Are you looking for effective ways to assess and manage operational risks in your organization? Look no further than RCSA risk management. This comprehensive guide will provide the tools and strategies necessary to identify potential risks, develop mitigation plans, and monitor the effectiveness of your own risk assessments and management processes.
Operational risks can arise from various, including technical failures, human error, regulatory compliance issues, or even natural disasters. These risks can have serious consequences for your business operations without proper planning and prevention measures.
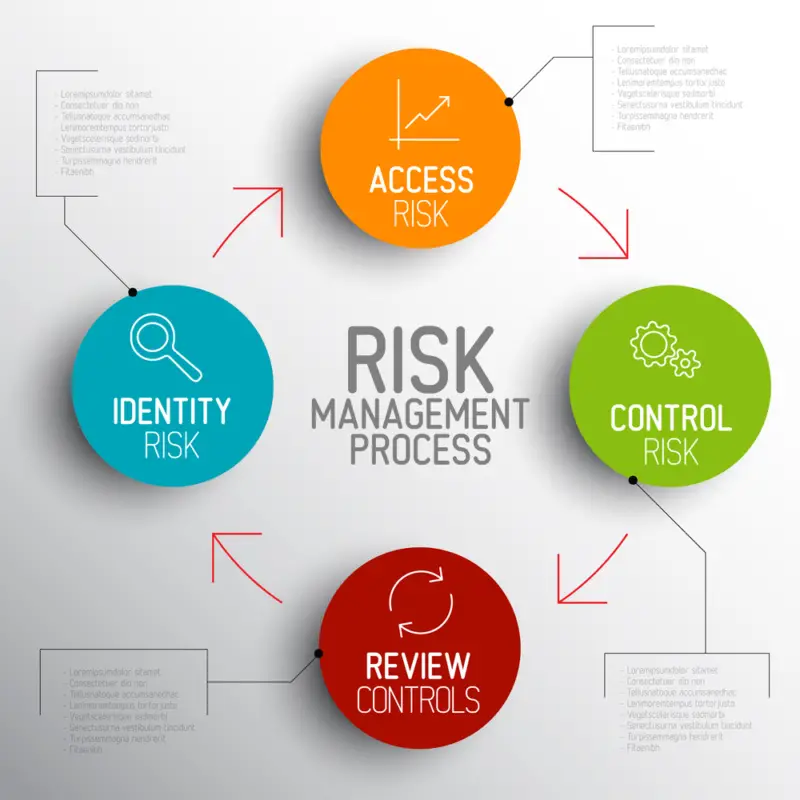
The RCSA approach to risk management offers a systematic framework for assessing potential threats and implementing controls to minimize their impact. With this guide as your roadmap, you can ensure that your organization is prepared to handle any challenges that may come its way.

Understanding Operational Risks
The RCSA process involves understanding the organisation’s risk profile, identifying potential risks and assessing their likelihood of occurrence. The assessment also includes evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls in mitigating those risks.
Organizations should also consider external factors such as market conditions, economic trends, regulatory changes and technological advancements when assessing their risk profile. By considering these external factors, organizations can better anticipate potential risks and develop strategies for managing them effectively.
In addition to identifying potential risks, organizations should also have processes in place for monitoring and reporting on those risks on an ongoing basis. This helps ensure that any changes in risk levels are identified quickly so that appropriate action can be taken before losses occur.
Overall, Risk Control Self Assessment (RCSA) is essential for managing operational risks effectively. Organizations can protect themselves from financial losses and ensure their long-term success by understanding the organisation’s risk profile and taking proactive steps to mitigate potential losses due to operational risks.
Operational risks arise from or are associated with controls in the day-to-day operations of a company, and they can manifest in many different ways. This can include anything from product defects to employee errors and everything in between.
Companies must employ risk control measures such as control processes and risk management to manage these operational risks effectively.
Risk assessment is a key component of this process, as it allows businesses to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities before they become major issues.
One key risk indicator is identified, and residual risks can be managed through various strategies such as avoidance or mitigation. Take proactive steps to manage operational risks, companies can minimize their exposure to potential losses while ensuring their operations’ continued success.
Identifying and Assessing Risks
In this section, we’ll learn how to identify and evaluate potential hazards to mitigate them effectively. The RCSA process involves identifying risks affecting your business unit or organization’s operations and assessing their likelihood and impact.
This is a critical step in operational risk management as it allows you to prioritize and allocate resources toward mitigating the most significant risks.
To begin identifying risks, start by reviewing past incidents or near-misses. Look for patterns or trends across your organisation’s different departments, business units, or functions.
Next, engage with front-line staff who have direct knowledge of day-to-day operations. They can provide valuable insights into where potential hazards may lie.
Once identified, assess each risk based on its likelihood of occurrence and potential impact on your organization’s business objectives only.
Finally, use a risk self-assessment tool to document your findings, assess risks, and ensure all stakeholders know the risks and mitigation strategies.

Developing Effective Risk Management Strategies
The first step in developing effective operational risk events and management strategies is to understand the impact of operational risks on your business processes. This is where rcsa risk management comes in handy.
To mitigate operational risks, you need to create a controlled environment to identify risks before they occur. This means implementing controls that monitor business processes and detect any anomalies or deviations from expected outcomes.
Once these risks have been identified, you can prioritize them according to their potential impact on the organization and develop mitigation plans accordingly. Taking a proactive approach to risk management can minimize the likelihood of costly setbacks and ensure your organization runs smoothly over the long term.
The first step in developing a risk management strategy is to identify the key risks that the organization faces. This can include internal and external risks, such as financial losses, operational disruptions, cyber security threats, and reputational damage. Once these risks have been identified, the next step is to assess their likelihood and impact on the organization.
Once the risks have been identified and assessed, organizations should develop strategies to mitigate or reduce them. This can include implementing policies and procedures to address specific risks or investing in technology solutions to protect against cyber threats. Organizations should also consider investing in insurance policies to cover potential losses due to unforeseen events.
Finally, organizations should regularly review and update their risk management strategies as needed. This will help ensure that they are adequately prepared for any potential risks that may arise in the future.
Implementing Risk Controls and Mitigation Plans
The first step is identifying the control weaknesses in your financial institution’s operational risk management framework. This can be achieved through conducting a Risk Control Self Assessment (RCSA), which will highlight areas that require improvement.
Once identified, mitigation plans should be developed to address these risks and control self-weaknesses. These plans should include practical measures that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
It’s important to involve all stakeholders when developing these internal control and mitigation plans to ensure buy-in and ownership of the process.
Implement effective risk controls and mitigation plans, you can minimize the likelihood of setbacks occurring within your organization and protect it from financial or reputational harm.
Risk controls can be taken to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk event. These can include implementing policies and procedures, training staff on best practices, conducting regular audits, or investing in technology solutions to monitor activities.
Mitigation plans outline the steps an organization should take if a risk event does occur. This could involve setting up emergency response protocols, establishing communication channels with stakeholders, or taking specific actions to limit damage or losses.
Organizations should regularly review their RCSA processes to ensure they are up-to-date and effective in mitigating risks. This includes evaluating existing risk controls and mitigation plans for effectiveness and making changes where necessary.
Additionally, organizations should consider adding new risk control measures as needed based on changing business conditions or emerging threats.
This helps them maintain operational continuity while minimizing financial impacts from potential disruptions or incidents.
Monitoring and Reviewing Risk Management Processes
You can easily keep tabs on your organization’s risk controls and mitigation plans by regularly monitoring and reviewing your processes. This involves conducting periodic self-assessments to identify gaps in existing controls and evaluating the effectiveness of implemented risk mitigation strategies.
As an operational risk manager, it’s essential that you have a comprehensive understanding of the rcsa risk management framework and be able to use self-assessment tools to identify potential risks effectively.
Once you’ve identified potential risks through self-assessment and risk control self-assessments, evaluating residual risk levels is important. Residual risk refers to the level of risk that remains after controls have been put in place.
Operational risk managers must ensure that residual risk exposure levels are acceptable and within the organization’s tolerance. Regular monitoring and review of your organization’s processes will enable you to adapt to changes in the business environment and continuously improve your operational risk management practices.
Conclusion
Following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively identify potential risks, develop strategies to mitigate them and implement controls to reduce their impact on your organization.
Remember that risk management is ongoing and should be continuously monitored and reviewed.
Regularly assessing and updating your risk management plan will help ensure that your business is prepared to face any unexpected challenges that may arise.
With the knowledge gained from this guide, you can confidently navigate operational risks and protect your business from harm.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.