Operational risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that can adversely affect the ability of a financial institution to achieve its objectives.
It is a broad concept that encompasses all risks that arise from the various activities and processes carried out by an institution to provide services to its customers. Operational risk in banks aims to protect the institution’s assets, reputation, and earnings.
Operational risk management is critical for the financial industry because it helps them identify and mitigate risks that could negatively impact their business. For example, in 2007-2008, the global financial crisis was largely caused by operational risk management failings at major banks.
Operational risk management is a relatively new field. Still, it has become increasingly important in recent years due to the increasing complexity of financial institutions and the global interconnectedness of markets. Best strategy for corporate risk management is to align operations risk management with business operations.
Many different types of operational risks can affect financial institutions. Some of the most common operational risk types include:
- Credit risk is the risk that a borrower will default on a loan or other obligation. Credit risk can also refer to the risk of loss arising from changes in the value of collateral or security deposits.
- Market risk is the risk of loss due to changes in market prices, interest rates, or exchange rates.
- Liquidity risk: This is the risk that an institution will be unable to meet its obligations as they come due because it does not have enough cash or other liquid assets on hand.
- Compliance risk: is the risk of incurring fines or other penalties for violating laws or regulations.
- Reputational risk: This is the risk of damage to an institution’s reputation due to adverse publicity or other negative events.
- Legal is the risk of losing a legal case or incurring damages due to legal action against an institution.
Operational risk in banking operations has no recent significance. But it was elevated recently into a specific risk category and impacted the risk profiles of financial institutions. This rise largely comes from the BBS Basel Committees.
In a document about operational risk, the BCBS defined this risk as the loss caused by inadequately functioning internal processes. Since 2008’s global financial crisis, many financial firms have developed sophisticated controls over risk and liquidity. Unfortunately, these companies have not effectively mastered operational risk yet.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) traditionally focuses on ensuring an optimal balance between risk and reward. Occasionally a corporation accepts higher risks to gain the opportunity of growing faster, and at different points, the focus shifts to managing risks with slower growth.
Over the past twenty-five years, the method of analyzing internal control systems has increased in standard form. Standardization came as government agencies and investors demanded greater insight into risks and a more unified approach to controlling them.
Making many banks create an operational risk management function in their operations. The functions are solely headed by operational risk managers who implement an operational risk management program.
The implementation of the internal controls and integrated framework in 1992 and the Sarbanes-Oxley Compliance Act of 2002 have increased scrutiny for organizations to have a robust operational security management system.
In this post, we will explore operational risk management and discuss some key considerations in its implementation. We will also look at real-world examples of how operational risks have impacted organizations.

What is Operational Risk Management’s primary objective?
The primary objective of Operational Risk Management is to prevent loss and minimize the impact of unforeseen events. This includes assessing potential risks, implementing controls and procedures to address them, and monitoring their effectiveness.
It is not just about preventing financial losses but also ensuring an organisation’s or business’s smooth operation. By identifying and addressing potential problems before they occur, Operational Risk Management enables a company to operate more efficiently and effectively. It also helps to protect against reputational damage from incidents such as data breaches, human error or regulatory non-compliance.
According to the name, operating risk managers aim to reduce the risks incurred in their daily operations. Operating Risk Management focuses on business activities and excludes the risk areas of strategic risks and financial risks.
Other risk management disciplines, like ERM, emphasize optimizing risk appetite and maximizing potential rewards. ORM processes focus primarily on controls and the elimination of risk. The ORM framework begins with the risk assessment.
Regulations
The risk associated with not complying with regulations is present almost everywhere. Some industries have higher regulation levels than other industries. However, the entire regulation consists of operationalizing internal controls. Rules have become increasingly complicated in the past decade, and penalties have increased.
Understanding risk sources will assist in determining who manages operational risk. Enterprise Risk Management and operational risk management address risk from various perspectives. Some organizations are now working on IRM as their primary approach; the purpose is to consolidate these disciplines into one single discipline if necessary.
Technology
Technology risks include hardware, computer hardware, data security, and privacy. Technology risk varies from company to company. Hardware constraints might inhibit productivity, especially when working remotely.
The software can also reduce productivity if the application increases but staff lack skills in the field or cannot learn. It is important to note that software impacts how customers interact with a company.
The threat to external data is posed by hackers who try to hack into computers to steal information. It could cause the leakage of customers’ data and privacy concerns for consumers.
People
The people categories include employee, customer, vendor and other stakeholders. Employee risk is human errors or intentional wrongdoing, like fraud. Risk factors include policy breaches, inadequate instruction, lack of training, discipline or fraud.
Outside a business, there may be several operational risks involving human resources. Employees, consumers and vendors have to take heightened risks on social media. Controlling personnel risks and assessing the impact is a broad covered area.

Operational Risk vs. Financial Risk: What’s the Difference?
Operational risk refers to the possibility of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or policies. In contrast, financial risk relates to the potential loss stemming from financial market changes.
To manage these risks, companies often use a combination of insurance coverage and control procedures. While both types of risk can significantly impact a company’s bottom line, it’s important to note that they are not interchangeable.
For example, a company may invest heavily in data security measures to mitigate operational risk while at the same time monitoring fluctuations in interest rates to minimize potential financial losses.
Incorrectly addressing operational risk may increase the financial risk for a company, but the two groups are considered different. Financial risks refer to companies that may fail to comply with their financial obligations.
For example, to pay off their debt, meet weekly payroll obligations if needed and maintain adequate investment in the business infrastructure. Therefore, financial risk relates directly to the quality of investment decisions and financial strategies. Credit and market risk can also be categorized as financial risk types.
Operational Risks versus Strategic Risks
Operational risks are day-to-day concerns that can affect the smooth running of a business, such as supply chain disruptions or IT failures. On the other hand, strategic risks refer to broader issues that could impact a company’s long-term success, like changes in the market or shifts in public opinion.
As with any risk management, communication and flexibility are key factors in effectively navigating operational and strategic risks. This can help a business weather challenges and ultimately become stronger on the other side.
In banking operations, the risk is frequently confused with strategic risk. Both concepts are distinct but should be handled separately. Strategic risk arises whenever the original strategic plan fails to deliver the expected results and impacts financial development.
This risk is caused by technological changes, new competitors, or changes in consumer demand. Different kinds of operational risks are also triggered primarily through internal procedures that have failed in an attempt to prevent employees from using them.
How does Operational Risk Management work?
Operational risk management is identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks inherent in business operations. This involves analyzing data, processes, and past events to identify potential risks and their impact on the organization.
Once identified, measures can be taken to reduce or eliminate these risks. This may include implementing new policies or procedures, conducting regular training, or investing in new technologies. The ultimate goal of operational risk management is to ensure efficient and effective operations while minimizing financial loss or damage to the company’s reputation. It is an ongoing process that should be regularly revisited and adjusted as necessary to adapt to changing circumstances and mitigate emerging risks.
Whenever dealing with operational risks, the organization must be aware of the scope of its objectives. Since operating risk is omnipresent, the goal is to reduce and control the risk, whether internal or external events. How to carryout operational risk management is same as ERM process.
Operating Risk Management helps reduce risks in operations by identifying risks, measuring risk and mitigation, and evaluating the risk while also deciding who manages operation risk.
Monitoring and reporting
Risks can be monitored through continuous risk analysis to determine changes in the future. Whenever a change occurs, risks are referred directly to the management team for management to improve decisions.
Measurement and mitigation
The risk assessment focuses on a consistent scale that allows risk classification of various risk categories. It also measures costs associated with managing exposure risks.

Operational Risk Management Strategies for Banks and Financial institutions
Operational risk management has proven useful in organizations with high security. The organisation is required, therefore, to develop a robust operational risk control program using a series of methods:-
Develop key risk indicators
Identifying key risk indicators is useful in alerting the leadership about possible problems. Real-time testing of operating process control measures and risk metrics may help identify factors influencing risk, like spikes in transaction volume or areas operating under tension. Organizations can utilize these risk indicators to identify, classify, and mitigate risk.
Training for employees
For an efficient operational risk management plan, employees must be notified of any risks. This is especially important if a business department plans to do something new, like changing customer services, implementing new product offerings and adopting business process outsourcing.
Combine cyber security with operational risk modeling
Operational risks are intrinsically linked to the risks associated with cyber-attacks. Combining cybersecurity best practices and operational risk models will assist in preparing and managing operational risks.
Evaluate the Risk Profile
Financial companies must analyze their risk profile to improve data privacy and security. A business process assessment must determine its resilience in the event of a disaster or other situation that arises.
How do banks identify operational risks?
Operational risks will be posed due to overlap between humans, processes and technologies within banks, especially human errors. This can be a good approach in terms of identifying operational risks.
Identify critical dependencies
Bank employees may see operational risks daily without realizing the risk is disguised as a critical dependency. Critical dependency is the work and process required in certain ways. Financial institutions may face delays, breaches, or other operational risks if this is not done. This step is essential to ensure effective operational risk management.
Risk-based audit
Identifying and measuring potential operational risks may be useful for banks as it helps evaluate their current risk management structure. Upon identification, potential risks are positioned onto a risk assessment matrix and can then be determined as their priority.
Brainstorm
Gather stakeholders to brainstorm operational risks and re-evaluate the company’s future plans. This session is best left to determine, and leaders must prepare primarily to identify and mitigate possible risks.
Top operational risks in banking and financial services
New business models, complicated value chains, regulatory issues and increasing digitization have recently prompted unknown operational risks for banks. This includes:
Internal and external fraud
Approximately 50 – 60 per cent of digital financial services firms experienced increased fraud. Operating risks of internal fraud include asset misappropriation fraud and forgery, tax violations, bribe fraud and other theft. Fraud attributed to external entities consists of checks, theft and several unauthorized activities.
Cybersecurity Risks
Although banks are expanding security measures to prevent cyberattacks, cyber risk has recently increased, affecting operational continuity, among these threats being ransomware and phishing. Especially after an epidemic where threats exploit weak security systems of firms to commit serious – and even profitable – cyber attacks.
Business disruptions and system failures
Hardware, software, and power failures may affect a financial organization and result in financial loss. Additional risk events may also cause damage to financial organizations, enhance their reputation, or cause legal difficulties.
Third-party risks
Financial institutions increasingly rely on third-party services that require identification, evaluation, and control of third-party risks throughout their relationship with them. With a rise in data storage and digitalization, banks must be careful about third parties dealing with them.
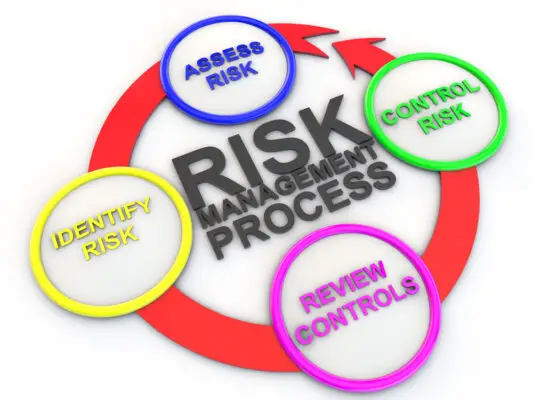
How many steps are involved in ORM?
Operational risk management is commonly applied as 5 step process. Each step must be followed as part of best business practices.
Identification of risks
It’s important to identify and control risk. Risk detection begins by identifying organizational objectives. Risks are situations that prevent organizations from reaching their target.
Risk assessment
Risk assessments provide a systematic means to assess risks on likelihood and effect. A risk assessment results in a priority list of identified potential risks. The risk assessment process might be the same for internal auditors.
Risk mitigation
The risk mitigation step is selecting the right way to control particular risks. In operational risk management, four possibilities can help mitigate risk: removal, acceptance, or control. Most transfer processes are carried out outsourced and insured. In outsourcing, a company has no control over risks. The insurers responsible will be able to transfer a certain amount of risk to the insurance company. One example of transferring risks in cloud computing services.
Control. Implementation
Once a risk reduction decision is made, it’s time to implement the plan. The controls have been created purely to protect against risk. Controls, rationale, objectives and activities should clearly explain to facilitate communication and execution. Controls are implemented to focus on preventative actions of policies and procedures.
Monitoring
It’s necessary to monitor the control because it is sometimes done by someone who makes mistakes or changes the environment. Control surveillance consists of checking control effectiveness, design implementation effectiveness and operational performance. The manager must report any problems or issues if they are not addressed and Action Plans are created. Several financial companies, primarily in finance, have adopted monitoring systems built on KRIs for monitoring risk.
Conclusion
Operational risk management is crucial for any financial institution. Institutions can protect themselves from potential losses by understanding the sources of operational risk and implementing systems and controls to mitigate these risks. Adopting an effective operational risk management framework can help financial institutions minimize losses and maximize profits.

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.