Operational risk management (ORM) identifies, assesses, monitors, and controls risks arising from an organization’s day-to-day operations.
The primary objective of operational risk management is to minimize the impact of operational risks on the organization’s financial and operational stability and strategic objectives.
This is achieved by ensuring that potential risks are identified promptly, adequately assessed, and effectively mitigated, reducing operational disruptions’ likelihood and/or impact.
Operational risks can arise from a wide variety of sources, including:
Internal Processes: Inefficient, outdated, or flawed business processes can lead to operational risks.
People: Errors, misconduct, or lack of skills/knowledge among employees can also create operational risks.
Systems and Technology: System failures, cyberattacks, data breaches, and other technology-related issues can pose significant operational risks.
External Events: Natural disasters, changes in regulation, market changes, and other external events can also lead to operational risks.
Managing these risks effectively, ORM helps to:
- Improve the reliability and efficiency of business operations.
- Protect the organization’s reputation and stakeholder trust.
- Comply with regulatory requirements.
- Enable more informed decision-making.
- Promote a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to handling operational uncertainties and challenges.
- Support the achievement of strategic objectives and long-term business resilience.
The goal of operational risk management isn’t to eliminate all risks. Rather, it’s about making informed decisions about which risks to accept (because the potential benefits outweigh them) and which to mitigate and implementing effective measures to manage them.
Risks can arise from various sources, including internal processes, people, systems, or external events. These risks can lead to financial loss or customer service disruption and significantly negatively impact the organization’s reputation and business continuity.
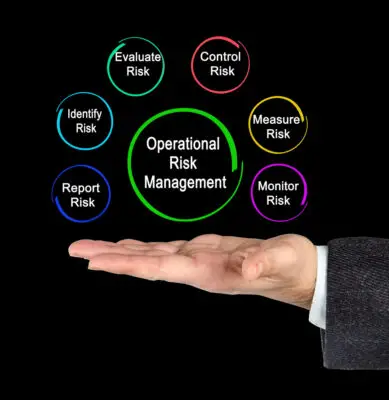
The primary objective of ORM is to identify, assess, measure, and mitigate operational risks related to daily operations. The ORM framework includes comprehensive procedures to reduce threats, minimize losses, protect the organization, and ensure business continuity.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the primary objective of ORM along with its principles, challenges, and benefits while exploring different types of operational risks that organizations face in today’s dynamic business environment.

Reducing Threats
The primary objective of Operational Risk Management (ORM) is to reduce threats to acceptable levels, and this is achieved through a set of processes that focus on controls and eliminating risk.
The ORM framework identifies risks and decides mitigation strategies to protect the organization from operational risks. The ultimate goal of ORM is to ensure continuity in business operations while minimizing losses due to ineffective or failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events.
To achieve its primary objective, ORM involves various stages such as risk assessment, measurement, and mitigation, monitoring, and reporting. A thorough understanding of potential risks allows organizations to assess the likelihood of them occurring and their potential impact.
Based on this information, mitigation strategies can be developed, which involve transferring, avoiding, accepting, or controlling risks.
Continuous monitoring or early warning systems built around key risk indicators are important in Operational Risk Management as they enable organizations to respond quickly when necessary.
Risk reporting is essential in ORM by providing information about significant operational risks that could affect an organization’s strategic objectives.
This information enables decision-makers at all levels of the organization to make informed decisions about how best to manage identified risks effectively.
Following these processes for identifying risks, assessing them appropriately, developing mitigation strategies, and continuously monitoring these efforts against previously established metrics
Success ensures that the primary objective of reducing threats remains achievable for any organization implementing operational risk management practices.
Minimizing Loss
To reduce potential negative outcomes, minimizing loss is critical to effective operational risk mitigation. Minimizing losses requires organizations to develop robust risk mitigation strategies integrated into their core operations.
Such strategies should be tailored to address specific risks identified during the risk assessment and continuously monitored for effectiveness.
Risk assessment techniques are essential for identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing appropriate responses. A cost-benefit analysis can help prioritize which risks to address first in the mitigation process.
Once an organization has developed its risk mitigation plan, monitoring effectiveness is crucial in ensuring it remains relevant in a constantly changing environment.
Operational resilience measures should also be implemented to ensure business continuity even when unexpected events occur. In conclusion, minimizing loss is a fundamental objective of operational risk management.
It helps organizations protect themselves against financial losses or reputational damage caused by internal or external factors. Effective implementation of risk mitigation strategies involves conducting regular assessments, applying cost-benefit analysis techniques, continuous monitoring, and adapting plans where necessary.
Organizations that invest resources in strengthening their operational resilience measures will be better positioned to mitigate potential losses associated with unexpected events such as cybersecurity breaches, natural disasters, or supply chain disruptions.
Protecting the Organization
Protecting the organization from potential negative outcomes is a crucial aspect of effective risk mitigation, requiring robust strategies tailored to address specific risks and continuously monitored for effectiveness.
Operational Risk Management (ORM) processes focus on identifying and assessing potential risks that could result in financial loss or disruption to customer service, including employee conduct, technology risks, and external threats. Once these risks are identified, ORM professionals develop mitigation strategies to minimize their impact on the business.
To develop effective mitigation strategies, organizations must conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential hazards and assess related risks. This step involves detecting potential sources of harm, such as natural disasters or human error, and analyzing their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact on the organization.
This analysis allows ORM professionals to implement feasible control measures to mitigate the identified risks. These mitigation strategies may include transferring risk through insurance policies, avoiding exposure by changing business practices, or accepting the risk while implementing controls to reduce its impact.
Effective operational risk management requires continuous monitoring of implemented controls to ensure they remain effective. This ongoing process allows organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats by identifying new sources of harm that may arise in response to changes in technology or other external factors.
| Risk Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Employee Conduct | Fraudulent activities; Intentional wrongdoing |
| Technology Risks | Cybersecurity attacks; System failures |
| External Threats | Natural disasters; Supply chain issues |
| Risk Assessment Strategies | Identifying hazards; Analyzing likelihood/impact; Implementing feasible control measures; Continuous monitoring |
Ensuring Business Continuity
Ensuring the continuity of business operations is a critical aspect of effective risk mitigation, requiring organizations to develop comprehensive strategies that minimize potential disruptions and maintain stakeholder trust.
Business continuity planning involves identifying risks that could disrupt operations and developing measures to mitigate those risks. Risk assessment is a key component of continuity planning, as it helps organizations identify potential threats and prioritize them based on their likelihood and impact.
Mitigating disruptions requires crisis preparedness, which involves implementing plans for responding to unforeseen events that could impact business operations. This includes having backup systems for critical functions, such as IT infrastructure and supply chain management.
Additionally, ensuring employee safety through emergency response procedures can help mitigate the effects of natural disasters or other unexpected incidents.
Ensuring business continuity is an essential objective of operational risk management. By identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing comprehensive plans for mitigating those risks, organizations can maintain stakeholder trust while minimizing financial losses due to operational disruptions.
Effective continuity planning requires ongoing monitoring and updating to address new threats as they emerge.
Improving Efficiency
Improving efficiency is a critical aspect of operational continuity planning, as it enables organizations to maintain productivity and minimize financial losses during operational disruptions.
Streamlining processes, optimizing operations, increasing productivity, enhancing performance, and maximizing resources are essential to improving efficiency.
One way to enhance efficiency is by implementing technology solutions that automate manual processes and reduce human error.
For example, organizations can use robotic process automation (RPA) to accurately handle repetitive tasks and data entry. RPA can also work around the clock without requiring breaks or vacations, significantly reducing processing time and improving turnaround times for critical business processes.
Another approach is adopting agile methodologies prioritizing continuous improvement over traditional project management approaches. Agile allows teams to iterate quickly on projects while collecting feedback from stakeholders.
This iterative approach enables organizations to identify issues faster and respond more efficiently than they would if they were using a traditional project management methodology.
Table: Benefits of project management methodologies
| Methods | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Streamlining Processes | Reduces waste; Improves effectiveness |
| Implementing Technology Solutions | Automates manual processes; Reduces human error; Improves turnaround times |
| Adopting Agile Methodologies | Prioritizes continuous improvement; Identifies issues faster |
Improving efficiency is an important part of effective operational risk management since it helps ensure business continuity by minimizing financial losses resulting from unexpected disruptions in operations.
Organizations must focus on streamlining processes, implementing technology solutions such as RPA, and adopting agile methodologies to improve operational efficiencies continually. These strategies enable businesses to maximize resource allocation while maintaining high productivity levels.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key principles that guide the process of Operational Risk Management?
The key principles that guide operational risk management include accepting risks only when benefits outweigh costs, avoiding unnecessary risks, planning for risk events, and making risk decisions at the appropriate level. The process involves identifying, assessing, mitigating, monitoring, and reporting risks.
How can technology enable the Operational Risk Management process?
Technology solutions provide automation benefits to the operational risk management process, allowing for efficient risk identification and enabling effective mitigation strategies. Data analytics tools can also aid in monitoring and reporting risks.
What are the different types of operational risks that organizations face?
Operational risks faced by organizations include people, technology, reputational, and regulatory risks. Risk assessment techniques are used to identify common mitigation strategies.
Industry-specific risks and emerging operational risks require monitoring. Real-world examples include employee misconduct and cybersecurity attacks.
How have standardization and regulation impacted the discipline of Operational Risk Management?
Industry standards and regulatory compliance have emphasized risk assessment and mitigation strategies in operational risk management. This has impacted stakeholders by promoting effective internal controls, reducing potential loss, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
What are some of the challenges that organizations face when implementing an Operational Risk Management program?
Challenges in implementing ORM include resource allocation, cultural resistance, communication breakdowns, data integration issues, and understanding risk appetite.
An analytical and strategic approach is necessary to overcome these obstacles and establish an effective ORM program.
Conclusion
Operational Risk Management (ORM) is a critical process that organizations must implement to protect themselves from potential operational risks.
The primary objective of ORM is to mitigate these risks related to daily operations through risk identification, assessment, measurement and mitigation, monitoring, and reporting. The framework helps reduce threats, minimize loss, protect the organization, ensure business continuity, and improve efficiency.
However, implementing an efficient ORM framework has its challenges. Organizations face difficulties in identifying all potential operational risks that could disrupt their operations. Furthermore, the cost of implementing an effective ORM program can be high as it requires resources such as time and money.
Nevertheless, the benefits of an effective ORM framework far outweigh the costs. It enhances organizational resilience by minimizing losses caused by disruptions in daily operations and creates a culture of awareness among employees about how they can contribute towards managing operational risks.
Organizations must prioritize implementing an ORM framework as it protects them from potential financial losses and ensures customer satisfaction by maintaining seamless operations even during crises or disruptions.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

