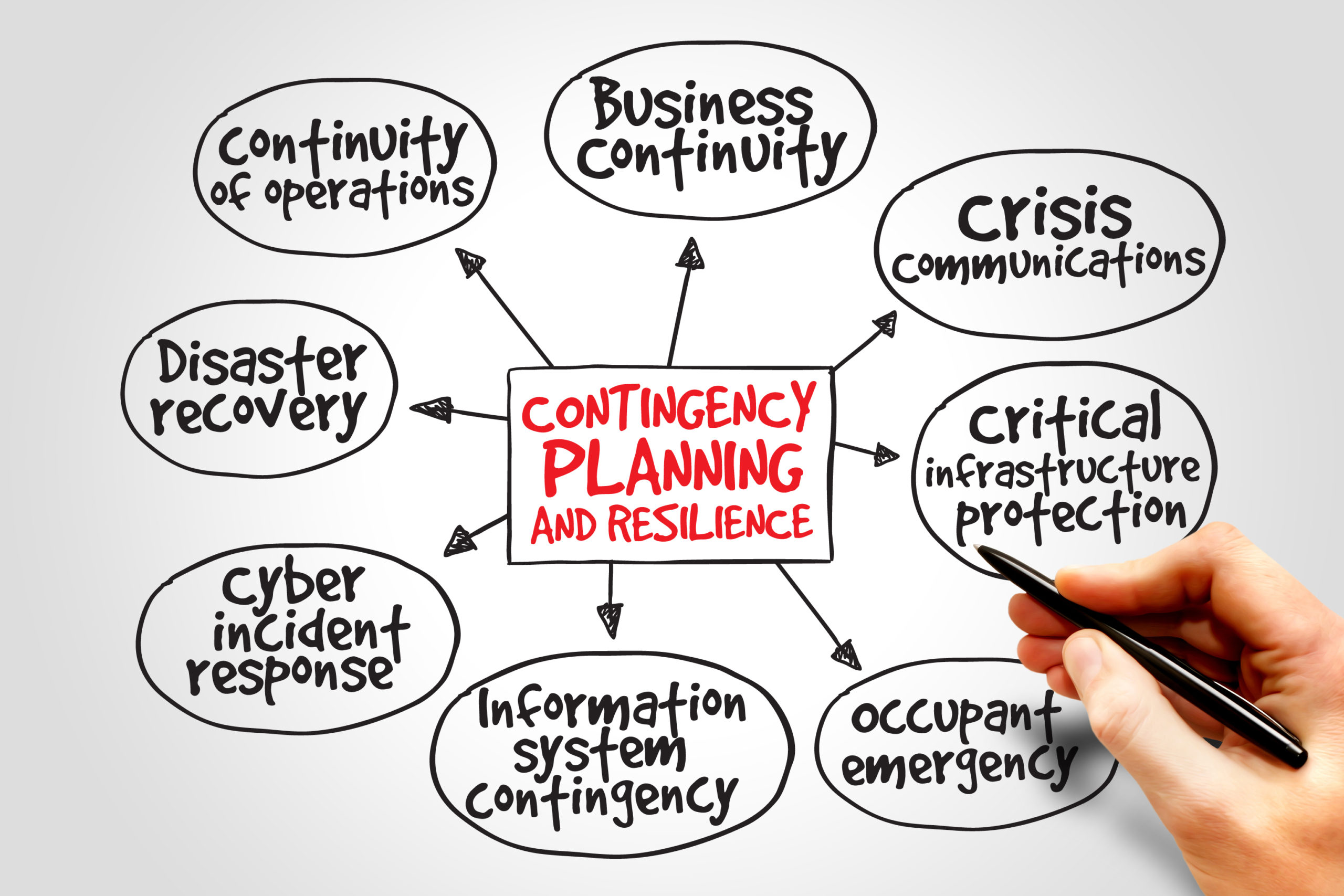
It’s no secret that businesses, of all sizes, are increasingly susceptible to data breaches, cyber attacks and other IT-related issues that can lead to business disruption. In order to mitigate the risk of such disruptions, it is important for businesses to implement a sound business continuity management system (BCMS). A BCMS can help organizations prevent, or at least minimize, the impact of any potential downtime. By implementing a BCMS, businesses can ensure that they have processes and procedures in place to quickly recover from any type of outage or disaster.
Organizations need to implement a business continuity management system (BCMS). A BCMS is a framework that helps organizations identify and manage risks that could disrupt their business. By implementing a BCM system, businesses can create a plan that will help them resume operations as quickly as possible in the event of an emergency. Disruption of business continuity can have a devastating impact on organizations, whether it is a small company or a large multinational.
ISO 22301:2019 : Security and Resilience – Business continuity management requirements. A management system standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization specifies the requirements to design and establish a documented business continuity plan and operation system.
The key to preventing any unnecessary business disruption is by having a well-developed business continuity management system (BCMS). BCMS is a systematic approach to ensuring that critical functions within an organization are continually operational, in spite of any potential disruptions. This article will discuss the essential components of BCMS and how they can help your organization maintain continuous operations.
business continuity management
Business continuity management (BCM) is a strategic business function that helps organizations prepare for and respond to disruptions. By having a BCM plan in place, organizations can minimize the impact of an interruption and resume operations more quickly.
There are three key components to BCM:
– Risk assessment: Organizations need to identify which risks could have the biggest impact on operations and develop plans to mitigate those risks.
– Business continuity planning: Once risks have been identified, organizations need to develop plans for how to keep critical functions running in the event of an interruption.
– Testing and exercise: Plans need to be tested regularly to ensure they are effective and up-to-date. Organizations should also conduct exercises to simulate disruptions and practice their response.
business continuity
Business continuity is the ability of an organization to maintain its core functions and operations in the event of a disaster. A well-developed business continuity plan helps to ensure that vital personnel, equipment, and supplies are available when needed, and that essential services can be quickly restored. The key components of a business continuity plan include risk assessment, data backup and recovery, and communication.
Risk assessment is the process of identifying potential threats to an organization’s operations and determining the likelihood and impact of those threats. An effective risk assessment takes into account the organization’s vulnerabilities, the resources available to mitigate risks, and the likelihood and severity of potential disruptions.
Data backup and recovery is a critical component of any business continuity plan. In the event of a system failure or data loss, organizations need to be able to quickly restore vital information. Data backup should be performed regularly, and backups should be stored in a secure location that is accessible in the event of a disaster.
Communication is another essential element of business continuity planning. In the event of a disruption, clear and concise communication can help to ensure that employees, customers, and other stakeholders are kept informed of the situation. A well-developed communication plan should identify who needs to be notified in the event of a disruption, how they will be notified, and what information will be communicated.
business continuity plan
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a document that outlines how a business will continue to operate during and after an interruption in service. The goal of a BCP is to minimize the impact of an interruption on the business, including financial loss, reputation damage, and legal liability.
There are four key components to a successful BCP:
1. Risk Assessment: The first step in creating a BCP is to conduct a risk assessment to identify potential threats to the business. This will help determine what steps need to be taken to keep the business running in the event of an interruption.
2. Business Impact Analysis: Once potential risks have been identified, a business impact analysis (BIA) can be conducted to determine the potential impact of each threat on the business. This information can then be used to prioritize the development of contingency plans.
3. Contingency Planning: Contingency planning involves developing plans for how the business will continue to operate in the event of an interruption. These plans should be tailored to specific threats and may include alternate locations, backup systems, and alternative suppliers.
4. Implementation and Testing: The final step in creating a BCP is to implement the contingency plans and test them to ensure they are effective. Regular updates and testing are essential to maintaining a successful BCP.
federal emergency management agency
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security, tasked with responding to natural disasters and helping to protect American citizens from terrorist attacks. FEMA was created in 1979 in response to the growing threat of earthquakes and other natural disasters, and its mission is to “lead the effort to prepare the nation for all hazards and manage federal response and recovery efforts following any national incident.” FEMA has become a crucial part of the American government’s disaster response efforts, and it plays a vital role in protecting citizens from the potentially devastating effects of hurricanes, tornadoes, and other natural disasters.
FEMA’s responsibilities include:
– Coordinating the federal government’s response to natural disasters
– Providing financial assistance to state and local governments for disaster relief efforts
– Supporting first responders with resources and training
– assisting individuals and families affected by natural disasters
– coordinating long-term recovery efforts following a disaster.
what is business continuity management system
A Business continuity management system (BCMS) is a framework for identifying an organization’s risk of exposure to internal and external threats. The goal of a BCMS is to reduce the likelihood of disruptions to operations and to ensure that the organization can quickly resume critical functions in the event of a major incident.
A BCMS typically includes three components:
* A business continuity plan (BCP), which outlines the steps that need to be taken in order to resume critical functions in the event of an incident;
* A business impact analysis (BIA), which identifies the potential effects of disruptions to operations; and
* A risk assessment, which identifies the risks that could threaten the organization’s ability to continue its operations.
Organizations implement BCMSs in order to comply with regulatory requirements, minimize losses in the event of an incident, and protect their reputation. BCMSs are typically overseen by a business continuity management team, which is responsible for developing and implementing the plans.
+business continuity system
A business continuity system (BCS) is a set of processes and technologies designed to help an organization continue operating during and after a major disruption. The key components of a BCS include:
* A risk management plan that identifies the potential threats to an organization’s operations and outlines the steps that will be taken to mitigate those risks.
* A business continuity plan that outlines the steps that will be taken to keep essential functions running in the event of a major disruption.
* A incident response plan that outlines the steps that will be taken to recover from a major disruption.
* A crisis communication plan that outlines the steps that will be taken to communicate with stakeholders during and after a major disruption.
* A training and exercise program that ensures all employees are familiar with the BCS and know how to respond in the event of a major disruption.
What is ISO 22301 Business Continuity Management System?
BCM refers to risk management, which focuses on the risk that an enterprise is affected by external or internal factors. This includes arrangements that ensure that you are responding as efficiently as possible in a disruption to ensure mission-critical services remain acceptable. A successful business continuity system is best achieved by integrating a business continuity management system with ISO 22301.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the key components of a BCM system and how it can help your business stay up and running during times of crisis. we will also explore what BCMS is and how it can help businesses stay resilient in the face of disruptions.

Business Continuity Management System
BCMS help in identifying potential threats in the day-to-day operations or implementation project. Business impact analysis can be carried out in the BCMS for critical business functions. This aids formation of a plan. It differs business continuity differs from risk management. The danger of business disruption, taking into account the current cyber threat landscape has prompted business leaders to understand and resource recovery strategies.
The ISO 22301:2019 international standard on BCM specific requirements and essential areas foresee an increase in cyber-attacks and such attacks need an effective bcm. Cyber attacks will be prevented by services and processes that are of importance to customers. To implement a BCMS software employees need to identify potential threats to a process and determine tailored strategies that benefit governance.
Business Continuity Plans Process Diagram – Text version When businesses get disrupted they can have significant financial losses. A decrease in profits and additional costs will result. This insurance is not a replacement for customers who have defected against the competitor. It’s crucial to establish business continuity plans for continued business operation. The process for developing the business continuity planning involves 4 steps – Information technology (IT) includes many components, including networks. Managing office productivity and enterprise software are critical.
Why is Business Continuity Management System so Important?
BCM involves preparing your company early for disruption and analyzing the impacts on daily operations. A BCM is essential to ensure an organization provides an acceptable service level despite the disaster and protects corporate credibility resulting from a failure in its business. In the future, it can improve coverage rates and provide new contracts. The cyber attack landscape reflects the increasing need to respond quickly and effectively to cyber threats.
Importance of BCMS
- BCM or Business Continuous Improvement is aimed at planning disruptive events.
- Organizations try to detect threats and analyze the impact on daily operations.
- Effective BCM ensures an organization provides an acceptable service during a disaster, thereby preserving its reputation and increasing revenues.
- A business continuity management system (BCMS) is a framework of policies and procedures that enables an organization to continue its essential operations during and after a disruptive event.
- BCMS helps an organization to protect its people, property, and profits by ensuring that critical business functions can be recovered quickly in the event of a disruption.
- To protect employees – Organizations have a responsibility to protect their employees’ safety. A BCMS can help to ensure that critical functions can be resumed quickly following a disruption, which reduces the risk of injury or illness to employees.
- To protect property – Disruptions can cause damage to property.
Qualities of a good BCMS
- A BCM program includes plans, processes, and procedures to ensure critical functions can be resumed quickly after a disruption
- The BCMS should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization, and should incorporate risk assessments to help identify potential disruptions and their potential impacts.
- The BCMS should also include plans for testing and exercising the continuity plan regularly.
Benefits of Business Continuity Management System
The most significant reason to use BCMS is to keep your business processes operational in the case of an interruption. Despite these reasons, there is still much reason for adopting such systems. If the public is pleased, you are able to react quickly after the disruption of business operations.
Those negative feelings are mitigated by a reduction in productive capacity. When an organization’s system is properly managed, the employee’s needs are realized and it proves management has considered their needs. An effective BCMS shows that the organization is well managed and encourages those who work with you.
Other benefits include:-
- A business continuity management system (BCMS) can help an organization protect its people, property, and reputation in the event of a major incident.
- BCMSs can help organizations save money by minimizing the impact of disruptive events.
- BCMSs can improve organizational resilience, which is the ability to quickly adapt and bounce back from disruptions.
- BCMSs are often required by regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom.
- BCMSs can help organizations comply with industry standards such as ISO 22301:2012 “Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Requirements.
How Does BCMS Work?
A BCMS is a documented system that establishes the organization’s requirements for continuity of operations and outlines how the organization will recover from disruptive events.
A BCMS typically includes the following components:
– Risk Assessment: Identification of risks and assessment of their impact on business operations
– Business Continuity Planning: Development of plans to restore critical business functions after a disruptive event
– Incident Response Procedures: Procedures for responding to and managing incidents
– Disaster Recovery Plan: Plan for recovering IT systems and data after a major outage or disaster.
Business continuity management system basically acts as insurance for business continuity. It allows organizations the security of knowing that disasters are not too big. Without such a plan, disruptions can cause additional work or stress and may also be detrimental to the organization’s ability to perform work.
A BCMS system helps ensure that it does not happen. The Integrated Framework for Adaptive Management of Organizational Risk provides organizations with the ability to maintain, monitor, and deploy effective planning plans, and account for organizational risks and abilities, as well as business needs.

Business Processes
A business continuity plan will help prepare for an emergency situation, and reduces disruption. Using effective emergency management you can ensure everyone on your team is following a planned action plan when disaster occurs. Using a comprehensive Risk Management System, Integrated Risk Management framework will help your organization reduce the risk of disaster.
A BCMS combines methods, procedures and rules that ensure continuity of important processes and may include existing management tools. Each strategy is based around your requirements.
How its integrated to business processes
- BCMS assists business processes by automating and managing the flow of information between departments and systems. This helps to improve efficiency and coordination, while also reducing the risk of data loss or corruption.
- BCMS can help to automate tasks such as report generation, data entry, and invoice processing. This can save time and reduce the potential for human error.
- BCMS also provides a single point of access for all company information, which can make it easier to find and share information. This can improve communication between employees and departments.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster response planning prioritizes full recovery and full functionalities in case of a disaster whereas BCM focuses on ensuring the organization is capable of operating efficiently. In spite of this, there remains an obvious overlap, as disaster recovery fits into any organisations business Continuity framework. Disaster recovery plans typically are relatively technical and focuses on recovery of certain activities, functions and applications. BCPs may contain disaster recovery strategies, or references to those.
There are a few key steps to creating an effective disaster recovery plan for your business continuity management system (BCMS):
- Assess your risks and vulnerabilities. What could potentially happen to disrupt your operations and how prepared are you to deal with those disruptions?
- Develop response plans for different types of incidents. What will you do if a tornado hits your office building, or the power goes out, or there’s a data breach?
- Test your plans regularly. simulating different types of emergencies can help ensure that your team is ready to respond quickly and effectively when disaster strikes.
- Update your plans as needed. As your business changes and grows, so too will your risks and vulnerabilities
Ways to embed
- Establish a clear chain of command and decision-making process
- Identify and categorize your essential systems and data
- Develop a plan for backup and disaster recovery for each system
- Ensure you have adequate backup storage space and bandwidth
- Test your disaster recovery plan regularly
- Train all employees on your disaster recovery plans
- Creation of crisis management and free green paper plans
Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Business continuity management includes process procedures based on developing, testing the BCP that allows organizations to operate after disasters and quickly restore to their current state. The BCP can be characterized by being the heart of a BCS. The best method for forming such plans is defined within ISO 22301 and BCI a growing body of business continuity experts.
Business continuity planning (BCP) is the process of creating a plan to ensure that critical business functions will continue to be available in the event of a major disruption. The goal of BCP is to minimize the impact of a disruption on business operations.
There are several steps involved in creating a BCP:
- Assess your risk factors – What could cause a major disruption to your business? Example Natural disasters, human error, cyber-attacks, etc.
- Establish recovery objectives – What are your priorities? Ensuring that customers can still access their data, maintaining communication with employees, keeping the lights on, etc.
- Create a strategy for recovering from each type of disruption – How will you respond if you determine that strategies for BCM have few resources that support BCM programs.
How BCMS Can Meet Regulatory Requirements?
BCMS can meet regulatory requirements in a number of ways.
First, by establishing and implementing a formal quality management system, BCMS can ensure that all activities are conducted according to the required standards. In addition, BCMS can establish and adhere to performance metrics that will demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements. Finally, BCMS can conduct routine audits of its operations to ensure compliance with both regulatory and internal standards.
The law also requires organizations to demonstrate resilience in important areas; implementing effective business continuity measures would be a helpful way to start.
There are key things that BCMS can do in order to meet regulatory requirements:
- Establish and enforce a quality management system (QMS). This system should be designed to ensure that all products and services meet or exceed regulatory standards.
- Implement process controls throughout the production process. These controls should be aimed at preventing defects and ensuring consistent quality.
- Track product performance throughout the supply chain. This information can help identify potential issues and prevent them from impacting customers.
- Maintain thorough documentation of all processes, products, and inspections. This documentation can help regulators assess compliance with regulatory standards.
Business Continuity Management System Softwares
A Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) is software that helps businesses maintain continuity in the event of a disruption. A BCMS can help organizations manage risks, protect their people and assets, and resume operations quickly after an incident.
There are many different types of BCMS software available, and each one has its own strengths and weaknesses. It’s important to choose a BCMS that will meet the specific needs of your business.
When evaluating BCMS software, you should consider the following factors:
- The features of the software
- The pricing model
- The level of support offered by the vendor
- The ease of use
They might include:-
- Oracle Risk Management Cloud
- iGrafx
- ZenGRC
- OneTrust
- LogicManager
- Fusion Framework System
- BC in the Cloud
- FICO Decision Central
- Castellan Software Suite
- SAI360
Conclusion
In conclusion, a BCMS is essential for any business looking to protect itself from potential business disruptions. By implementing a BCMS, businesses can ensure that they have processes and procedures in place to quickly get back up and running if and when an incident occurs. If you’re interested in learning more about BCMS or need help implementing one for your business, contact us today. We would be happy to help!

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.