused by system downtime or data loss.
What legal and regulatory compliance issues should a company consider when developing a disaster recovery plan?
When developing a disaster recovery plan, companies must consider various legal and regulatory compliance issues that could affect their operations.
One of the most critical aspects is ensuring that the plan adheres to relevant laws and regulations governing data protection, privacy, and security.
Additionally, companies must review industry-specific requirements, such as healthcare or financial services.
The company must also ensure that they comply with contractual obligations with clients or partners regarding disaster preparedness and recovery.
Failure to meet these requirements could result in costly penalties, legal liabilities, and reputational damage for the organization.
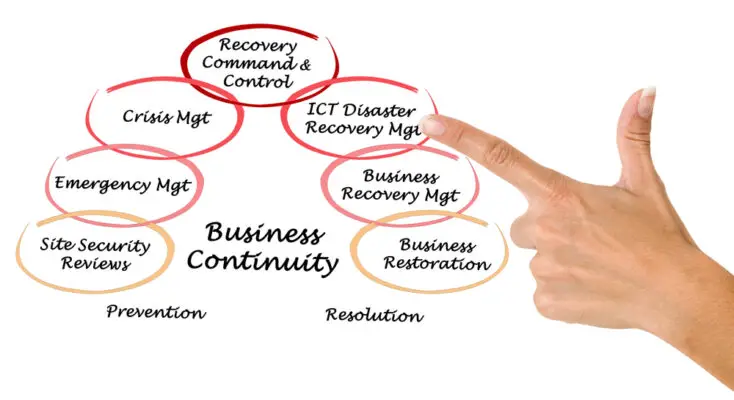
Conclusion
Disaster recovery is a critical component of any organization’s business continuity planning. It involves identifying potential disruptive events that could impact your business operations, developing a comprehensive plan to mitigate those risks, and implementing and testing that plan to ensure its effectiveness.
The first step in disaster recovery is understanding the basics. This means analyzing your current infrastructure, identifying critical systems and processes, assessing potential risks and vulnerabilities, and determining your downtime or data loss tolerance.
Once you clearly understand these factors, you can begin developing a disaster recovery plan that outlines specific steps for responding to different disruptions.
The key to successful disaster recovery is preparation. Your plan should include detailed procedures for backing up data, restoring systems and applications, communicating with stakeholders during an outage, and resuming normal operations as quickly as possible.
Regular testing is also essential to ensure your plan works as intended and identify areas for improvement.
Effective disaster recovery requires ongoing attention and investment from IT leaders and business executives. By taking proactive steps to protect against disruptive events, organizations can minimize the impact of unexpected downtime or data loss on their operations while maintaining the trust of customers and other stakeholders.
The cost of not having such plans in place cannot be understated, as it could lead to significant financial losses or even reputational damage. Therefore, businesses must invest time in assessing their risks thoroughly before developing strategies tailored specifically toward them while ensuring regular testing to maintain readiness.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

