Do you know how to manage project portfolios with risk in mind? Learn about project portfolio risk management and how you can identify, analyze, and respond to risks that could potentially impact the success of projects or groups of projects.
Project portfolio risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risks that could potentially impact the success of a project or group of projects. Risks can be related to any number of factors, including schedule, budget, scope, resources, and quality.
There are many different types of risks that need to be considered when managing project portfolios. Some of these risks are internal to the organization, such as changes in personnel or unexpected delays in approvals.
Other risks are external, such as market conditions or political instability. Still, others are strategic in nature, such as the risk of not being able to complete a project on time or within budget. Regardless of their source, all risks need to be carefully analyzed and responded to ensure the success of the project in project managemnt.
Project portfolio risk management is a critical function for any organization that is looking to improve its chances of success. By taking a proactive approach to risk management, organizations can minimise the negative impact of risks and maximize the positive potential of opportunities. In doing so, they can improve their chances of achieving their project goals and objectives.
Portfolio risk management allows organisations to manage risk levels within their portfolio. Organizations with an aim to improve their portfolio management discipline should start to develop their portfolio risk management once they establish work intake and prioritization processes.COVID-19 was cited by many as an example of establishing a risk-management system for a project portfolio that will protect the assets of the portfolio.
It’s much simpler to manage risks in an organization as it only requires some control of certain factors. In other instances, a portfolio risk management strategy should be used. In fact, it doesn’t take much effort to fail for an entire organization to meet its strategic goals. Portfolio Risk Management however means not merely eliminating riskier activities entirely to achieve the same results.
A note about the Titanic’s story shows that risk isn’t just something random, it is something unpredictable. Despite the risks involved, there was a significant factor affecting the outcome of these situations as in some other cases.
The most important step in effective risk management is to consider risks as uncertainties to identify their potential outcomes and probability and look for influencing factors and to manage those factors in such a way as to raise their probability.In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of project portfolio risk management and provide tips for effectively managing risk in your project portfolio.
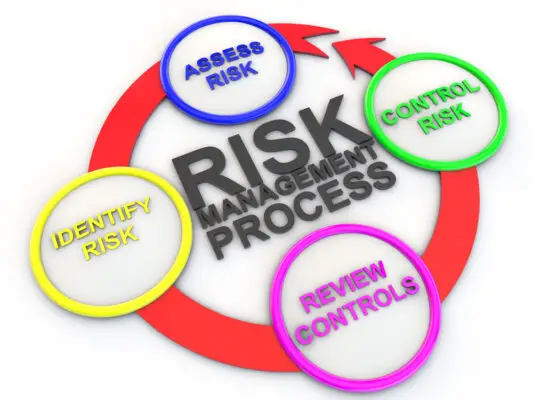
Definition of Risk Management
ISO 31000:2018 Describes risks as the ”effect of uncertainty on objectives. portfolio risk consists of the uncertainty that could affect the portfolio objectives. Diverse factors contribute to portfolio risks and their effects are not necessarily predictable.
It requires portfolio risk management to reduce risk and mitigate damages to avoid portfolio derailment if it happens. Risk management involves identifying, evaluating, and implementing risk and mitigation measures.
In projects, it can negatively impact the expected outcome. Project teams and project managers supervise the entire process throughout the project. They identify project risks and manage the risks. Optimising portfolio security measures analyses portfolio risk in order to reduce threats.
Project risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risk. It includes maximizing the probability and consequences of positive events and minimizing the probability and consequences of adverse events to project objectives.
There are four elements to project risk management:
3) Risk response
4) Risk monitoring and control

What is Portfolio Risk Management?
Portfolio Risk Management is a process for measuring risk within a portfolio by measuring and identifying its risk. The steps used in this follow the same procedures as traditional risk assessment.
In contrast to project risk management which focuses on the events that impact the project portfolio risk management consists primarily of events related to the achievement of strategic targets. Portfolio risk management extends beyond program and project risk management and requires high leadership involvement.
Portfolio management is the art and science of making decisions about investment mix and policy, matching investments to objectives, asset allocation for individuals and institutions, and balancing risk against performance. A portfolio manager is a professional who makes decisions about investment mix and policy, matches investments to objectives, assigns assets to specific projects and balances risk against performance.
The terms “portfolio management” and “project portfolio” are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. A project portfolio is a collection of projects that are grouped together to achieve a common goal. The projects in a project portfolio may be related or unrelated. Project portfolios are often managed by project managers with the assistance of the project team.
Project portfolios are managed using a variety of methods, including traditional project management methods, agile methods, and lean methods. Project portfolios are often managed using software tools, such as Microsoft Project or JIRA.
Project portfolios can have a large number of projects, and managing them can be a challenge. The goal of portfolio management is to select the right mix of projects that will maximize value for the organization.
Selecting the right mix of projects requires an understanding of the organization’s objectives, the resources available, and the risks involved.
What is Project Portfolio Risk Management?
Portfolio risk management includes identifying, assessing and managing risks within the portfolio, targeting events that cause a detrimental impact and focusing on them. Portfolio risk is far more extensive than program and project risk. It includes all sources of risk that can impact the achievement of objectives.
Project portfolio risk management (PPRM) is a process for managing risks across an organization’s multiple projects. The goal of PPRM is to optimize the chances of achieving organizational objectives by identifying and managing project portfolio risks.
Optimizing the chances for success of organizational objectives directly related to the project portfolio requires an understanding of how different projects interact with each other, and how they are impacted by common external factors.
Projects are often interdependent, and a change to one project can have a ripple effect on other projects in the portfolio. For example, a delay in one project might cause a domino effect of delays in other projects that are dependent on the first project.
Similarly, a change in an external factor, such as economic conditions, might impact multiple projects in the portfolio. For example, a decrease in consumer spending could cause delays in multiple projects that are reliant on consumer spending.
Differentiating between Project Risk Management and Portfolio Risk Management
Differentiating between Project Risk Management and Portfolio Risk Management terms is essential to ensure the successful implementation of projects. Project risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risks. It includes the identification of risks, the assessment of their probability and impact, and the development of response strategies.
Portfolio risk management, on the other hand, is the process of evaluating and managing risk across a portfolio of projects. It seeks to identify, assess, and respond to risks that could impact the achievement of objectives. It also takes into account the interdependencies between projects and differentiates between strategic and Operational Risks.
A project dealing with possible danger which could harm a project and its operations. Portfolio risk management is primarily focused on analysing risks in an integrated sense with an integrated strategy of analysis. Project-driven companies do not want project failure to happen anywhere.
On the one hand, portfolios try and find appropriate risks despite the fact that the investment will be well worth the effort. Project issues are generally specific to the programs. The portfolio is largely determined by its financial value, aligned to strategic objectives and the balance of the projects and programmes it possesses.
The objective of project risk management is to ensure that the project is completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. The goal of portfolio risk management is to ensure that the overall portfolio of projects is aligned with the strategic objectives of the organization.
Project risk management focuses on individual projects, while portfolio risk management looks at the entire portfolio of projects. Portfolio risk management is a higher-level view of risk management that considers the impact of risks across the entire portfolio of projects.
Why Risk Management is Crucial to Project & Portfolio Management?
Projects are temporary endeavours undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. They are complex, have uncertain outcomes, and require the coordinated efforts of multiple people and organizations. Each project is subject to risks that could impact its success. Risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risks. It is an essential component of project management and must be performed throughout the project lifecycle.
Risk management helps you to identify and assess risks early on in the project so that you can proactively address them. By identifying risks early, you can avoid or mitigate their impact on the project. This, in turn, reduces the likelihood of cost overruns, schedule delays, and other negative outcomes.
In addition, risk management helps you to build a culture of risk awareness within the project team. This can improve team morale and performance as team members feel more confident that they are working on a safe and well-managed project.
Risk Managing for Project Portfolio Managers aims at limiting the effect of negative effects on Portfolios. Portfolios have a very strong dynamic. They change as they progress, change postponement or modify their plans for portfolio balance and strategic performance.
Portfolio risk management is therefore essential to all portfolio management stakeholders. Risk management in portfolios and project management will not necessarily ensure success.
Project portfolio management is an essential aspect of the organization’s value-driven process. Choosing the correct portfolio development software may be helpful in the new approach.
Portfolio Risk Tolerance
A key aspect of Portfolio Risk Management is Risk Tolerance in Portfolio Management. Project portfolio management is built upon the financial portfolio management system which is primarily about diversifying risks with diversified investments across a large range.
Investment professionals know that riskier investments are more likely to yield high returns while fewer risk investments such as US bonds have fewer returns. Therefore, the investor should be able to understand their individual risk tolerance in order to predict future returns. Portfolio management will be an important aspect of ongoing projects.
Assess project riskiness
It is possible to evaluate portfolio risk differently, but we prefer to use the prioritization score information you collect. prioritization is used on how organizations should integrate risk into their scoring system. This risk score assesses the relative hazardiness of each particular project and helps determine a total portfolio risk assessment, which we’ll cover below.
Outputs of measuring portfolio risk
Portfolio risk measurement is a simple visual representation of relative portfolio risk levels at any given moment. Organisations that assess the risks of projects and manage the budget for them are well-positioned in their portfolios to assess the potential risks. If you multiplied the Budget Contribution and the risk score. For example; The Portfolio Risk score (is 16.9 compared with the maximum Portfolio Risk Score of 25). This allows us to create a risk management portfolio.
Measure the relative contribution of each project or program to the overall portfolio
For example; Currently, we measure the relative contribution of projects/programmes to the entire portfolio. We’ll start by describing a couple of fundamental factors that can affect the portfolio’s risk tolerance. It must be analyzed how one project can contribute in relation to the overall portfolio risk score.
Importance of Risk Management in Project & Portfolio Management
Risk management is an important part of project and portfolio management because it helps to identify, assess, and respond to risks that could impact the success of a project or portfolio. By identifying risks early, project and portfolio managers can take steps to mitigate them before they cause problems.
Additionally, risk management can help to identify opportunities that could improve the chances of success. For example, if a project is at risk of exceeding its budget, risk management can help to identify cost-saving measures that could be implemented.
Portfolio Risk Management is an important component in providing additional business value. Integrated portfolio risk management is more suited for taking on greater risks and enhancing the value of the portfolio which will result in higher success rates.
Projects and portfolios enable a business to protect while balancing its risk. Focused risk management processes are key factors for improving a firm’ s portfolio management discipline. Risk management focuses on finding potential risks and developing a strategy to mitigate them.
Managing the Opportunity Portfolio
Managing the opportunity portfolio is vital to any organization that wants to create and sustain a competitive advantage. The opportunity portfolio includes all the initiatives that an organization is pursuing or considering pursuing in order to drive growth.
Managing this portfolio effectively requires a clear understanding of the organization’s priorities and how each initiative fits into the overall strategy. It also requires regular review and adjustment, as circumstances change and new opportunities arise.
A company’s opportunity portfolio should be managed in a way that best fits the organization’s resources and objectives. The first step is to prioritize opportunities by aligning them with the company’s strengths. Then, a company should conduct a SWOT analysis to identify the most promising opportunities.
From there, a company should develop plans for how to pursue each opportunity. This may include allocating resources, forming partnerships, or making acquisitions. By carefully managing its opportunity portfolio, a company can maximize its chances of success.
Management of Opportunities Portfolios is a risk-based process. It helps businesses enhance productivity by identifying projects beyond the first job description and managing them.
As with risk, there may well be better opportunities and more valuable. Consequently, poor timing can be a factor affecting the ability to take advantage of certain opportunities. This is when the tool is needed to manage a project portfolio.
Summary
Portfolio Risk Management supports portfolio value and allows Portfolio Governance Groups to manage risks in a portfolio more effectively. Through proactive risk management organizations may take more risks to manage risk, thereby increasing overall portfolio value.
Company risk tolerance needs to be determined and measured appropriately to ensure better management of the portfolio. Many companies are risk-tolerant (for example biotech firms), while others are less risk-prone such as retail banking or health care. The level of risk in the portfolio should be monitored and reviewed periodically to ensure it is aligned with company goals.
There are different ways to measure and manage risk. One method is by using Value at Risk (VaR). VaR measures the maximum loss that a portfolio may experience over a given time horizon at a certain confidence level. For example, a one-month 99% VaR of $10 million means that there is a 1% chance that the portfolio will lose more than $10 million over the next month.
Other methods for measuring risk include Expected Shortfall (ES), which is similar to VaR but measures the expected loss instead of the maximum loss; and Standard Deviation, which measures the volatility of a portfolio.
When managing risk, it is important to consider both the upside and downside potential of a portfolio. For example, a portfolio with a high potential return but also a high potential for loss is considered to be riskier than a portfolio with lower potential returns but also lower potential losses.
Management of Portfolio Risks
In general portfolio, risk managers manage certain portfolio risk types. These threats may affect the success of strategic objectives. Investing in Portfolio Risk Management aims to reduce the risk of adverse effects on project portfolios. These aspects of portfolio risk management generally occur in a ‘protect portfolio value’ lifecycle.
Opportunity Management
Opportunity management refers to the process of identifying and managing the risk of projects and enabling companies to achieve more value or perform better than planned by definition, going beyond the original plan. Sometimes an opportunity can evolve into dedicated projects, or working to capture the opportunity can extend the scope of existing projects or programs.
Even though ideas and possibilities are great they are sometimes very expensive and may have very good value. For some reason, timing may not work well. This can be a great opportunity for the company to learn and grow.
When it comes to opportunity management, there are a few key things to keep in mind:
- Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the opportunity is and what it entails.
- Work with your team to identify any risks associated with the opportunity.
- Develop a plan to seize the opportunity while minimizing risk.
- Be prepared to adapt your plan as needed as the opportunity develops.
- Be ready to take advantage of new opportunities that arise during the course of pursuing the original opportunity.
External business risks
Business dangers external can be events that take place inside the external environment that cannot be managed by a company or the company at all. Examples are: External business risks are likely to cause the business strategy to be altered, which may make some projects obsolete due to their ineffectiveness.
The situation may affect the current portfolio severely requiring strong portfolio management.
A company can also face a Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) where it decides to move some of its processes or activities to an external provider in order to focus on its core competencies.
External business risks are events that happen outside of a company’s control and can seriously impact the company’s ability to achieve its objectives. Some examples of external business risks include:
-Economic recession
-Political instability
-Natural disasters
-Technological advancements
-Competition from new entrants
-Changes in consumer tastes or preferences.
Portfolio Risk Management Process
Portfolio risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and managing risk across a portfolio of investments. The goal of portfolio risk management is to maximize return while minimizing risk. The first step in the process is to identify the risks associated with each investment in the portfolio.
The next step is to assess the severity of each risk. Once the risks have been identified and assessed, the final step is to develop and implement a plan to manage those risks. This may involve hedging strategies, diversification, or other methods. By following a disciplined approach to risk management, investors can help ensure that their portfolios are well-positioned to weather market volatility and achieve their long-term financial goals.
These steps cover the management process for portfolio risks. According to PMI Standard for Portfolio Management the portfolio is managed through four primary risk processes. The Managing Portfolio Risk Standard and Experienced project managers know how to use the project risk matrix/risk register.
Types of portfolio risk
Investment portfolios are subject to different types of risk that can impact their overall performance. One type of risk is market risk, which is the chance that the value of the securities in a portfolio will decline due to general economic or market conditions. Another type of risk is interest rate risk, which is the possibility that changes in interest rates will have a negative impact on the return of a portfolio.
Another type of risk is credit risk, which is the chance that a borrower will default on a loan. Finally, another type of risk is liquidity risk, which is the chance that an investor will not be able to sell his or her securities when needed. Each type of risk must be carefully considered when constructing an investment portfolio.
Diversification across asset classes and individual securities can help to mitigate some of these risks. However, no investment portfolio is completely free from risk. Investors must be aware of the various types of risks that exist in order to make informed investment decisions.
The portfolio risk management processes can start with identifying the common kinds of portfolio level risk: external business risks and external business risks and execute risks. After that, the portfolio risk management processes can go deeper into the details of each risk and home in on the sources, triggers, and consequences.
Execution-related risks
Project risk includes project dependencies, major project risks that impact 2 or 3 different projects and project management quality.
Project risks should be identified, monitored and managed throughout the project life cycle. There are different ways to identify project risks, but some common methods include brainstorming with project team members, reviewing literature or conducting a stakeholder analysis.
Once identified, risks should be prioritized based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurring. Risk mitigation strategies should then be developed and implemented to address the risks.
The most common types of project risks are schedule, cost, performance, quality and scope risks. Schedule risk is the risk that the project will not be completed on time. Cost risk is the risk that the project will exceed its budget. Performance risk is the risk that the project will not meet its performance objectives. Quality risk is the risk that the project will not meet its quality standards. Scope risk is the risk that the project will not meet its scope objectives.
Project risks can have a positive or negative impact on the project. Positive impacts are typically related to cost and schedule savings, while negative impacts are typically related to cost overruns and schedule delays.
Project risks should be monitored throughout the project life cycle to ensure that they are being effectively managed. The project manager is typically responsible for monitoring and managing project risks.
Internal business risks
Business interruption may be an issue affecting project or program execution. Amongst the most common internal risks is:
– Inadequate planning
– Lack of management commitment and/or ownership
– Lack of skilled resources
– Lack of clear roles and responsibilities
– Lack of communication
– Poorly defined objectives and success criteria
Other risks that may impact the successful execution of a project or program include:
– inadequate change control procedures;
– inadequate configuration management;
– inadequate quality assurance; and
– unrealistic assumptions.
External risks are often beyond the control of the program or project manager, but may have an impact on project or program success. Political instability, natural disasters, and economic downturns are all examples of external risks that could affect a project or program.
Internal risks are often more manageable than external risks, but can still have a significant impact on project or program success. Here are some tips for managing internal risks:
– Make sure that roles and responsibilities are clearly defined and communicated to all team members.
– Establish strong lines of communication between the project manager, the project team, and senior management.
– Make sure that objectives and success criteria are well-defined and communicated to all team members.
– Implement effective change control procedures to manage changes to the project or program.
– Implement effective configuration management procedures to track and manage changes to project or program artefacts.
– Implement effective quality assurance procedures to ensure that deliverables meet quality standards.
– Make sure that assumptions are realistic and well-documented.
What are Common Types of Project Portfolio Risks?
A portfolio risk includes the external business threat (industry disruption, mergers, acquisitions or other economic conditions, political conditions, regulatory changes and new legislative requirements and natural events like COVIDA-19) or internal business risk.
A project portfolio risk can also include the technical risk of new technology not working as planned or an integration issue with existing technology.
There are four common types of project portfolio risks:
- Strategic Risk
- Implementation Risk
- Operational Risk
- Financial Risk
Strategic risk is the risk that the project will not achieve its objectives and deliver the expected value.
Implementation risk is the risk that the project will not be executed as planned.
Operational risk is the risk of poor performance or unanticipated problems during project execution.
Financial risk is the risk that the project will not generate the expected return on investment.
Steps in Developing a Risk Management Plan
Managing portfolio risks requires four phases: identification and analysis, developing response strategies and monitoring and controlling possible threats.
- Identification and Analysis: The first step in risk management is identifying which risks could affect your portfolio. This includes both market risks (like changes in interest rates or asset prices) and non-market risks (like regulatory changes or political instability). Once you’ve identified the potential risks, you need to analyze them to determine how likely they are to occur and how severe their impact could be.
- Developing Response Strategies: Once you’ve identified and analyzed the risks, you need to develop strategies for dealing with them. This might involve buying insurance, hedging your investments or simply diversifying your portfolio to reduce your overall exposure to risk.
- Monitoring and Controlling Risks: Even after you’ve developed response strategies, you need to monitor the risks to make sure they haven’t changed. This includes keeping an eye on things like changes in the financial markets or political conditions in countries where you’re invested.
- Reviewing and Updating Your Plan: As your portfolio grows and changes, you’ll need to review and update your risk management plan. This will help you make sure that your plan is still appropriate and that you’re prepared for any new risks that might arise.
Identifying risks
The Identification of Risks is a critical element of portfolio risk management and helps assess where risk is occurring and assess their sources. A project’s main risks can be described as either external, internal structural, or execution risks.
External risks include anything that can affect the project’s schedule, budget, or quality. These can be things like changes in the political landscape, natural disasters, or even problems with the client.
Internal structural risks are risks that come from within the project team itself. These can be things like communication breakdowns, unclear deliverables, or even unrealistic expectations.
Execution risks are risks that come from the execution of the project itself. These can be things like problems with the contractor, issues with the quality of work, or even delays in the project schedule.
When it comes to identifying risks, it is important to think about both the potential impact of the risk and the probability of it occurring. A risk that has a high impact but a low probability of occurring is not as much of a concern as a risk that has a low impact but a high probability of occurring.
Once the risks have been identified, they can be assessed and prioritized. The assessment process helps to determine the potential impact of the risk and the likelihood of it occurring. The priority of the risk will help to determine the course of action that needs to be taken to mitigate the risk.
There are a few different methods that can be used to assess and prioritize risks. One popular method is the use of a Risk Heat Map. This is a visual representation of the risks that have been identified, with the risks that have a high impact and high probability of occurring being represented by a red color, and the risks that have a low impact and low probability of occurring being represented by a green color.
Another popular method is the use of a Risk Register. This is a list of all the risks that have been identified, along with their assessment and priority. This can be a helpful tool for keeping track of all the risks and their status.
Once the risks have been assessed and prioritized, the next step is to develop a plan to mitigate them. This will involve identifying the actions that need to be taken to reduce the impact of the risk or the probability of it occurring. The mitigation plan will need to be monitored and updated as the project progresses and new risks are identified.
Analyzing Project & Portfolio Risks
Once you identify the potential risks, then you must analyse and develop responses to monitor the risks. Project risks identified are often evaluated by cost-benefit studies, statistical models or sensitivity analyses. Risk is prioritized and dealt with in accordance with analysis and possible impact on portfolio performance.
Risk in a portfolio is the most important. Project resource managers or portfolio management team members can identify possible solutions and address these threats. Using the risk analysis, the risk management team helps determine how the risks affect the expected results and minimize risk.
Determining Portfolio Risk Tolerance
The ability to determine risk tolerance in organizations is a vital aspect in the portfolio risk management plan. Portfolios are thus categorized as either tolerant or fearful. Managing project portfolio PMP provides an essential concept for managing risk in an integrated way. Similar to the finance principles, greater risks have higher returns, while lesser risk has lower returns.
Organizations should use a systematic approach to determine their risk appetite or the level of risk that they are willing and able to take. The first step is to articulate the organization’s goals, objectives, and values. Once these have been determined, the next step is to create a clear picture of what an ideal future state looks like for the organization. With this information in hand, the organization can now begin to identify what level of risk is required to achieve its desired future state.
The final step is to put all of this information together and make a decision about what level of risk the organization is willing to take on. This will serve as the basis for all future decisions regarding risk in the organization.
Executing the Risk Management Plan
The Risk Management plan combines all of the previously described stages of identifying, analyzing, and managing risks in a project and their possible mitigation. Risk management plans evaluate alternative ways of reaching a project goal based on identified risk factors.
These contingency plans give companies the opportunity to overcome potential project risks or obstacles. Next, the budget will go towards the contingency plan. The most important part of risk management is to be proactive and have a plan in place should something go wrong.
Risk management plans can be monitored semi-annually or annual depending on the risk management policy of the organization. Plans should be updated as project goals or objectives change.
If changes in goals or objectives are not accounted for, the risk management plan will be rendered obsolete and useless. The goal of risk management is to minimize the negative effects of risks on a project and to maximize the chances of achieving its objectives.
Conclusion
Managing a project portfolio is never an easy task, but by taking into account the various risks involved, it can be made a bit easier. By using risk management techniques such as those outlined in this article, you can help to ensure that your projects are completed on time and within budget, while still meeting all of your original objectives. Have you had success using project portfolio risk management in your organization? Let us know in the comments below!

Chris Ekai is a Risk Management expert with over 10 years of experience in the field. He has a Master’s(MSc) degree in Risk Management from University of Portsmouth and is a CPA and Finance professional. He currently works as a Content Manager at Risk Publishing, writing about Enterprise Risk Management, Business Continuity Management and Project Management.

