Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) is crucial to any organization’s operations. It is a comprehensive management framework that helps organizations identify potential threats, assess their impact, and develop mitigation strategies.
Implementing BCMS standards ensures an organization’s resilience in unexpected disruptions.
There are several methods that organizations can use to implement BCMS standards effectively. These methods include planning and developing a BCMS framework, formulating BCMS policy and strategy, implementing and operating the BCMS, testing, maintenance, and continual improvement, and response, recovery, and crisis management.
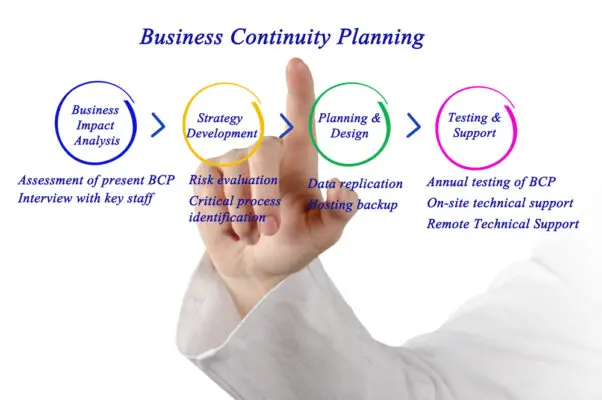
Each method is crucial to successfully implementing BCMS standards and must be carefully considered and executed.
Key Takeaways:
- Implementing BCMS standards ensures an organization’s resilience in unexpected disruptions.
- There are several methods that organizations can use to implement BCMS standards effectively, including planning and developing a framework, formulating policy and strategy, implementing and operating the BCMS, testing, maintenance, and continual improvement, and response, recovery, and crisis management.
- Each method is crucial to successfully implementing BCMS standards and must be carefully considered and executed.
Understanding BCMS and Its Importance
Fundamentals of Business Continuity Management
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a systematic approach to identify potential organizational threats and risks and develop strategies to minimize their impact.
It involves a set of processes, policies, and procedures to ensure the continued operation of critical business functions during and after a disruptive event.
The BCM process includes risk assessment, business impact analysis, developing recovery strategies, and implementing and testing the plan. The ISO 22301 standard provides a framework for implementing a BCMS and ensuring its effectiveness.
Benefits of Implementing BCMS
Implementing a BCMS provides several benefits to an organization. Firstly, it ensures the continuity of critical business functions during and after a disruptive event, reducing the event’s impact on the organization’s operations. Secondly, it increases confidence in the organization’s ability to respond to and recover from a disruptive event, enhancing its reputation.
Thirdly, implementing a BCMS provides a competitive advantage by demonstrating the organization’s commitment to resilience and its ability to manage risks effectively. Finally, it enables the organization to comply with legal and regulatory requirements related to business continuity.
In summary, implementing a BCMS is essential for organizations to ensure the continuity of critical business functions during and after a disruptive event.
It provides several benefits, including increased confidence, reputation, and competitive advantage. The ISO 22301 standard provides a framework for implementing a BCMS and ensuring its effectiveness.
Planning and Developing a BCMS Framework
Planning and developing a BCMS framework is crucial in implementing BCMS standards. The following subsections describe organizations’ key activities when planning and developing a BCMS framework.
Defining the Scope and Objectives
The first step in planning and developing a BCMS framework is to define the scope and objectives of the framework. This involves identifying the boundaries of the BCMS, including the processes, functions, and locations that the framework will cover.
The scope should be defined in terms of the services or products provided by the organization and the critical business processes that support them.
Once the scope has been defined, the objectives of the BCMS should be established. These objectives should align with the organization’s strategic goals and be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
The objectives should also consider the needs and expectations of the organization’s stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers, and regulators.
Conducting Business Impact Analysis
The next step in planning and developing a BCMS framework is to conduct a business impact analysis (BIA). The BIA is a process that identifies the critical business processes, systems, and resources that are required to support the organization’s products and services.
The BIA also identifies the potential impacts of disruptions to these critical processes, systems, and resources.
The BIA provides the foundation for developing the BCMS framework by identifying the organization’s risks and potential threats.
The BIA also helps to prioritize the organization’s recovery efforts by identifying the critical processes, systems, and resources that must be restored first in the event of a disruption.
Assessing Risks and Potential Threats
The final step in planning and developing a BCMS framework is to assess the risks and potential threats that the organization faces.
This involves identifying the events or incidents that could cause disruptions to the organization’s critical processes, systems, and resources. The risks and potential threats should be assessed regarding their likelihood and impact on the organization.
Once the risks and potential threats have been identified and assessed, the organization can develop a risk management strategy that includes risk mitigation, transfer, avoidance, and acceptance.
The risk management strategy should be aligned with the organization’s overall risk appetite and reviewed and updated regularly.
In conclusion, planning and developing a BCMS framework is critical in implementing BCMS standards. The framework should be designed to meet the organization’s specific needs and should be aligned with the organization’s overall strategic goals.
The framework should also be based on a thorough understanding of the organization’s critical processes, systems, and resources and should be designed to mitigate the risks and potential threats that the organization faces.
BCMS Policy and Strategy Formulation
When implementing BCMS standards, it is essential to establish a business continuity policy and develop a business continuity strategy. These two elements are the backbone of a successful BCMS implementation.
Establishing a Business Continuity Policy
A business continuity policy is a set of guidelines that outlines the organization’s approach to business continuity management. It should be designed to align with the organization’s overall strategy and objectives.
The policy should also be tailored to the organization’s risks, challenges, and opportunities.
To establish a business continuity policy, the organization should follow these steps:
- Identify the scope of the policy.
- Define the policy’s purpose and objectives.
- Identify the roles and responsibilities of key personnel.
- Establish the policy’s scope, including the organization’s business continuity management system (BCMS).
- Define the policy’s implementation and maintenance requirements.
- Establish the policy’s communication and awareness requirements.
Developing a Business Continuity Strategy
A business continuity strategy is a set of plans and procedures that enable the organization to continue operating during and after a disruptive event.
The strategy should minimize the event’s impact on the organization’s operations, reputation, and bottom line.
To develop a business continuity strategy, the organization should follow these steps:
- Identify the organization’s critical business functions and processes.
- Conduct a business impact analysis (BIA) to identify the potential impact of a disruptive event on the organization’s critical business functions and processes.
- Develop a business continuity objective set that aligns with the organization’s overall strategy and objectives.
- Develop business continuity plans and procedures that enable the organization to continue operating during and after a disruptive event.
- Test the business continuity plans and procedures to ensure they are effective and efficient.
- Maintain and update the business continuity plans and procedures to remain relevant and effective.
In summary, establishing a business continuity policy and developing a business continuity strategy are crucial elements of a successful BCMS implementation.
These elements should be designed to align with the organization’s overall strategy and objectives and should be tailored to the organization’s specific risks, challenges, and opportunities.
Implementation and Operation
Roles and Responsibilities Allocation
Assigning roles and responsibilities within an organization is a critical step in implementing a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS). This includes designating individuals responsible for managing the BCMS and those responsible for specific procedures and processes.
Ensuring that all personnel know their roles and responsibilities and are adequately trained to carry out their assigned tasks is important. Job descriptions, training programs, and regular performance evaluations can achieve this.
Establishing Procedures and Processes
Procedures and processes are the backbone of a BCMS. They provide a framework for responding to disruptions and minimizing the impact on the organization.
Establishing clear and concise procedures and processes that are easy to follow and understand is important. This can be achieved through the use of flowcharts, checklists, and other visual aids.
It is also important to ensure that procedures and processes are regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the organization’s operations and environment.
Resource Management and Training
Effective resource management is essential for the successful implementation of a BCMS. This includes ensuring adequate resources are available to support the BCMS, such as personnel, technology, and facilities.
Ensuring that personnel are adequately trained to carry out their assigned tasks is also important. This can be achieved through training programs, drills, and exercises.
Regular training and testing can help ensure that personnel are prepared to respond to disruptions and minimize the impact on the organization.
In summary, implementing a BCMS requires careful planning and attention to detail. Assigning roles and responsibilities, establishing procedures and processes, and ensuring adequate resource management and training are all critical components of a successful BCMS implementation.
By following these best practices, organizations can improve their resilience and minimize the impact of disruptions on their operations.
Testing, Maintenance, and Continual Improvement
Implementing a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) is not a one-time task. It requires ongoing maintenance, testing, and improvement to ensure its effectiveness.
Here are some essential aspects of testing, maintenance, and continual improvement of a BCMS.
Conducting Exercises and Testing
Organizations must conduct regular exercises and tests to ensure their BCMS is functional and effective. These tests help identify gaps, risks, and areas that require improvement. Testing can be done in various ways, such as tabletop exercises, simulations, and full-scale rehearsals.
During the testing phase, the organization can evaluate its response to various scenarios, such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or other disruptions. The results of these tests can be used to refine the BCMS and improve its effectiveness.
Regular Maintenance and Revisions
Maintaining a BCMS involves regular reviews and updates to remain relevant and effective. This includes reviewing the risk assessment, business impact analysis, and recovery strategies.
The organization should also update its training and communication plans to ensure all employees know their roles and responsibilities.
The BCMS should be revised to align with the organization’s goals and objectives. This includes updating the plan to consider organizational structure, technology, or process changes.
Strategies for Continual Improvement
Continual improvement is an essential aspect of a BCMS. Organizations must continually review and improve their plans to remain effective and relevant.
This involves tracking metrics, such as recovery time objectives and testing frequency, to identify improvement areas.
The organization should also seek employee, stakeholder, and customer feedback to identify improvement areas. This feedback can refine the BCMS and ensure that it remains aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Testing, maintenance, and continual improvement are critical to implementing a BCMS. Organizations must conduct regular exercises and tests, maintain their plans, and continually review and improve their strategies to ensure the effectiveness of their BCMS.
Response, Recovery, and Crisis Management
When implementing BCMS standards, it is essential to have a comprehensive plan for response, recovery, and crisis management. This plan should include incident response and management, recovery plans and strategies, and crisis communication and management.
Incident Response and Management
Incident response is the process of identifying, assessing, and responding to a security incident. This process is critical to minimize the impact of an incident and prevent it from escalating into a crisis.
Incident response teams should be established and trained to respond quickly and effectively to any incident.
Recovery Plans and Strategies
Recovery plans and strategies are designed to restore critical business functions and processes after an incident. These plans should be developed in advance and tested regularly to ensure their effectiveness.
Recovery plans should include procedures for restoring data, applications, and infrastructure.
Crisis Communication and Management
Crisis communication and management are essential components of any BCMS. Communication plans should be developed and tested to ensure all stakeholders are informed during a crisis.
Crisis management teams should be established and trained to manage the crisis and ensure the organization can continue operating.
In summary, response, recovery, and crisis management are critical components of any BCMS. Organizations should establish incident response teams, develop recovery plans and strategies, and create crisis communication and management plans.
By doing so, organizations can minimize the impact of incidents and ensure they can continue operating during a crisis.
BCMS Certification and Compliance
Organizations implementing BCMS standards must comply with the relevant legal and regulatory requirements. Compliance is essential to ensure the organization is not exposed to legal or financial risks.
Certification is a process that verifies that an organization’s BCMS meets the relevant standards and is compliant with the legal and regulatory requirements.
ISO 22301 Compliance and Certification
ISO 22301 is the international standard for BCMS. Compliance with this standard demonstrates that the organization has implemented a robust BCMS to manage disruptive incidents.
Certification to ISO 22301 is a formal process that verifies that the organization’s BCMS meets the standard’s requirements.
Organizations certified to ISO 22301 can benefit from improved resilience, increased customer confidence, and reduced insurance premiums.
The certification process involves an independent auditor who examines the organization’s BCMS and verifies that it meets the standard’s requirements.

Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Organizations implementing BCMS standards must comply with the relevant legal and regulatory requirements. Compliance involves identifying the legal and regulatory requirements that apply to the organization and ensuring that the BCMS meets these requirements.
Legal and regulatory requirements can vary depending on the industry and location of the organization. For example, healthcare organizations may need to comply with HIPAA regulations, while financial organizations must comply with SEC regulations.
Internal Audits and Accreditation
Internal audits are an essential part of the BCMS implementation process. Audits help to identify weaknesses in the BCMS and provide recommendations for improvement.
Organizations can use internal audits to ensure their BCMS complies with legal and regulatory requirements.
Accreditation is a process that verifies that the organization’s BCMS meets the requirements of the relevant standard. An independent third-party organization usually performs accreditation.
Accreditation assures stakeholders that the organization’s BCMS is effective and compliant with legal and regulatory requirements.
In summary, compliance and certification are essential for organizations that implement BCMS standards. Compliance ensures that the organization is not exposed to legal or financial risks, while certification assures stakeholders that the organization’s
BCMS meets the requirements of the relevant standard. Internal audits and accreditation are also important for ensuring the BCMS remains effective and compliant with legal and regulatory requirements.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

