NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators are essential metrics used to assess and monitor the effectiveness of cybersecurity strategies.
These indicators enable organizations to identify and evaluate potential risks and vulnerabilities, allowing them to make informed decisions to enhance their security stance.
They encompass various aspects, such as the number of detected and resolved security incidents, the percentage of incidents mitigated through proactive measures, and the level of employee security awareness.
Organizations can gain valuable insights into their cybersecurity posture by consistently tracking and analyzing these indicators, enabling them to take appropriate measures to mitigate risks.
This article aims to comprehensively understand NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators, highlighting their significance in helping organizations protect their sensitive data and systems from cyber threats.
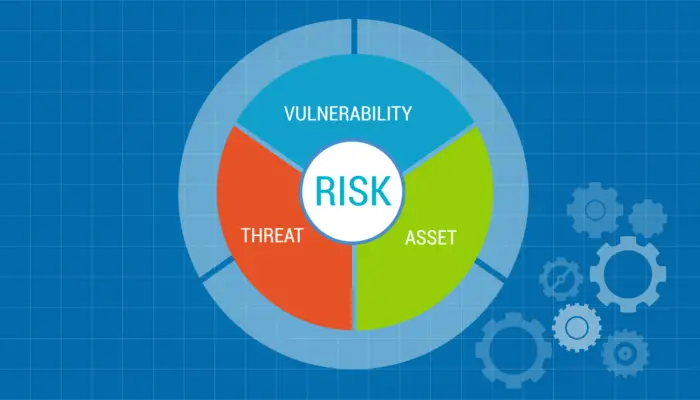
What are NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators?
NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) provide organizations with valuable insights into their cybersecurity risk posture.
Monitoring and analyzing these indicators can help organizations identify potential risks and vulnerabilities.
This allows them to make informed decisions and appropriately mitigate these risks.
Using NIST Cybersecurity KRIs can improve an organization’s security posture and enhance its overall cybersecurity efforts.

Benefits of Using NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators
Using NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators provides organizations with valuable insights into their cybersecurity risk posture and aids in proactive decision-making. Organizations can obtain multiple benefits by utilizing key risk indicators.
- Improved risk management program: NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators help organizations identify potential risks and vulnerabilities, allowing them to take proactive measures to mitigate them. This leads to a more effective risk management program.
- Enhanced decision-making: By monitoring key risk indicators, organizations can make informed decisions about their cybersecurity strategies. They can identify areas that require improvement and allocate resources accordingly.
- Better understanding of risk profile: NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators provide insights into an organization’s risk profile. They help organizations assess the effectiveness of their security measures and identify areas that need attention.
Understanding the Different Types of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators
It is important to consider various aspects of security controls and processes to understand the different types of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators.
Administrative controls and procedures involve policies and procedures that govern the organization’s security practices.
Technical security controls and processes encompass the technologies and tools that protect the organization’s systems and data.
Physical security controls and processes involve measures to protect physical assets and facilities.
Logical access control systems ensure proper authorization and authentication for accessing systems and data.
Lastly, network security devices and policies focus on securing the organization’s network infrastructure.
Administrative Controls & Procedures
Understanding the different types of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators involves comprehensively examining administrative controls and procedures.
Administrative controls and procedures are essential to cybersecurity risk management practices within organizations. They provide a framework for managing potential security risks and protecting sensitive information.
It’s important to note that administrative controls and procedures play a crucial role in measuring an organization’s overall risk exposure and security performance with regard to NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators.
Here are three important points to consider regarding administrative controls and procedures in the context of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators:
- Administrative KRIs help assess the effectiveness of an organization’s incident response plan and its ability to handle security incidents.
- Monitoring system access and assessing compliance with security best practices are examples of administrative KRIs that can provide valuable insights into an organization’s security posture.
- Good administrative KRIs should be closely aligned with the organization’s risk management procedures and governance/control frameworks, ensuring that they are relevant and effective in measuring cyber risk.
Technical Security Controls & Processes
Technical security controls and processes are critical in measuring and evaluating different types of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators (KRIs).
These indicators help organizations assess the potential risks and vulnerabilities in their information security systems and processes.
Organizations can mitigate potential risks by monitoring technical security controls and processes.
Some key technical security risk indicators include the identification of unpatched and misconfigured systems, the presence of malware, and the assessment of third-party risks.
Additionally, metrics related to system access and security, monitoring and response effectiveness, and vulnerability management are essential in understanding the effectiveness of technical security controls and processes.
These metrics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and vendor risk assessments contribute to a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s security posture and ability to protect sensitive information and reduce the attack surface.
Physical Security Controls & Processes
Organizations can gain valuable insights into potential vulnerabilities and risk mitigation by monitoring physical security controls and processes as part of understanding the different types of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators.
Physical security controls are crucial in protecting an organization’s assets, including its data, facilities, and personnel.
Organizations can improve their overall security posture by tracking physical security KRIs to ensure business operations integrity.
Key considerations for physical security controls and processes include:
- Access controls: Monitor access control systems and ensure that only authorized individuals can enter restricted areas.
- Surveillance systems: Implementing and monitoring surveillance systems to detect and deter potential security risks.
- Perimeter security: Implementing fences, gates, and security personnel measures to protect the organization’s physical assets.
Organizations can enhance their cyber defense capabilities by incorporating physical security controls and processes into their cybersecurity framework, thereby mitigating the risk of security breaches.
This is particularly crucial for industries such as financial services, where protecting sensitive data is paramount.
Additionally, it is important to align physical security controls with security policies and third-party risk management to ensure a comprehensive approach to risk mitigation within an organization.
Logical Access Control Systems
Logical access control systems are essential components of cybersecurity frameworks, allowing organisations to restrict unauthorized access to their computer systems and networks.
These systems involve monitoring system access metrics and measuring access control effectiveness, which are key risk indicators (KRIs) for logical access control systems.
Organizations can evaluate access control effectiveness and detect unauthorized attempts by monitoring Key Risk Indicators (KRIs).
This helps in improving system access security and enhancing monitoring and response capabilities.
Moreover, evaluating incident detection and response time is crucial in maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture.
Security professionals and risk managers can utilize cybersecurity metrics and security tools to ensure data security and manage risk posture effectively.
It is important to consider external factors and continuously update and improve logical access control systems to mitigate potential risks.
In today’s dynamic business environment, organizations must align their risk management process with strategic goals to safeguard their business objectives.
Each business unit plays a crucial role in this framework, guided by senior management, who ensure that the overall risk management strategy is coherent and effective.
The cybersecurity risk management program is central to this strategy, a key component in protecting against threats such as malware infections.
Understanding risk trends and the types of risks that can impact an organization over a certain period of time is essential. This is where asset management and action plans become pivotal.
The risk management team, often closely coordinating with the supply chain risk management unit, develops these plans to mitigate specific risks identified through ongoing risk monitoring.
Risk identification is a continuous process of adapting to the evolving risk landscape. It’s not just about security governance; it’s also about understanding how these risks can impact the company’s financial performance.
An effective approach to risk management encompasses both these aspects, ensuring that the organization remains resilient and agile in the face of changing threats and opportunities.
Network Security Devices & Policies
The effectiveness of network security devices and policies can be examined through understanding the different types of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators.
These indicators provide valuable insights into the overall security posture of an organization and help identify potential vulnerabilities and risks.
When it comes to network security devices and policies, there are several key risk indicators to consider:
- Mean time to detect: This metric measures the average time to detect a security incident. A shorter mean time to detect indicates a more effective network security system.
- Average cost of cyber attacks: This indicator measures the financial impact of cyber attacks on an organization. A higher average cost suggests that network security devices and policies may need improvement.
- Number of critical vulnerabilities: This metric reflects the vulnerabilities identified in network security devices. A higher number indicates a higher potential impact of cyber attacks and the need for stronger data protection measures.
User Authentication & Authorization System
Understanding the different types of NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators for User Authentication & Authorization Systems is essential for effective risk management in organizations.
The user authentication & authorization system plays a critical role in data management and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators related to this system focus on monitoring system access, evaluating access control effectiveness, and identifying unauthorized access attempts.
These indicators provide insights into user behavior, the security of employee credentials, and the overall risk to the organization.
Organizations can identify vulnerabilities by incorporating cybersecurity metrics into risk management procedures, enabling them to take proactive measures to strengthen their user authentication and authorization systems.
This helps security teams to secure access points and improve enterprise risk management.

How to Identify and Monitor NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators?
Organizations need to establish a baseline for their security posture to identify and monitor NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators (KRIs).
This involves analyzing the existing environment for potential risks and vulnerabilities.
Once the baseline is established, organizations can implement strategies and tools to monitor the identified KRIs and track their performance over time.
This enables them to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Establishing a Baseline for Your Security Posture
A crucial step in establishing a baseline for your security posture is identifying and monitoring NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators.
These cybersecurity metrics are essential for organizations to manage and prevent data breaches effectively.
Organizations can identify areas for security improvement by analyzing metrics. Some critical metrics used to monitor security posture include:
- The number of security incidents detected and resolved.
- The percentage of incidents prevented through proactive measures.
- The response times for cyber incident management.
Incorporating these metrics into data management and risk assessment processes can help organizations make informed decisions and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
Analyzing Your Existing Environment for Potential Risks
In examining your existing environment for potential risks, it is essential to identify and monitor NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) to ensure a proactive and effective approach to cybersecurity.
Analyzing your existing environment involves assessing the current state of your cybersecurity posture and identifying any potential risks or vulnerabilities.
Monitoring key risk indicators such as the number of detected and resolved security incidents can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your cybersecurity measures.
This monitoring process allows you to identify security issues, manage risk, and make informed decisions to enhance your data management and business continuity.
Implementing Strategies and Tools to Monitor Key Risk Indicators
How can organizations effectively identify and monitor NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators to enhance their cybersecurity efforts?
Implementing strategies and tools to monitor key risk indicators is crucial in identifying potential cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
Organizations can proactively manage cybersecurity risk by allocating resources and making informed decisions.
Here are three key points to consider when monitoring NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators:
- Utilize appropriate tools: Organizations should leverage cybersecurity tools and technologies to effectively collect and analyze key risk indicator data. These tools can provide real-time insights into the organization’s cybersecurity performance.
- Establish clear data management processes: Developing robust data management processes is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of key risk indicator data. This includes data gathering, analysis, and reporting procedures.
- Align with business goals: Key risk indicators should be closely linked to the organization’s business goals and risk management procedures. By aligning the indicators with the business, organizations can gain valuable insights into their cybersecurity posture and make strategic decisions to enhance their security.
Common Challenges in Monitoring NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators
Monitoring NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators presents several challenges for organizations. These challenges include difficulty in identifying relevant KRIs, data gathering and analysis challenges, lack of predictive KRIs, resource-intensive monitoring processes, and maintaining consistency and comparability over time.
| Challenges | Description |
|---|---|
| Difficulty in identifying relevant KRIs | Organizations struggle to identify the most pertinent key risk indicators that align with their risk management procedures and governance frameworks. |
| Data gathering and analysis challenges | Establishing an effective system for monitoring and analyzing key risk indicator data can be complex, requiring a robust process for comparison against risk appetites to identify warning signals. |
| Lack of predictive KRIs | It is challenging to establish key risk indicators that can predict and identify potential risks early, which is crucial for proactive risk management. |
| Resource-intensive monitoring processes | Monitoring key risk indicators may require significant resources, including technology and personnel, for efficient data collection, analysis, reporting, and cost-effectiveness. |
| Consistency and comparability over time | Ensuring that key risk indicators remain consistent and comparable over time is challenging, requiring ongoing attention to maintain accuracy and relevance in measuring the effectiveness of risk management. |
Overcoming these challenges is essential to effectively monitor NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators and inform organizations about potential cybersecurity risks.
Best Practices for Managing NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators
To effectively manage NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators, organizations should implement best practices that enhance their ability to identify and mitigate potential cybersecurity risks.
These best practices provide a structured approach to managing KRIs and help reduce the overall risk exposure.
Some of the best practices for managing NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators include:
- Understanding the potential risks: Organizations should clearly understand the risks they face and the potential impact on their business. This includes identifying critical assets, evaluating vulnerabilities, and assessing the impact of a breach on the supply chain.
- Incorporating a holistic approach to managing cybersecurity: It is important to involve the entire organization in managing cybersecurity. This includes establishing clear roles and responsibilities for the security team, promoting a culture of security awareness among employees, and regularly reviewing and updating security policies and procedures.
- Collecting and analyzing relevant data points: Organizations should collect and analyze relevant data points to measure the effectiveness of their cybersecurity efforts. This includes tracking key metrics such as the number of security incidents detected and resolved, the percentage of incidents prevented through proactive measures, and the level of employee security awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Key Risk Indicators for Cyber Security?
Key risk indicators for cybersecurity are specific events that negatively impact an organization’s goals and provide early warning signals for risk assessment and prevention.
They include cyber incidents, exposed data records, incident response times, and technology, operational, financial, and human resources indicators.
What Is the NIST Definition of Risk in Cybersecurity?
The NIST definition of risk in cybersecurity refers to potential events or situations that can have a negative impact on an organization’s operations and objectives.
It emphasizes understanding risk exposures and establishing key risk indicators (KRIs) to manage and prevent risks effectively.
What Are the Key Points of NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides organizations with a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks.
It includes key risk indicators (KRIs) that measure and track the effectiveness of cybersecurity efforts, allowing organizations to make informed decisions and improve their security posture.
What Are the 5 Factors of Nist?
NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators are metrics that organizations use to measure and track the effectiveness of their cybersecurity efforts.
These indicators help identify and assess potential risks and vulnerabilities, enabling informed decision-making and security improvement.
Conclusion
NIST Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators provide organizations with valuable insights into their cybersecurity posture and help them make informed decisions to enhance their security stance.
These indicators include security incident detection and resolution, proactive measures taken, and employee security awareness.
Organizations can mitigate risks and protect their sensitive data and systems from cyber threats by consistently tracking and analysing these indicators.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

