Risk management is a systematic process that businesses and individuals undertake to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that could impact their operations or projects.
According to the organization’s risk management framework, it involves systematically analyzing and managing potential threats and opportunities to minimize negative impacts and maximize positive outcomes.
At its core, risk management is about recognizing and understanding the uncertainties that exist within various aspects of a business or project. It’s a formal process that can be applied to future projects and project level either using a reactive approach or a defined risk management solution.
Through proactively identifying and assessing potential risks, organizations can create a risk register/risk matrix that categorizes and prioritizes different types of risks, considering their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
There are several types/categories of risks that organizations need to consider, including Financial Risks, operational risks, strategic risks, and external risks. Financial risks pertain to potential losses or adverse impacts on financial resources, while operational risks involve problems with daily operations or the operating environment.
Strategic risks relate to uncertainties associated with the organization’s long-term goals and objectives, and external risks refer to threats arising from external factors such as legal or regulatory issues, market volatility, or natural disasters. This is one of the major risk of an organization.
The risk management process consists of several steps. First is risk identification, which involves brainstorming and gathering information to identify potential threats and opportunities. This is followed by risk assessment, where risks are analyzed and evaluated based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
Once risks are prioritized, especially in project risk management, organizations can develop a risk management plan outlining strategies and actions to mitigate or respond to identified risks. This plan may include contingency, risk mitigation, and risk response plans.
Effective risk management requires continuous monitoring and evaluation of potential threats and existing risks. This involves regular risk assessments and reviews to ensure that risk exposure is minimized and that risk management strategies are still relevant and effective.
Furthermore, risk management should not be seen as a one-time activity but rather an ongoing process that should be integrated into the organization’s daily operations.
Risk management plays a crucial role in safeguarding businesses and projects from potential threats and ensuring their success.
Benefits of Risk Management
Risk management is an essential practice that benefits organizations across various industries. Here are some key benefits of risk management:
1. Minimizing potential risks:Conducting risk assessments and identifying potential threats, organizations can proactively take steps to minimize the impact of these risks. This helps in reducing financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Risk management enables businesses to develop contingency plans and implement preventive measures to mitigate potential risks. This prevents minor inconveniences.
2. Improved decision-making: A robust risk management process provides valuable insights into the potential risks and rewards associated with different business decisions. It allows organizations to make informed choices by considering different outcomes’ potential impacts and likelihoods.
This helps avoid unnecessary risks and make strategic decisions that align with the organization’s objectives.
3. Increased operational efficiency: Implementing risk management practices helps identify and address operational risks hindering efficiency and productivity.This results in improved performance and cost savings.
4. Enhanced stakeholder confidence: Stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees, value organizations that demonstrate strong risk management practices. Having a comprehensive risk management program in place instills confidence and trust in stakeholders, as it ensures that potential risks are being actively managed and mitigated.
This can lead to improved relationships, increased investments, and a stronger market position.
5. Compliance with regulations: Organizations must adhere to Many industries’ specific regulations and requirements. Risk management helps businesses stay compliant with these rules and regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and legal consequences.
6. Seizing opportunities: Risk management is not merely about mitigating negative risks but also identifying and exploiting positive risks or opportunities.
Identifying Risks
As such, it’s crucial for businesses to have a robust risk management strategy in place to identify and mitigate potential project risks. The first step in this process is to identify and assess risks effectively using either a risk assessment matrix or risk register.
Risk identification involves systematically uncovering, analyzing, and documenting potential risks affecting an organization’s objectives. This process should be comprehensive and cover all business areas, including financial, operational, strategic, and external factors.
There are several methods and tools that businesses can employ to identify risks. One commonly used approach is conducting risk assessments, which involve evaluating the likelihood and impact of specific risks.
This can be done through qualitative and quantitative analysis, considering factors such as the probability of occurrence, potential impact, and existing control measures.
Another effective method for identifying risks is by creating a risk register. A risk register is a centralized database that captures and categorizes all identified risks. It provides a comprehensive overview of the potential threats the organization faces, allowing for better visibility and management of risks.
The risk register also serves as a valuable reference tool for the ongoing monitoring and evaluation of risks. It records current risks i.e., market risk, through quantitative risk analysis and risk categories.
It’s important to note that risks can arise from both internal and external sources. Internal risks include operational inefficiencies, human errors, and system failures.
External risks, on the other hand, stem from factors outside the organization’s control, such as market volatility, regulatory changes, and natural disasters.
Organizations should involve multiple stakeholders to enhance the risk identification process, including subject matter experts and project teams. Different perspectives and expertise can help uncover risks that may be overlooked by individuals working in isolation.
Collaboration and effective communication across departments and levels of the organization is key to ensuring comprehensive risk identification.
Once risks are identified, they should be evaluated and prioritized based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This allows organizations to allocate resources and focus on the most critical risks that require immediate attention.
Risks with higher potential impact and likelihood may require more robust mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
Risk identification gives businesses the foundation to effectively navigate uncertainties, protect their interests, and seize opportunities for growth and success.
Risk Identification Process
The risk identification process is a crucial step in effective risk management. It involves identifying and understanding potential risks impacting an organization’s objectives, operations, and overall success.
The first step in the risk identification process is to gather information about the organization’s operations, industry, and external factors. Use of risk identification sessions.
This can be done through various methods, such as conducting interviews with key stakeholders, reviewing historical data, analyzing industry trends, and consulting subject matter experts. Following a risk assessment process.
The goal is to gather as much relevant information as possible to identify internal and external risks and risk factor of each risk.
Internal risks arise within the organization, such as operational inefficiencies, employee errors, or system failures. These risks can hinder productivity, impact customer satisfaction, and disrupt business operations.
To identify internal risks, organizations can review their processes, procedures, and systems and identify areas where vulnerabilities or potential weaknesses exist.
On the other hand, external risks stem from factors outside the organization’s control. These include market volatility, regulatory changes, natural disasters, cyber threats, and geopolitical events.
Organizations must stay updated on external factors that can impact their industry and operations and regularly assess the potential risks these factors pose.
Once potential risks are identified, they should be documented and categorized in a risk register or a centralized database. This allows for easy reference and ongoing monitoring. Each risk should be clearly described, including its cause, potential impact, and likelihood of occurrence.
In the risk identification process, it’s essential to involve different stakeholders from various departments and levels of the organization. This ensures a comprehensive and diverse perspective on potential risks.
Collaboration and effective communication are key to uncovering risks that may be overlooked by individuals working in isolation. Organizations can leverage their expertise and insights to identify risks more effectively by involving different stakeholders.
Regular reviews and updates of the risk identification process are necessary to ensure its continued effectiveness. As the business landscape evolves, new risks can arise, and existing risks may change in nature or severity.
Therefore, organizations should regularly assess and update their risk identification process to stay proactive and prepared.
Through collaboration, regular reviews, and staying informed about internal and external factors, organizations can strengthen their risk identification process and be better equipped to navigate the uncertainties of the business landscape.
Types of Risks
Organizations can develop effective strategies to minimize their negative impact and capitalize on positive risks by identifying and categorizing these risks. Here are some common types of risks that organizations should be aware of depending on the risk culture and types of risk management in an organization :
1. Financial Risks: These are risks associated with an organization’s financial health and stability. Examples include market volatility, economic downturns, currency fluctuations, and changes in interest rates. Financial risks can impact a company’s profitability, cash flow, and ability to meet financial obligations.
2. Operational Risks: These are risks related to the day-to-day operations of a business. They include ineffective processes, supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, and employee errors. Operational risks can lead to productivity losses, customer dissatisfaction, reputational damage, and financial losses. Security risks can be operational.
3. Strategic Risks: Strategic risks arise from the decisions and actions taken by an organization’s leadership or board of directors. These risks include entering new markets, launching new products, or significantly changing the business model.
Strategic risks can impact the organization’s long-term goals, competitive position, and sustainability.
4. Compliance Risks: Compliance risks are related to non-compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards. Organizations operating in highly regulated industries like healthcare or finance are particularly susceptible to compliance risks.
Failure to comply with legal and regulatory requirements can lead to legal consequences, fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
5. Reputational Risks: Reputational risks can arise from negative public perception, customer dissatisfaction, or damage to the organization’s brand image. Various factors, including product recalls, ethical misconduct, data breaches, or poor customer service, can cause these risks.
Reputational risks can have long-lasting effects on customer loyalty, investor confidence, and overall business success.
6. Environmental Risks: Environmental risks are associated with natural disasters, climate change, and environmental regulations. Organizations that operate in areas prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, or floods face additional risks.
Failure to manage environmental risks can lead to property damage, production disruptions, legal liabilities, and reputational harm.
7. Technology Risks: Organizations face various technology-related risks in today’s digital world. These include cyber threats, data breaches, IT system failures, and technological obsolescence. Technology risks can impact data security, customer privacy, business continuity, and operational efficiency.
Organizations must conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and prioritize the business risks most relevant to their industry, operations, and objectives.
Sources of Risks
Let’s take a closer look at some common sources of risks.
1. Internal Sources: Internal sources of risks originate from within the organization itself. These can include inadequate internal controls, poor management decisions, operational inefficiencies, employee errors or misconduct, and ineffective processes.
Use of failure mode and root cause analysis tools can identify sources of risk.
2. External Sources: External sources of risks arise from factors outside of the organization’s control. These can include changes in economic conditions, market volatility, political instability, regulatory changes, and industry disruptions. They might be competitive risks affecting strategy.
External risks can significantly impact a business’s operations, financial health, and overall sustainability. It is crucial for organizations to monitor and stay informed about external factors that could potentially affect their operations.
3. Environmental Sources: Environmental sources of risks are related to natural disasters and climate change. Organizations operating in areas prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, or other natural calamities face additional risks.
These events can cause significant property damage, disrupt production processes, and lead to safety concerns for employees and customers.
Businesses need contingency plans to address environmental risks and ensure the safety and continuity of their operations. Thus mitigating safety risks.
4. Technological Sources: Organizations are exposed to various technological risks in today’s technology-driven world. These include cyber threats, data breaches, IT system failures, and technological obsolescence. With the increasing reliance on digital systems and data, businesses must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, backup and recovery systems and stay proactive in keeping up with technological advancements to manage these risks effectively.
5. Financial Sources: Financial sources of risks are associated with economic and financial factors that can impact an organization’s financial health and stability. These can include market volatility, economic downturns, interest rate fluctuations, currency exchange rate changes, and inadequate financial planning or management.
Mitigating financial risks involves careful financial analysis, monitoring financial markets, and implementing risk management strategies to safeguard the organization’s financial well-being.
6. Human Sources: Human sources of risks are related to the actions or behavior of individuals within or outside the organization. These include employee errors, fraud, theft, labor disputes, and unethical behavior.
Managing human risks involves implementing effective recruitment and training processes, promoting a positive and ethical work culture, and establishing strong internal controls to prevent or detect potential risks.
A comprehensive risk management plan that addresses these sources can help businesses improve their resilience, protect their assets, maintain operational continuity, and ensure long-term success in today’s dynamic and unpredictable business environment.
Assessing and Analyzing Risks
Assessing and analyzing risks is a crucial step in the risk management process. It involves thoroughly evaluating an organization’s potential risks and analyzing their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. The tools can be qualitative risk analysis or qualitative risk assessment.
This allows businesses to prioritize and allocate resources effectively to mitigate and respond to risks ensuring high-quality risk management processes. Here are some key steps in assessing and analyzing risks.
1. Identify and categorize risks: The first step in assessing risks is to identify and categorize them based on their nature and potential impact. This can include operational risks, financial risks, technological risks, human risks, environmental risks, or any other specific categories that are relevant to the organization.
2. Gather data and information: Once risks are identified, gathering relevant data and information is crucial to assess and analyze them. This can include historical data, industry trends, market research, financial statements, internal reports, and external sources of information.
3. Evaluate likelihood and impact: Assessing risks involves evaluating their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact on the organization. Likelihood can be assessed by considering historical data, industry trends, expert opinions, and internal assessments.
The impact can be evaluated by considering each risk’s potential financial, operational, reputational, and strategic consequences. Businesses can prioritize risk management efforts by assigning a rating or score to the likelihood and impact of risks.
4. Conduct risk analysis: Risk analysis involves further analyzing the identified risks to understand their characteristics and potential consequences better. This can include conducting qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Qualitative analysis involves assessing risks based on their qualitative characteristics such as severity, urgency, and strategic importance. Quantitative analysis uses data and statistical models to calculate the financial impact or probability of risks occurring. This analysis helps businesses make data-driven decisions and allocate resources appropriately.
5. Prioritize risks and develop risk response plans: Once risks are assessed and analyzed, they can be prioritized based on their likelihood and impact. This helps organizations focus their resources on managing the most significant risks first.
Businesses can develop appropriate risk response strategies and action plans with this prioritized list. These may include risk mitigation strategies, risk transfer through insurance, risk acceptance, or contingency plans.
6. Monitor and review risks: Risk assessment and analysis are ongoing processes. As the business environment and internal factors change, new risks may emerge, and the impact and likelihood of existing risks may evolve.
It is crucial for organizations to regularly monitor and review their risk assessments to ensure they remain up-to-date and relevant.
Regular monitoring and reviewing of risk assessments are essential to ensure ongoing risk management effectiveness. With a robust business performance and analysis process, organizations, especially from the financial sector, can protect themselves from potential threats and seize opportunities in an ever-changing business landscape.
Risk Analysis and Assessment Processes
Risk analysis and assessment are integral components of any robust risk management process. They involve evaluating and understanding an organization’s potential risks, determining their likelihood and impact, and developing appropriate strategies to mitigate or respond to them.
The first step in the risk analysis and assessment is identifying and categorizing risks. This involves identifying potential risks that could impact various areas of the organization, such as operational, financial, technological, or environmental risks.
Categorizing risks helps businesses comprehensively understand the different types of risks they face, enabling them to develop targeted risk management strategies.
Once risks are identified, the next step is to gather relevant data and information. This includes collecting historical data, industry trends, market research, financial statements, and other sources of information.
After gathering data from business teams, evaluating each identified risk’s likelihood and potential impact is crucial. This assessment helps quantify the level of risk posed to the organization. Likelihood can be assessed by considering historical data, expert opinions, and internal assessments.
At the same time, the impact can be evaluated by considering the potential financial, operational, reputational, and strategic consequences.
The next step in the risk analysis and assessment process is thoroughly analyzing the identified risks. This involves further investigating the characteristics and potential consequences of each risk.
The qualitative analysis assesses risks based on their severity, urgency, and strategic importance. In contrast, quantitative analysis utilizes statistical models and data to calculate the financial impact or probability of risks occurring.
This analysis provides businesses valuable insights for making data-driven decisions and allocating resources appropriately.
Prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and impact enables organizations to focus on managing the most significant risks first. With a well-defined, prioritized list, businesses can develop appropriate risk response strategies and action plans.
These may include risk mitigation strategies, risk transfer through insurance, risk acceptance, or contingency plans.
Lastly, risk analysis and assessment are ongoing processes that require regular monitoring and review. As the business environment and internal factors change, new risks may emerge, while the impact and likelihood of existing risks may evolve.
It is crucial for organizations to regularly monitor and review their risk assessments to ensure they remain up-to-date and relevant. This proactive approach allows businesses to identify and address emerging risks, optimize risk management strategies, and enhance organizational resilience.
Risk analysis and assessment are critical processes for effective risk management and action items for the planning process.
Risk analysis and assessment also enable organizations to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and proactively manage risks in an ever-changing business landscape.
Probability and Impact of Potential Risks
Analyzing the probability and impact of potential risks is crucial in any risk management process. This step allows organizations to evaluate the likelihood of a risk occurring and its potential consequences on various aspects of their operations.
The probability of risk refers to the likelihood of it happening. This assessment is based on historical data, expert opinions, and internal assessments of key elements.
Expert opinions, such as those from risk managers or industry professionals, provide additional insights into the likelihood of risks. Internal assessments involve analyzing internal processes, controls, and vulnerabilities to gauge the potential for particular risks to materialize.
On the other hand, the impact of risk relates to the potential consequences and severity it can have on the organization. A risk’s impact can be assessed by evaluating its potential financial, operational, reputational, and strategic consequences.
Financial impact considers the potential monetary losses or gains resulting from the risk, while operational impact assesses the disruption it may cause to business processes and daily operations.
Reputational impact concerns the potential damage to the organization’s brand or image, while strategic impact considers the risk’s potential consequences on long-term goals and objectives.
Analyzing the probability and impact of potential risks is an iterative process. Businesses collect data, assess probabilities and impacts, develop risk response strategies, and then monitor and review the effectiveness of their actions.
This continuous evaluation allows organizations to refine their risk assessment and make data-driven decisions to adapt to changes in the operating environment.
The probability and impact of risks are often visualized using a risk matrix. A risk matrix is a graphical representation that categorizes risks based on their probability and impact ratings.
It provides a clear overview of the different levels of risks the organization faces and helps prioritize them for further analysis and response planning.
Considering the probability and impact of potential risks is essential for effective risk analysis and assessment.
This proactive approach to risk analysis allows organizations to develop comprehensive strategies to mitigate or respond to potential risks, enhancing their overall resilience and minimizing negative impacts on their operations.
Strategies for Managing Identified Risks
Organizations need to develop effective management strategies once potential risks have been identified and assessed. With the right approach, businesses can reduce risks’ likelihood and potential impact, protecting their operations and ensuring long-term success. Here are some strategies for managing identified risks:
1. Risk Mitigation:
This strategy focuses on reducing the likelihood of a risk occurring or minimizing its potential impact. It involves implementing preventive measures such as strengthening security systems, enhancing quality control processes, or implementing redundancy measures.
Organizations can proactively reduce the probability of risks manifesting by addressing vulnerabilities and weak points.
2. Risk Transfer:
In some cases, it may be beneficial to transfer the potential financial impact of a risk to another party.
This can be done by purchasing insurance policies or entering into contractual agreements with suppliers or partners that assume responsibility for certain risks. Transferring risks can help mitigate financial losses and support managing unforeseen events.
3. Risk Acceptance:
Not all risks can be eliminated or transferred. Organizations may accept certain risks and focus on developing contingency plans in such cases. By acknowledging the existence of risks and preparing for their occurrence, businesses can minimize the negative impact.
This strategy involves developing backup plans, establishing emergency response procedures, and ensuring business continuity despite unforeseen events. Cost control measures of the same.
4. Risk Avoidance:
In certain situations, the best strategy may be to avoid the risk altogether. This can be done by refraining from engaging in activities or ventures that expose the organization to significant risks.
Risk avoidance requires careful evaluation and analysis of the potential benefits versus the associated risks. Although it may limit potential opportunities, it can also prevent significant losses or damage to the organization.
5. Risk Monitoring and Response:
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance. Organizations should establish mechanisms for monitoring and reviewing identified risks regularly. This includes keeping a close eye on internal and external factors that may affect the likelihood or impact of risks.
Timely and proactive monitoring, organizations can quickly respond to emerging risks and implement appropriate corrective actions.
6. Collaborative Risk Management:
Managing risks can be complex, especially for larger organizations with multiple stakeholders. In identifying, assessing, and managing risks, collaborative risk management involves involving all relevant parties, such as employees, suppliers, customers, and industry partners.
Implementing these strategies requires a systematic and integrated approach to risk management. Organizations should establish clear processes, allocate resources, and designate accountability for managing identified risks.
Mitigating and Controlling Risks
Mitigating and controlling risks is essential to effective risk management for any organization.
One of the key approaches to risk management is risk mitigation. This strategy focuses on identifying potential risks and implementing measures to reduce their occurrence or severity. Organizations can achieve this by strengthening security systems, implementing quality control processes, or establishing redundancy measures.
Another important aspect of risk management is risk control. This involves implementing measures and procedures to control and minimize the impact of identified risks. Organizations can achieve this by developing contingency plans, establishing emergency response procedures, and ensuring business continuity despite unforeseen events.
Risk transfer is another strategy that organizations can use to mitigate risks. In some cases, it may be beneficial to transfer the potential financial impact of a risk to another party. This can be done by purchasing insurance policies or entering into contractual agreements with suppliers or partners that assume responsibility for certain risks.
Transferring risks can help mitigate financial losses and support managing unforeseen events.
However, not all risks can be eliminated or transferred. Organizations may accept certain risks and focus on developing effective response plans in such cases. Risk acceptance involves acknowledging the existence of risks and preparing for their occurrence.
This strategy requires developing backup plans, establishing emergency response procedures, and ensuring business continuity despite unforeseen events.
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance. Organizations should establish mechanisms for monitoring and reviewing identified risks regularly.
This includes keeping a close eye on internal and external factors that may affect the likelihood or impact of risks. With timely and proactive monitoring, organizations can quickly respond to emerging risks and implement appropriate corrective actions.
Lastly, collaborative risk management is crucial, particularly for larger organizations with multiple stakeholders. By involving all relevant parties, such as employees, suppliers, customers, and industry partners, in identifying, assessing, and managing risks, organizations can develop comprehensive strategies that address potential risks from all angles.
Establishing a Risk Mitigation Strategy
These risks can arise from both internal and external factors, from financial uncertainties to natural disasters. Organizations must have a robust risk mitigation strategy to safeguard their interests and ensure a smooth and resilient business operation.
A risk mitigation strategy is a proactive approach to identifying, assessing, and reducing organizational risks. It involves systematically analyzing potential risks, evaluating their potential impact, and developing appropriate measures to mitigate their occurrence or minimize their severity. Here are some key steps to establish an effective risk mitigation strategy:
1. Risk Identification: The first step in creating a risk mitigation strategy is to identify and understand the potential risks that your organization may face. This can be done by conducting a thorough risk assessment, analyzing historical data, consulting with subject matter experts, and reviewing industry best practices.
It is important to consider both internal risks, such as operational or financial risks, and external risks, such as market fluctuations or regulatory changes.
2. Risk Assessment: Once the risks have been identified, assessing their potential impact on your organization is essential. This involves evaluating the likelihood of occurrence and the potential negative consequences if the risks materialize.
3. Risk Mitigation Strategies: Based on the assessment, organizations can develop specific and targeted strategies to mitigate each identified risk. These strategies include implementing control measures, strengthening security systems, diversifying supply chains, or developing contingency plans.
The goal is to reduce the probability of risks manifesting and limit their potential impact on business operations.
4. Action Plans and Implementation: Organizations should develop detailed action plans to implement risk mitigation strategies effectively. These plans should outline specific actions, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing the identified mitigation measures.
It is crucial to involve relevant stakeholders, assign clear roles and responsibilities, and allocate all necessary resources for successful implementation.
5. Monitoring and Review: Risk mitigation is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance. Organizations should establish a robust monitoring and review mechanism to assess the effectiveness of the implemented mitigation measures.
Regular monitoring helps identify emerging risks, evaluate the success of the strategies, and make necessary adjustments if needed.
6. Collaborative Approach: Risk mitigation is not the responsibility of one individual or department alone. It requires a collaborative effort involving all stakeholders within the organization.
Implementing a Risk Mitigation Plan
A risk mitigation plan is a proactive strategy that aims to minimize the impact of potential risks through identification, assessment, and appropriate measures.
Conducting a thorough risk assessment is the first step in implementing a project risk management plan. This process involves identifying and analyzing potential risks that could negatively affect your organization by the chief risk officer.
The chief risk officer must consider internal risks, such as operational and financial vulnerabilities, and external risks, including market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and natural disasters.
Once the risks have been identified, the next step for the chief risk officer is to assess their potential impact on your organization. The chief risk officer can prioritize risk items based on severity by evaluating the likelihood of occurrence and the potential negative consequences. This assessment allows you to allocate resources and develop a roadmap for mitigation.
Based on the risk assessment, organizations can develop tailored risk mitigation strategies. These strategies involve implementing measures to reduce the probability of risks manifesting and minimizing their potential impact on daily operations.
These actions may include implementing control measures, enhancing security systems, diversifying supply chains, or developing contingency plans. The key is choosing strategies that effectively address the risks identified during the assessment phase.
To ensure the successful implementation of risk mitigation strategies, developing detailed action plans like project risk management plans is crucial.
These plans clearly outline specific actions, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing the identified mitigation measures. Involving relevant stakeholders and assigning clear roles and responsibilities are essential to holding individuals accountable and ensuring smooth execution.
Once the risk mitigation plan is in action, organizations must establish a robust monitoring and review mechanism. Regular monitoring helps gauge the effectiveness of the implemented mitigation measures and identify any emerging risks.
This ongoing evaluation enables organizations to adjust their mitigation strategies, ensuring they remain proactive and responsive to changing circumstances.
Implementing a risk mitigation plan should be a collaborative effort involving all stakeholders within the organization. The central risk team can use a risk assessment report to observe risk rating at various stages of the cybersecurity risk assessment.
Regular communication, training programs, and providing platforms for employees to report potential risks can promote a collaborative approach to risk management.
Implementing a risk mitigation plan is crucial for organizations aiming to safeguard their future. You can download a risk management plan template for use.
Monitoring the Risk Management Process
Monitoring the risk management process is a crucial step in ensuring the effectiveness of the implemented risk mitigation strategies. While the initial development and implementation of the plan are important, ongoing monitoring is necessary to identify any emerging risks and make necessary adjustments.
One of the main purposes of monitoring is to evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented mitigation measures. This evaluation allows for identifying any gaps or weaknesses in the plan, enabling organizations to take corrective actions as necessary.
Monitoring also helps identify new or emerging risks that may not have been initially considered. The business landscape is constantly evolving, and new risks can arise anytime.
Organizations can proactively identify and assess these risks by staying vigilant and continuously monitoring the external environment. This allows for the timely development and implementation of additional mitigation strategies to address them effectively.
Regulations and standards may change over time, and organizations must stay informed and update their risk management processes accordingly. Regular monitoring allows organizations to proactively identify gaps in compliance and take the necessary steps to rectify them, avoiding potential legal or reputational risks.
To effectively monitor the risk management process, organizations should establish a robust framework and metrics to measure progress and outcomes. This can include regular reporting on key risk indicators, conducting periodic risk assessments, and monitoring the implementation of action plans.
It is essential to involve all relevant stakeholders in the monitoring process, including risk owners, project teams, and senior management. Clear communication lines and documentation are crucial for effective monitoring and reporting.
Monitoring the risk management process should be an ongoing and iterative process. It is not a one-time activity but a continuous effort to assess and manage risks. Regular monitoring helps instill a culture of risk awareness and responsiveness within the organization, enabling it to navigate uncertainties confidently.
Communication and Reporting Risks
Effective communication and reporting are crucial components of a successful risk management process. Without clear and transparent communication, organizations run the risk of misinterpretation, misalignment, and, ultimately, ineffective risk mitigation strategies.
When it comes to managing risks, communication is essential at all levels of an organization. From frontline employees to senior management, everyone must be aware of the potential risks they may encounter daily.
This awareness allows for early identification and timely reporting of risks, which is vital for prompt action and mitigation.
Clear communication ensures that risk owners and stakeholders are on the same page regarding risk identification, assessment, and response plans. It enables a shared understanding of the potential impact and likelihood of occurrence of each risk, facilitating informed decision-making and prioritization of resources.
Reporting is a crucial element of risk management as it allows for the monitoring and tracking risks and the effectiveness of mitigation measures. Regular reporting ensures that risks are not forgotten or neglected and that action plans are implemented as intended.
It provides a platform for sharing risk-related information and progress updates with relevant stakeholders.
In reporting risks, it is important to provide accurate and comprehensive information. This includes describing the nature, potential impact, and likelihood of each risk and any existing mitigation strategies in place. It is also essential to communicate any changes or updates to risks as they occur, such as the emergence of new risks or a change in risk exposure.
Timeliness is crucial in reporting risks. Delayed or incomplete reporting can hinder the organization’s ability to take prompt action, resulting in a missed opportunity to prevent or minimize the negative consequences of a risk event.
Furthermore, effective communication and reporting extend beyond internal stakeholders. Organizations should also consider communicating with external parties, such as regulatory bodies, industry associations, or clients, when necessary. This external communication helps manage potential regulatory or reputational risks and promotes transparency and accountability.
Organizations should consider utilizing technology solutions to facilitate effective communication and reporting of risks. Risk management software tools can centralize risk data, automate reporting processes, and provide real-time updates and insights.
These tools enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of risk-related information, enabling better-informed decision-making and collaboration among stakeholders.
Conclusion
Communication and reporting are critical elements of a robust risk management process. Clear and transparent communication ensures that all relevant stakeholders effectively communicate, understand, and act upon risks.
Regular and timely reporting allows for monitoring and tracking risks and mitigation measures’ effectiveness.
Risk management is a systematic process that businesses and individuals undertake to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that could impact their operations or projects.
The organization’s risk management framework involves systematically analyzing and managing potential threats and opportunities to minimize negative impacts and maximize positive outcomes.
At its core, risk management is about recognizing and understanding the uncertainties that exist within various aspects of a business or project. It’s a formal process that can be applied to future projects and project level either using a reactive approach or a defined risk management solution.
Through proactively identifying and assessing potential risks, organizations can create a risk register/risk matrix that categorizes and prioritizes different types of risks, considering their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
There are several types/categories of risks that organizations need to consider, including financial risks, operational risks, strategic risks, and external risks. Financial risks pertain to potential losses or adverse impacts on financial resources, while operational risks involve problems with daily operations or the operating environment.
Strategic risks relate to uncertainties associated with the organization’s long-term goals and objectives, and external risks refer to threats arising from external factors such as legal or regulatory issues, market volatility, or natural disasters. This is one of the major risk of an organization.
The risk management process consists of several steps. First is risk identification, which involves brainstorming and gathering information to identify potential threats and opportunities. This is followed by risk assessment, where risks are analyzed and evaluated based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
Once risks are prioritized, especially in project risk management, organizations can develop a risk management plan outlining strategies and actions to mitigate or respond to identified risks. This plan may include contingency, risk mitigation, and risk response plans.
Effective risk management requires continuous monitoring and evaluation of potential threats and existing risks. This involves regular risk assessments and reviews to ensure that risk exposure is minimized and that risk management strategies are still relevant and effective.
Furthermore, risk management should not be seen as a one-time activity but rather an ongoing process that should be integrated into the organization’s daily operations.
Risk management is crucial in safeguarding businesses and projects from potential threats and ensuring their success.

Benefits of Risk Management
Risk management is an essential practice that benefits organizations across various industries. Here are some key benefits of risk management:
1. Minimizing potential risks:Conducting risk assessments and identifying potential threats, organizations can proactively take steps to minimize the impact of these risks. This helps in reducing financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Risk management enables businesses to develop contingency plans and implement preventive measures to mitigate potential risks. This prevents minor inconveniences.
2. Improved decision-making: A robust risk management process provides valuable insights into the potential risks and rewards associated with different business decisions. It allows organizations to make informed choices by considering different outcomes’ potential impacts and likelihoods.
This helps avoid unnecessary risks and make strategic decisions that align with the organization’s objectives.
3. Increased operational efficiency: Implementing risk management practices helps identify and address operational risks hindering efficiency and productivity.This results in improved performance and cost savings.
4. Enhanced stakeholder confidence: Stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees, value organizations that demonstrate strong risk management practices. Having a comprehensive risk management program in place instills confidence and trust in stakeholders, as it ensures that potential risks are being actively managed and mitigated.
This can lead to improved relationships, increased investments, and a stronger market position.
5. Compliance with regulations: Organizations must adhere to Many industries’ specific regulations and requirements. Risk management helps businesses stay compliant with these rules and regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and legal consequences.
6. Seizing opportunities: Risk management is not merely about mitigating negative risks but also identifying and exploiting positive risks or opportunities.
Identifying Risks
As such, it’s crucial for businesses to have a robust risk management strategy in place to identify and mitigate potential project risks. The first step in this process is to identify and assess risks effectively using either a risk assessment matrix or risk register.
Risk identification involves systematically uncovering, analyzing, and documenting potential risks affecting an organization’s objectives. This process should be comprehensive and cover all business areas, including financial, operational, strategic, and external factors.
There are several methods and tools that businesses can employ to identify risks. One commonly used approach is conducting risk assessments, which involve evaluating the likelihood and impact of specific risks.
This can be done through qualitative and quantitative analysis, considering factors such as the probability of occurrence, potential impact, and existing control measures.
Another effective method for identifying risks is by creating a risk register. A risk register is a centralized database that captures and categorizes all identified risks. It provides a comprehensive overview of the potential threats the organization faces, allowing for better visibility and management of risks.
The risk register also serves as a valuable reference tool for the ongoing monitoring and evaluation of risks. It records current risks i.e., market risk, through quantitative risk analysis and risk categories.
It’s important to note that risks can arise from both internal and external sources. Internal risks include operational inefficiencies, human errors, and system failures.
External risks, on the other hand, stem from factors outside the organization’s control, such as market volatility, regulatory changes, and natural disasters.
Organizations should involve multiple stakeholders to enhance the risk identification process, including subject matter experts and project teams. Different perspectives and expertise can help uncover risks that may be overlooked by individuals working in isolation.
Collaboration and effective communication across departments and levels of the organization is key to ensuring comprehensive risk identification.
Once risks are identified, they should be evaluated and prioritized based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This allows organizations to allocate resources and focus on the most critical risks that require immediate attention.
Risks with higher potential impact and likelihood may require more robust mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
Risk identification gives businesses the foundation to effectively navigate uncertainties, protect their interests, and seize opportunities for growth and success.
Risk Identification Process
The risk identification process is a crucial step in effective risk management. It involves identifying and understanding potential risks impacting an organization’s objectives, operations, and overall success.
The first step in the risk identification process is to gather information about the organization’s operations, industry, and external factors. Use of risk identification sessions.
This can be done through various methods, such as conducting interviews with key stakeholders, reviewing historical data, analyzing industry trends, and consulting subject matter experts. Following a risk assessment process.
The goal is to gather as much relevant information as possible to identify internal and external risks and risk factor of each risk.
Internal risks arise within the organization, such as operational inefficiencies, employee errors, or system failures. These risks can hinder productivity, impact customer satisfaction, and disrupt business operations.
To identify internal risks, organizations can review their processes, procedures, and systems and identify areas where vulnerabilities or potential weaknesses exist.
On the other hand, external risks stem from factors outside the organization’s control. These include market volatility, regulatory changes, natural disasters, cyber threats, and geopolitical events.
Organizations must stay updated on external factors that impact their industry and operations and regularly assess the potential risks these factors pose.
Once potential risks are identified, they should be documented and categorized in a risk register or a centralized database. This allows for easy reference and ongoing monitoring. Each risk should be clearly described, including its cause, potential impact, and likelihood of occurrence.
In the risk identification process, it’s essential to involve different stakeholders from various departments and levels of the organization. This ensures a comprehensive and diverse perspective on potential risks.
Collaboration and effective communication are key to uncovering risks that may be overlooked by individuals working in isolation. Organizations can leverage their expertise and insights to identify risks more effectively by involving different stakeholders.
Regular reviews and updates of the risk identification process are necessary to ensure its continued effectiveness. As the business landscape evolves, new risks can arise, and existing risks may change in nature or severity.
Therefore, organizations should regularly assess and update their risk identification process to stay proactive and prepared.
Through collaboration, regular reviews, and staying informed about internal and external factors, organizations can strengthen their risk identification process and be better equipped to navigate the uncertainties of the business landscape.

Types of Risks
Organizations can develop effective strategies to minimize their negative impact and capitalize on positive risks by identifying and categorizing them. Here are some common types of risks that organizations should be aware of depending on the risk culture and types of risk management in an organization :
1. Financial Risks: Risks associated with an organization’s financial health and stability. Examples include market volatility, economic downturns, currency fluctuations, and changes in interest rates. Financial risks can impact a company’s profitability, cash flow, and ability to meet financial obligations.
2. Operational Risks: These are risks related to the day-to-day operations of a business. They include ineffective processes, supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, and employee errors. Operational risks can lead to productivity losses, customer dissatisfaction, reputational damage, and financial losses. Security risks can be operational.
3. Strategic Risks: Strategic risks arise from the decisions and actions taken by an organization’s leadership or board of directors. These risks include entering new markets, launching new products, or significantly changing the business model.
Strategic risks can impact the organization’s long-term goals, competitive position, and sustainability.
4. Compliance Risks: Compliance risks are related to non-compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards. Organizations operating in highly regulated industries like healthcare or finance are particularly susceptible to compliance risks.
Failure to comply with legal and regulatory requirements can lead to legal consequences, fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
5. Reputational Risks: Reputational risks can arise from negative public perception, customer dissatisfaction, or damage to the organization’s brand image. Various factors, including product recalls, ethical misconduct, data breaches, or poor customer service, can cause these risks.
Reputational risks can have long-lasting effects on customer loyalty, investor confidence, and overall business success.
6. Environmental Risks: Environmental risks are associated with natural disasters, climate change, and environmental regulations. Organizations that operate in areas prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, or floods face additional risks.
Failure to manage environmental risks can lead to property damage, production disruptions, legal liabilities, and reputational harm.
7. Technology Risks: Organizations face various technology-related risks in today’s digital world. These include cyber threats, data breaches, IT system failures, and technological obsolescence. Technology risks can impact data security, customer privacy, business continuity, and operational efficiency.
Organizations must conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and prioritize the business risks most relevant to their industry, operations, and objectives.
Sources of Risks
Let’s take a closer look at some common sources of risks.
1. Internal Sources: Internal sources of risks originate from within the organization itself. These can include inadequate internal controls, poor management decisions, operational inefficiencies, employee errors or misconduct, and ineffective processes.
Use of failure mode and root cause analysis tools can identify sources of risk.
2. External Sources: External sources of risks arise from factors outside of the organization’s control. These can include changes in economic conditions, market volatility, political instability, regulatory changes, and industry disruptions. They might be competitive risks affecting strategy.
External risks can significantly impact a business’s operations, financial health, and sustainability. Organizations must monitor and stay informed about external factors affecting their operations.
3. Environmental Sources: Environmental sources of risks are related to natural disasters and climate change. Organizations operating in areas prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, or other natural calamities face additional risks.
These events can cause significant property damage, disrupt production processes, and lead to safety concerns for employees and customers.
Businesses need contingency plans to address environmental risks and ensure the safety and continuity of their operations. Thus mitigating safety risks.
4. Technological Sources: Organizations are exposed to various technological risks in today’s technology-driven world. These include cyber threats, data breaches, IT system failures, and technological obsolescence. With the increasing reliance on digital systems and data, businesses must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, backup and recovery systems and stay proactive in keeping up with technological advancements to manage these risks effectively.
5. Financial Sources: Financial sources of risks are associated with economic and financial factors that can impact an organization’s financial health and stability. These include market volatility, economic downturns, interest rate fluctuations, currency exchange rate changes, and inadequate financial planning or management.
Mitigating financial risks involves careful financial analysis, monitoring financial markets, and implementing risk management strategies to safeguard the organization’s financial well-being.
6. Human Sources: Human sources of risks are related to the actions or behavior of individuals within or outside the organization. These include employee errors, fraud, theft, labor disputes, and unethical behavior.
Managing human risks involves implementing effective recruitment and training processes, promoting a positive and ethical work culture, and establishing strong internal controls to prevent or detect potential risks.
A comprehensive risk management plan that addresses these sources can help businesses improve their resilience, protect their assets, maintain operational continuity, and ensure long-term success in today’s dynamic and unpredictable business environment.
Assessing and Analyzing Risks
Assessing and analyzing risks is a crucial step in the risk management process. It involves thoroughly evaluating an organization’s potential risks and analyzing their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. The tools can be qualitative risk analysis or qualitative risk assessment.
This allows businesses to prioritize and allocate resources effectively to mitigate and respond to risks ensuring high-quality risk management processes. Here are some key steps in assessing and analyzing risks.
1. Identify and categorize risks: The first step in assessing risks is to identify and categorize them based on their nature and potential impact. This can include operational risks, financial risks, technological risks, human risks, environmental risks, or any other specific categories that are relevant to the organization.
2. Gather data and information: Once risks are identified, gathering relevant data and information is crucial to assess and analyze them. This can include historical data, industry trends, market research, financial statements, internal reports, and external sources of information.
3. Evaluate likelihood and impact: Assessing risks involves evaluating their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact on the organization. Likelihood can be assessed by considering historical data, industry trends, expert opinions, and internal assessments.
The impact can be evaluated by considering each risk’s potential financial, operational, reputational, and strategic consequences. Businesses can prioritize risk management efforts by assigning a rating or score to the likelihood and impact of risks.
4. Conduct risk analysis: Risk analysis involves further analyzing the identified risks to understand their characteristics and potential consequences better. This can include conducting qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Qualitative analysis involves assessing risks based on their qualitative characteristics such as severity, urgency, and strategic importance. Quantitative analysis uses data and statistical models to calculate the financial impact or probability of risks occurring. This analysis helps businesses make data-driven decisions and allocate resources appropriately.
5. Prioritize risks and develop risk response plans: Once risks are assessed and analyzed, they can be prioritized based on their likelihood and impact. This helps organizations focus their resources on managing the most significant risks first.
Businesses can develop appropriate risk response strategies and action plans with this prioritized list. These may include risk mitigation strategies, risk transfer through insurance, risk acceptance, or contingency plans.
6. Monitor and review risks: Risk assessment and analysis are ongoing processes. As the business environment and internal factors change, new risks may emerge, and the impact and likelihood of existing risks may evolve.
It is crucial for organizations to regularly monitor and review their risk assessments to ensure they remain up-to-date and relevant.
Regular monitoring and reviewing of risk assessments are essential to ensure ongoing risk management effectiveness. With a robust business performance and analysis process, organizations, especially from the financial sector, can protect themselves from potential threats and seize opportunities in an ever-changing business landscape.
Risk Analysis and Assessment Processes
Risk analysis and assessment are integral components of any robust risk management process. They involve evaluating and understanding an organization’s potential risks, determining their likelihood and impact, and developing appropriate strategies to mitigate or respond to them.
The first step in the risk analysis and assessment is identifying and categorizing risks. This involves identifying potential risks that could impact various areas of the organization, such as operational, financial, technological, or environmental risks.
Categorizing risks helps businesses comprehensively understand the different types of risks they face, enabling them to develop targeted risk management strategies.
Once risks are identified, the next step is to gather relevant data and information. This includes collecting historical data, industry trends, market research, financial statements, and other sources of information.
After gathering data from business teams, evaluating each identified risk’s likelihood and potential impact is crucial. This assessment helps quantify the level of risk posed to the organization. Likelihood can be assessed by considering historical data, expert opinions, and internal assessments.
At the same time, the impact can be evaluated by considering the potential financial, operational, reputational, and strategic consequences.
The next step in the risk analysis and assessment process is thoroughly analyzing the identified risks. This involves further investigating the characteristics and potential consequences of each risk.
The qualitative analysis assesses risks based on their severity, urgency, and strategic importance. In contrast, quantitative analysis utilizes statistical models and data to calculate the financial impact or probability of risks occurring.
This analysis provides businesses valuable insights for making data-driven decisions and allocating resources appropriately.
Prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and impact enables organizations to focus on managing the most significant risks first. Businesses can develop appropriate risk response strategies and action plans with a well-defined, prioritized list.
These may include risk mitigation strategies, risk transfer through insurance, risk acceptance, or contingency plans.
Lastly, risk analysis and assessment are ongoing processes that require regular monitoring and review. As the business environment and internal factors change, new risks may emerge, while the impact and likelihood of existing risks may evolve.
It is crucial for organizations to regularly monitor and review their risk assessments to ensure they remain up-to-date and relevant. This proactive approach allows businesses to identify and address emerging risks, optimize risk management strategies, and enhance organizational resilience.
Risk analysis and assessment are critical processes for effective risk management and action items for the planning process.
Risk analysis and assessment also enable organizations to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and proactively manage risks in an ever-changing business landscape.
Probability and Impact of Potential Risks
Analyzing the probability and impact of potential risks is crucial in any risk management process. This step allows organizations to evaluate the likelihood of a risk occurring and its potential consequences on various aspects of their operations.
The probability of risk refers to the likelihood of it happening. This assessment is based on historical data, expert opinions, and internal assessments of key elements.
Expert opinions, such as those from risk managers or industry professionals, provide additional insights into the likelihood of risks. Internal assessments involve analyzing internal processes, controls, and vulnerabilities to gauge the potential for particular risks to materialize.
On the other hand, the impact of risk relates to the potential consequences and severity it can have on the organization. A risk’s impact can be assessed by evaluating its potential financial, operational, reputational, and strategic consequences.
Financial impact considers the potential monetary losses or gains resulting from the risk, while operational impact assesses the disruption it may cause to business processes and daily operations.
Reputational impact concerns the potential damage to the organization’s brand or image, while strategic impact considers the risk’s potential consequences on long-term goals and objectives.
Analyzing the probability and impact of potential risks is an iterative process. Businesses collect data, assess probabilities and impacts, develop risk response strategies, and then monitor and review the effectiveness of their actions.
This continuous evaluation allows organizations to refine their risk assessment and make data-driven decisions to adapt to changes in the operating environment.
The probability and impact of risks are often visualized using a risk matrix. A risk matrix is a graphical representation that categorizes risks based on their probability and impact ratings.
It provides a clear overview of the different levels of risks the organization faces and helps prioritize them for further analysis and response planning.
Considering the probability and impact of potential risks is essential for effective risk analysis and assessment.
This proactive approach to risk analysis allows organizations to develop comprehensive strategies to mitigate or respond to potential risks, enhancing their overall resilience and minimizing negative impacts on their operations.

Strategies for Managing Identified Risks
Organizations must develop effective management strategies once potential risks are identified and assessed. With the right approach, businesses can reduce risks’ likelihood and potential impact, protecting their operations and ensuring long-term success. Here are some strategies for managing identified risks:
1. Risk Mitigation:
This strategy focuses on reducing the likelihood of a risk occurring or minimizing its potential impact. It involves implementing preventive measures such as strengthening security systems, enhancing quality control processes, or implementing redundancy measures.
Organizations can proactively reduce the probability of risks manifesting by addressing vulnerabilities and weak points.
2. Risk Transfer:
In some cases, it may be beneficial to transfer the potential financial impact of a risk to another party.
This can be done by purchasing insurance policies or entering into contractual agreements with suppliers or partners that assume responsibility for certain risks. Transferring risks can help mitigate financial losses and support managing unforeseen events.
3. Risk Acceptance:
Not all risks can be eliminated or transferred. Organizations may accept certain risks and focus on developing contingency plans in such cases. By acknowledging the existence of risks and preparing for their occurrence, businesses can minimize the negative impact.
This strategy involves developing backup plans, establishing emergency response procedures, and ensuring business continuity despite unforeseen events. Cost control measures of the same.
4. Risk Avoidance:
In certain situations, the best strategy may be to avoid the risk altogether. This can be done by refraining from engaging in activities or ventures that expose the organization to significant risks.
Risk avoidance requires careful evaluation and analysis of the potential benefits versus the associated risks. Although it may limit potential opportunities, it can also prevent significant losses or damage to the organization.
5. Risk Monitoring and Response:
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance. Organizations should establish mechanisms for monitoring and reviewing identified risks regularly. This includes keeping a close eye on internal and external factors that may affect the likelihood or impact of risks.
Timely and proactive monitoring, organizations can quickly respond to emerging risks and implement appropriate corrective actions.
6. Collaborative Risk Management:
Managing risks can be complex, especially for larger organizations with multiple stakeholders. In identifying, assessing, and managing risks, collaborative risk management involves involving all relevant parties, such as employees, suppliers, customers, and industry partners.
Implementing these strategies requires a systematic and integrated approach to risk management. Organizations should establish clear processes, allocate resources, and designate accountability for managing identified risks.
Mitigating and Controlling Risks
Mitigating and controlling risks is essential to effective risk management for any organization.
One of the key approaches to risk management is risk mitigation. This strategy focuses on identifying potential risks and implementing measures to reduce their occurrence or severity. Organizations can achieve this by strengthening security systems, implementing quality control processes, or establishing redundancy measures.
Another important aspect of risk management is risk control. This involves implementing measures and procedures to control and minimize the impact of identified risks. Organizations can achieve this by developing contingency plans, establishing emergency response procedures, and ensuring business continuity despite unforeseen events.
Risk transfer is another strategy that organizations can use to mitigate risks. In some cases, it may be beneficial to transfer the potential financial impact of a risk to another party. This can be done by purchasing insurance policies or entering into contractual agreements with suppliers or partners that assume responsibility for certain risks.
Transferring risks can help mitigate financial losses and support managing unforeseen events.
However, not all risks can be eliminated or transferred. Organizations may accept certain risks and focus on developing effective response plans in such cases. Risk acceptance involves acknowledging the existence of risks and preparing for their occurrence.
This strategy requires developing backup plans, establishing emergency response procedures, and ensuring business continuity despite unforeseen events.
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance. Organizations should establish mechanisms for monitoring and reviewing identified risks regularly.
This includes keeping a close eye on internal and external factors that may affect the likelihood or impact of risks. With timely and proactive monitoring, organizations can quickly respond to emerging risks and implement appropriate corrective actions.
Lastly, collaborative risk management is crucial, particularly for larger organizations with multiple stakeholders. By involving all relevant parties, such as employees, suppliers, customers, and industry partners, in identifying, assessing, and managing risks, organizations can develop comprehensive strategies that address potential risks from all angles.
Establishing a Risk Mitigation Strategy
These risks can arise from internal and external factors, from financial uncertainties to natural disasters. Organizations must have a robust risk mitigation strategy to safeguard their interests and ensure a smooth and resilient business operation.
A risk mitigation strategy is a proactive approach to identifying, assessing, and reducing organizational risks. It involves systematically analyzing potential risks, evaluating their potential impact, and developing appropriate measures to mitigate their occurrence or minimize their severity. Here are some key steps to establish an effective risk mitigation strategy:
1. Risk Identification: The first step in creating a risk mitigation strategy is to identify and understand the potential risks that your organization may face. This can be done by conducting a thorough risk assessment, analyzing historical data, consulting with subject matter experts, and reviewing industry best practices.
It is important to consider both internal risks, such as operational or financial risks, and external risks, such as market fluctuations or regulatory changes.
2. Risk Assessment: Once the risks have been identified, assessing their potential impact on your organization is essential. This involves evaluating the likelihood of occurrence and the potential negative consequences if the risks materialize.
3. Risk Mitigation Strategies: Based on the assessment, organizations can develop specific and targeted strategies to mitigate each identified risk. These strategies include implementing control measures, strengthening security systems, diversifying supply chains, or developing contingency plans.
The goal is to reduce the probability of risks manifesting and limit their potential impact on business operations.
4. Action Plans and Implementation: Organizations should develop detailed action plans to implement risk mitigation strategies effectively. These plans should outline specific actions, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing the identified mitigation measures.
It is crucial to involve relevant stakeholders, assign clear roles and responsibilities, and allocate all necessary resources for successful implementation.
5. Monitoring and Review: Risk mitigation is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance. Organizations should establish a robust monitoring and review mechanism to assess the effectiveness of the implemented mitigation measures.
Regular monitoring helps identify emerging risks, evaluate the success of the strategies, and make necessary adjustments if needed.
6. Collaborative Approach: Risk mitigation is not the responsibility of one individual or department alone. It requires a collaborative effort involving all stakeholders within the organization.
Implementing a Risk Mitigation Plan
A risk mitigation plan is a proactive strategy that aims to minimize the impact of potential risks through identification, assessment, and appropriate measures.
Conducting a thorough risk assessment is the first step in implementing a project risk management plan. This process involves identifying and analyzing potential risks that could negatively affect your organization by the chief risk officer.
The chief risk officer must consider internal risks, such as operational and financial vulnerabilities, and external risks, including market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and natural disasters.
Once the risks have been identified, the next step for the chief risk officer is to assess their potential impact on your organization. The chief risk officer can prioritize risk items based on severity by evaluating the likelihood of occurrence and the potential negative consequences. This assessment allows you to allocate resources and develop a roadmap for mitigation.
Based on the risk assessment, organizations can develop tailored risk mitigation strategies. These strategies involve implementing measures to reduce the probability of risks manifesting and minimizing their potential impact on daily operations.
These actions may include implementing control measures, enhancing security systems, diversifying supply chains, or developing contingency plans. The key is choosing strategies that effectively address the risks identified during the assessment phase.
Developing detailed action plans like project risk management plans is crucial to ensure the successful implementation of risk mitigation strategies.
These plans clearly outline specific actions, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing the identified mitigation measures. Involving relevant stakeholders and assigning clear roles and responsibilities are essential to holding individuals accountable and ensuring smooth execution.
Once the risk mitigation plan is in action, organizations must establish a robust monitoring and review mechanism. Regular monitoring helps gauge the effectiveness of the implemented mitigation measures and identify any emerging risks.
This ongoing evaluation enables organizations to adjust their mitigation strategies, ensuring they remain proactive and responsive to changing circumstances.
Implementing a risk mitigation plan should be a collaborative effort involving all stakeholders within the organization. The central risk team can use a risk assessment report to observe risk rating at various stages of the cybersecurity risk assessment.
Regular communication, training programs, and providing platforms for employees to report potential risks can promote a collaborative approach to risk management.
Implementing a risk mitigation plan is crucial for organizations aiming to safeguard their future. You can download a risk management plan template for use.
Monitoring the Risk Management Process
Monitoring the risk management process is a crucial step in ensuring the effectiveness of the implemented risk mitigation strategies. While the initial development and implementation of the plan are important, ongoing monitoring is necessary to identify any emerging risks and make necessary adjustments.
One of the main purposes of monitoring is to evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented mitigation measures. This evaluation allows for identifying any gaps or weaknesses in the plan, enabling organizations to take corrective actions as necessary.
Monitoring also helps identify new or emerging risks that may not have been initially considered. The business landscape is constantly evolving, and new risks can arise anytime.
Organizations can proactively identify and assess these risks by constantly monitoring the external environment. This allows for the timely development and implementation of additional mitigation strategies to address them effectively.
Regulations and standards may change over time, and organizations must stay informed and update their risk management processes accordingly. Regular monitoring allows organizations to proactively identify gaps in compliance and take the necessary steps to rectify them, avoiding potential legal or reputational risks.
To effectively monitor the risk management process, organizations should establish a robust framework and metrics to measure progress and outcomes. This can include regular reporting on key risk indicators, conducting periodic risk assessments, and monitoring the implementation of action plans.
It is essential to involve all relevant stakeholders in the monitoring process, including risk owners, project teams, and senior management. Clear communication lines and documentation are crucial for effective monitoring and reporting.
Monitoring the risk management process should be an ongoing and iterative process. It is not a one-time activity but a continuous effort to assess and manage risks. Regular monitoring helps instill a culture of risk awareness and responsiveness within the organization, enabling it to navigate uncertainties confidently.
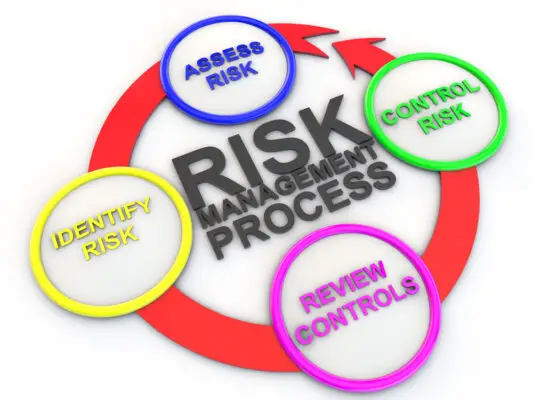
Communication and Reporting Risks
Effective communication and reporting are crucial components of a successful risk management process. Without clear and transparent communication, organizations run the risk of misinterpretation, misalignment, and, ultimately, ineffective risk mitigation strategies.
When it comes to managing risks, communication is essential at all levels of an organization. From frontline employees to senior management, everyone must be aware of the potential risks they may encounter daily.
This awareness allows for early identification and timely reporting of risks, which is vital for prompt action and mitigation.
Clear communication ensures that risk owners and stakeholders are on the same page regarding risk identification, assessment, and response plans. It enables a shared understanding of the potential impact and likelihood of occurrence of each risk, facilitating informed decision-making and prioritization of resources.
Reporting is a crucial element of risk management as it allows for the monitoring and tracking risks and the effectiveness of mitigation measures. Regular reporting ensures that risks are not forgotten or neglected and that action plans are implemented as intended.
It provides a platform for sharing risk-related information and progress updates with relevant stakeholders.
In reporting risks, it is important to provide accurate and comprehensive information. This includes describing each risk’s nature, potential impact, and likelihood and any existing mitigation strategies in place. It is also essential to communicate any changes or updates to risks as they occur, such as the emergence of new risks or a change in risk exposure.
Timeliness is crucial in reporting risks. Delayed or incomplete reporting can hinder the organization’s ability to take prompt action, resulting in a missed opportunity to prevent or minimize the negative consequences of a risk event.
Furthermore, effective communication and reporting extend beyond internal stakeholders. Organizations should also consider communicating with external parties, such as regulatory bodies, industry associations, or clients, when necessary. This external communication helps manage potential regulatory or reputational risks and promotes transparency and accountability.
Organizations should consider utilizing technology solutions to facilitate effective communication and reporting of risks. Risk management software tools can centralize risk data, automate reporting processes, and provide real-time updates and insights.
These tools enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of risk-related information, enabling better-informed decision-making and collaboration among stakeholders.
Conclusion
Communication and reporting are critical elements of a robust risk management process. Clear and transparent communication ensures that all relevant stakeholders effectively communicate, understand, and act upon risks.
Regular and timely reporting allows for monitoring and tracking risks and mitigation measures’ effectiveness.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

